In general, templates can contain HTML markup and PHP variables that output content contained within a Drupal database. Templates can be as small as a few lines of HTML that hold the presentational layer for a block that is displayed in a region on the page, or the actual page itself, with containers defined for header, content, and so on:
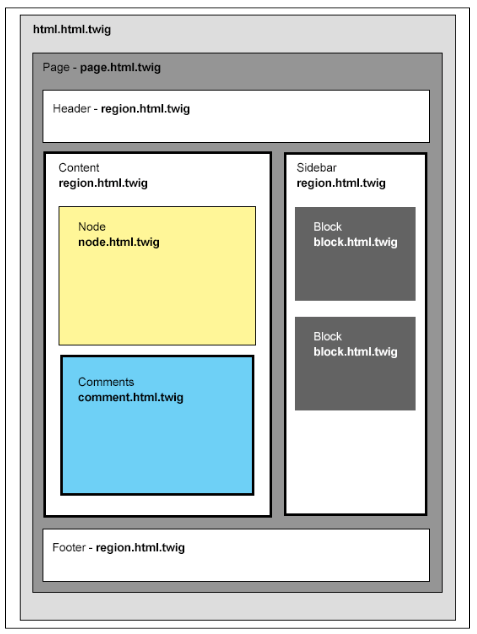
If we break down the image into logical sections of a website, we can begin to get an idea of what constitutes a template. A template can be any of the following:
- HTML wrapper: This contains the top-level HTML markup, including title, metadata, style sheets, and scripts, and it is commonly referred to as html. html.twig.
- Page wrapper: This contains the content generally found between the body tags of an HTML document, and it is commonly referred to as page.html.twig.
- Header: This is also known as a region, generally containing the header content of our web page. This can be part of the page.html.twig template or may reside in a region specified within our configuration file. This is commonly referred to as region.html.twig.
- Content: This is also considered a region, generally containing our main content. This can consist of multiple subcontent regions, such as nodes and comments. Nodes and comments each have their own respective templates referred to as node.html.twig and comment.html.twig.
- Sidebar: This is also considered a region. This can contain blocks of content. Blocks are either created by the end user or by Drupal itself. The content within these blocks generally resides within block.html.twig.
- Footer: This is another region containing HTML content as well as blocks of content.
Drupal and the theme engine it uses to convert the markup and variables into HTML interpret each individual template or series of templates. We have full control over what is the output of using the new Twig templating engine.
Once we begin theming, we will start to see a pattern of how templates are used, and as we gain more experience, we will find ourselves using fewer and fewer templates. However, to begin with, we will build examples of each to help clarify their functionality within Drupal.
