Before we can begin working with blocks, we need to be familiar with Block layout and Regions. We need to know where things are located, what blocks Drupal 8 provides us with, and the concept of Regions.
We can navigate to the Block layout page by directly entering /admin/structure/block, or by using the Admin toolbar and clicking on Structure | Block layout:
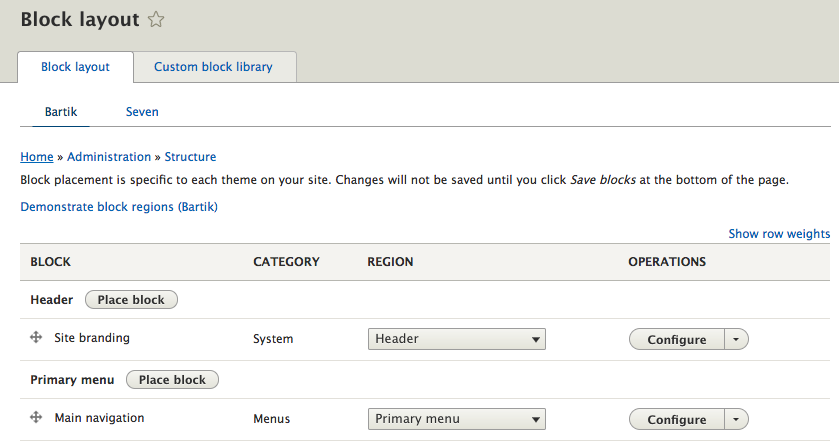
The Block layout page provides the interface that allows us to manage block content by placing blocks into regions. Blocks can be categorized based on their functionality, with the most common types including the following:
- Core: Blocks contained within the core installation consisting of items such as page title, primary admin actions, and tabs
- System: Blocks that provide system functionality consisting of breadcrumbs, main-page content, messages, site branding, and a few others
- Forms: Blocks that contain embedded forms such as the search form and user login
- Menus: Blocks that contain menus and menu items, such as Administration, Footer, Main navigation, and Tools
- Lists (Views): Blocks consisting of Views generated for block content. Generally, these types of block will be created during configuration or site building
- Custom: Blocks created from the Custom block library consisting of fieldable blocks with one or more display modes
If blocks consist of content, then we can think of regions as the containers that hold blocks and make up a theme's layout.
Drupal 8 provides the following regions:
- Header
- Primary menu
- Secondary menu
- Highlighted
- Help
- Content
- Sidebar first
- Sidebar second
- Footer
- Breadcrumb
In some cases, we may see additional regions available for use. However, keep in mind that anything outside of the default regions described above have been added to the active theme and are defined within the theme's configuration.
