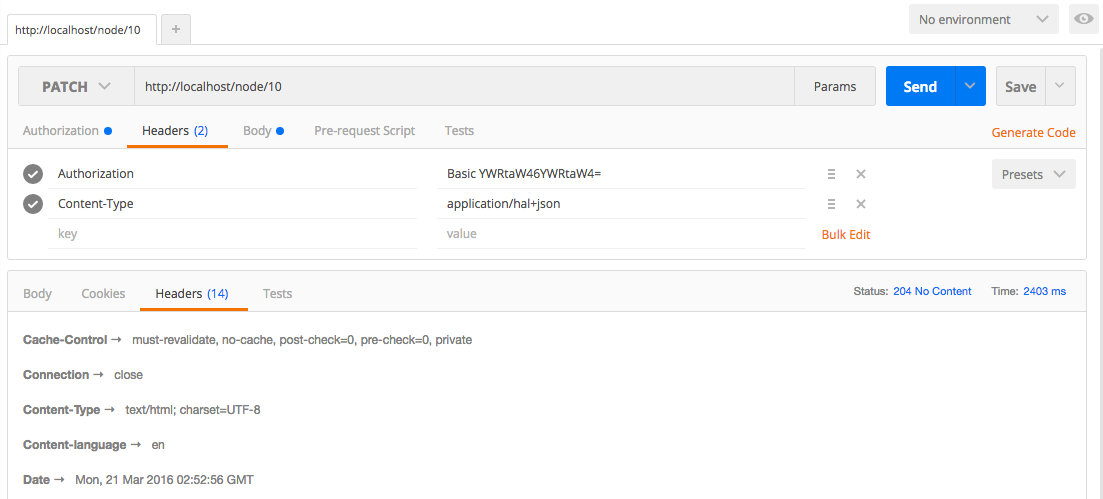
Updating a node involves a PATCH request to the URI of the entity. So, if we were going to update the node we just created, you would make a PATCH request to /node/10. The headers and data are similar to those you send for creating a node. When updating a node, you only need to send the information that you want to change. There is also some information that you cannot send since they it be changed; for instance, you cannot submit the UUID (Universally Unique Identifier) attribute even if it is the same value. Sending that in the PATCH request will return a 403 Forbidden response. There are also some pieces of information that must be sent; for instance, you must submit the entity type and bundle even though you cannot change this on a node. The entity type and bundle is required because the data must be deserialized before it can be passed to the REST controller.
To test this using cURL, you would make the following request:
curl --include --request PATCH --user myusername:mypassword --header 'Content-type: application/hal+json' http://localhost/node/[nid]--data-binary '{"_links":{"type":{"href":"http://localhost:8080/rest/type/node/article"}},"title":[{"value":"Example node title UPDATED!"}],"type":[{"target_id":"article"}]}'
You'd replace the [nid] with a real node ID of an article on your site. If the request is successful you will receive a 204 No Content response. In Drupal 8.1.0 or higher, the response will be a 200 OK response with the serialized version of the updated entity.