The Permissions panel displays various sections of the functionality within Drupal, grouped by task with each role displayed across the top of the page. Permissions allow us to control what each role can do or see within our site. The list of functionality and the permissions we can manage for each will continue to grow, based on the number of cores or contributed modules we enable or the number of content types we create.
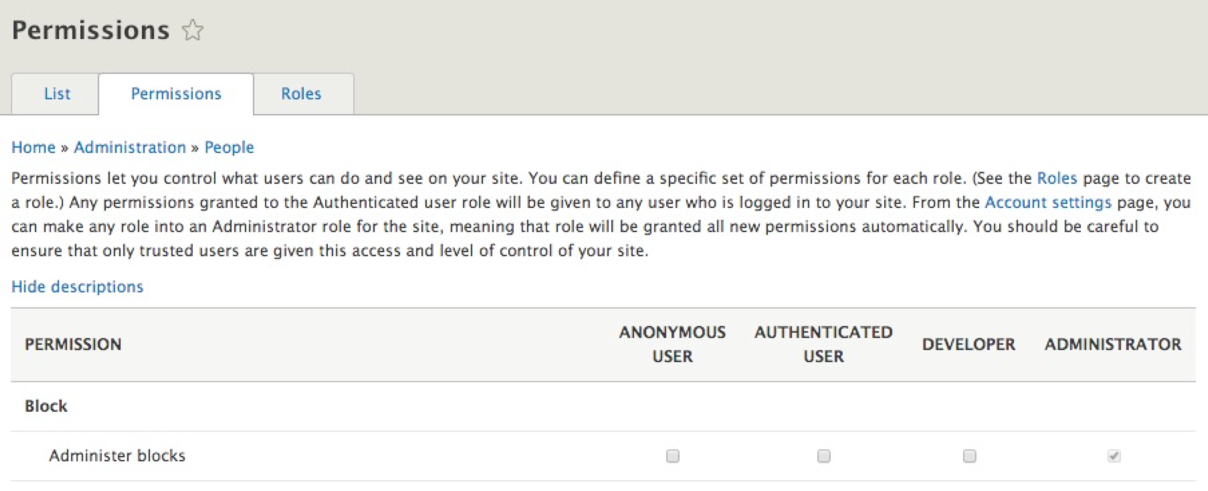
As we can see from the preceding screenshot, roles are arranged across the top of the Permissions page based on how they are ordered. Starting from the least permissive to the most permissive role, we can easily assign permissions to them by clicking on the checkbox next to the task or function.
Unlike Drupal 7, where we were required to constantly check off permissions for the administrator role, the administrator role automatically is assigned all permissions in Drupal 8 . This ensures that every time we add a new module or create a new content type, we don't have to revisit the Permissions page. The automatic assignment of permissions to the Administrator role is configurable from the Account settings page, which we will review a little later.
For now, if we want any other role to have the proper privilege, we need to first locate the functionality, then the role, and make sure that the permission is checked. To allow our DEVELOPER role to Administer blocks, all we will need to do is click on the checkbox under that role:
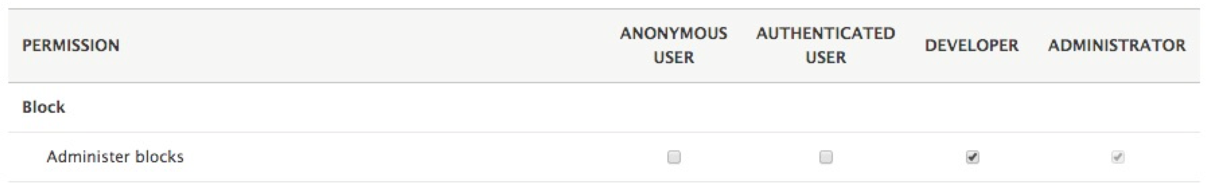
Keep in mind that whenever we modify permissions for a specific role, it is important to click on the Save permissions button located at the bottom of the Permissions page.
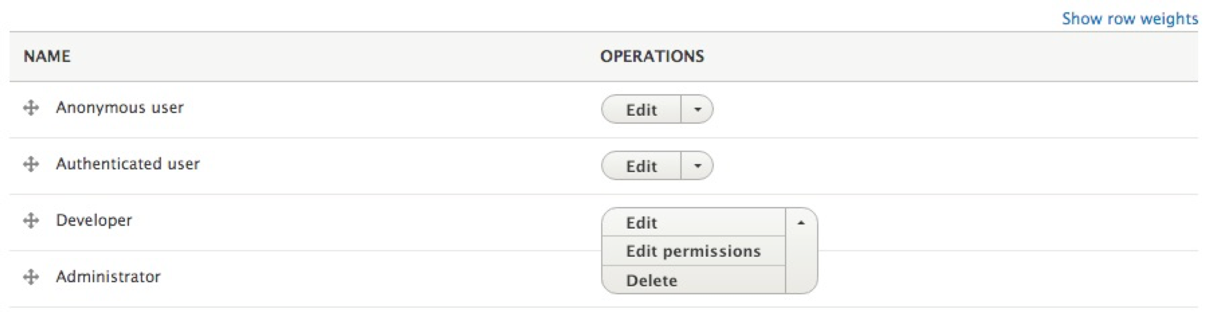
Depending on the number of roles, the Permissions page may become difficult to review. If for any reason we need to manage the permissions of a single role, we can always do so by returning to the Roles page, locating the specific role, and clicking on the Edit permissions button:
Editing the permissions from the Roles page will take us back to the Permissions page filtered by the individual role:
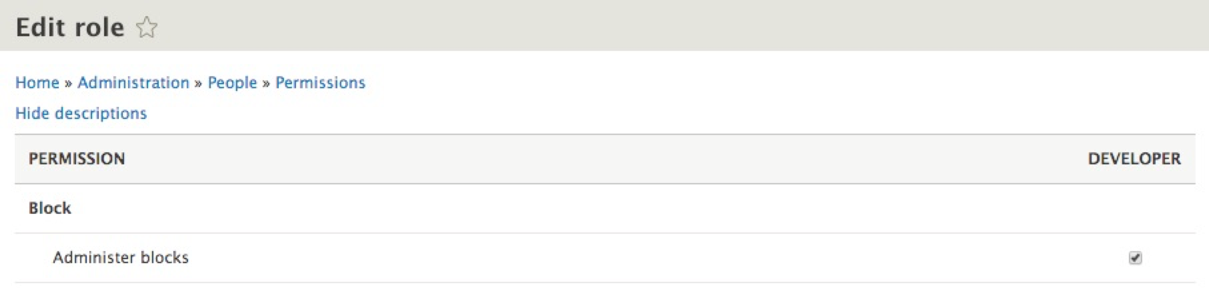
From this perspective, it is much easier to manage the permission for our role and locate the specific privilege that we need to enable or disable.
Don't forget to test the various roles and permissions when they are assigned--whether this means creating user accounts for each role that you can log in as or by using a common module such as Masquerade, https://www.drupal.org/project/masquerade, which allows you to switch from one user to another to test permissions.
A general rule of thumb is to fine-tune permissions closer to the end of a project to limit having to repeat these tasks.
Now that we have created our Developer role and assigned it the necessary permissions, it's time we create a new user and assign the Developer role to them.
