QGIS offers a very easy and convenient way to publish QGIS projects with its own spatial server. It is the CGI application QGIS Server, which we have already configured in Chapter 1, Setting Up Your Environment.
Similar to the popular UMN MapServer, QGIS Server is a simple CGI application which does not track the published data. While MapServer needs a configuration file where paths to the data sources are defined along with other configuration parameters, QGIS Server needs a QGIS project file, which contains the paths along with other information, like styling. We can provide the project file's absolute path in a map parameter.
Let's craft a URL which queries the WMS capabilities of QGIS Server using one of our QGIS projects. As we are on the same machine as the server, we can use the placeholder localhost instead of a domain name or an IP address:
http://localhost/cgi-bin/qgis_mapserv.fcgi?
map=/home/debian/practical_gis/
ch10.qgs&Service=WMS&Version=1.3.0&Request=GetCapabilities
The response should look similar to the following:

A long XML response shows if we have a working QGIS Server, which can access our projects. By installing QGIS Server, it automatically integrates itself in QGIS, and makes our projects publishable with WMS. To see what those published maps look like, we can use QGIS as a client. In order to load a WMS layer, we need to connect to a spatial server publishing WMS layers first, using the following steps:
- Click on the Add WMS/WMTS Layer button on the left toolbar.
- Click on New to define a new connection.
- Name the connection (it can be anything), and provide the URL to the QGIS Server application with the map parameter pointing at a QGIS project file (for example, http://localhost/cgi-bin/qgis_mapserv.fcgi?map=/home/debian/practical_gis/ch04.qgs). I will use the carefully styled map from Chapter 4, Creating Digital Maps.
- Click on OK to save the connection, and close the dialog.
- Click on connect to see every layer published as a WMS map.
- Select the topmost layer named after the project file to load every layer from the project. Add the whole map with the Add button:
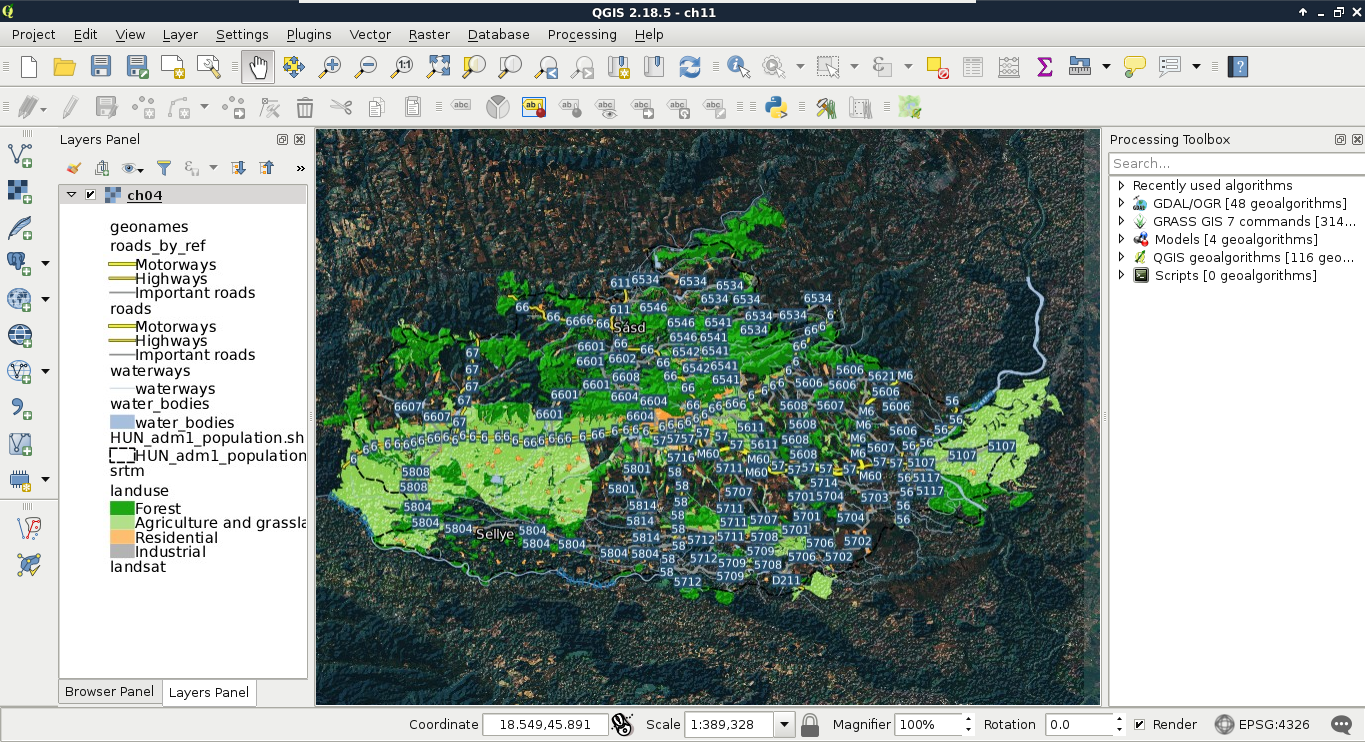
We can see the styled layers, although there are two very conspicuous problems--there are some layers published which we had disabled in our project, and it uses the projection EPSG:4326, making the map look distorted. The overall composition is not very aesthetic, which we can resolve by opening the project in QGIS:
- Open Project | Project Properties from the menu bar.
- Navigate to the OWS server tab.
As QGIS Server serves projects, we can configure the behavior of the QGIS Server in the project properties. There are several general sections in the dialog which are useful for basic configuration, like the following:
- Server capabilities: Basic metadata about the provider. If enabled and filled out, that data is supplied with the capabilities of XML by the server application.
- CRS restrictions: QGIS Server can create WMS images in up to three CRSs by default. Two of them are the popular EPSG:4326 and EPSG:3857 CRSs. If the published project uses a third CRS, it can be also used by default. To customize the CRSs, WMS layers can be queried, we can enable CRS restrictions, and manage the allowed projections manually.
- Exclude layers: By default, every layer in the project is published as a WMS image. In order to exclude some of the layers, we can add them in the Exclude layers section.
- WFS capabilities: Spatial data is not published by QGIS Server in raw vector format by default. We can enable WFS layer-wise, by checking the Published box on the appropriate vector layers. We can also enable WFS-T (WFS-Transaction) on some layers (that is, Update, Insert, and Delete). The only requirement is that the layer has to be in a format QGIS can write in place.
- WCS capabilities: Similar to WFS, we have to enable publishing raw raster data with WCS layer-wise.
For now, let's only exclude the disabled layers from the WMS service.
- Add the disabled layers in the Excluded layers list with the green plus icon.
- Apply the changes, and save the project.
- Open a new project, or an existing one used for this chapter.
- Add every layer from the previously saved project as a single WMS layer as we did previously. Before adding the layer, click on the Change button next to the default CRS's name (WGS 84), and select the local projection we use from the list.
Now we have a stack of styled layers ready to use in a web application:
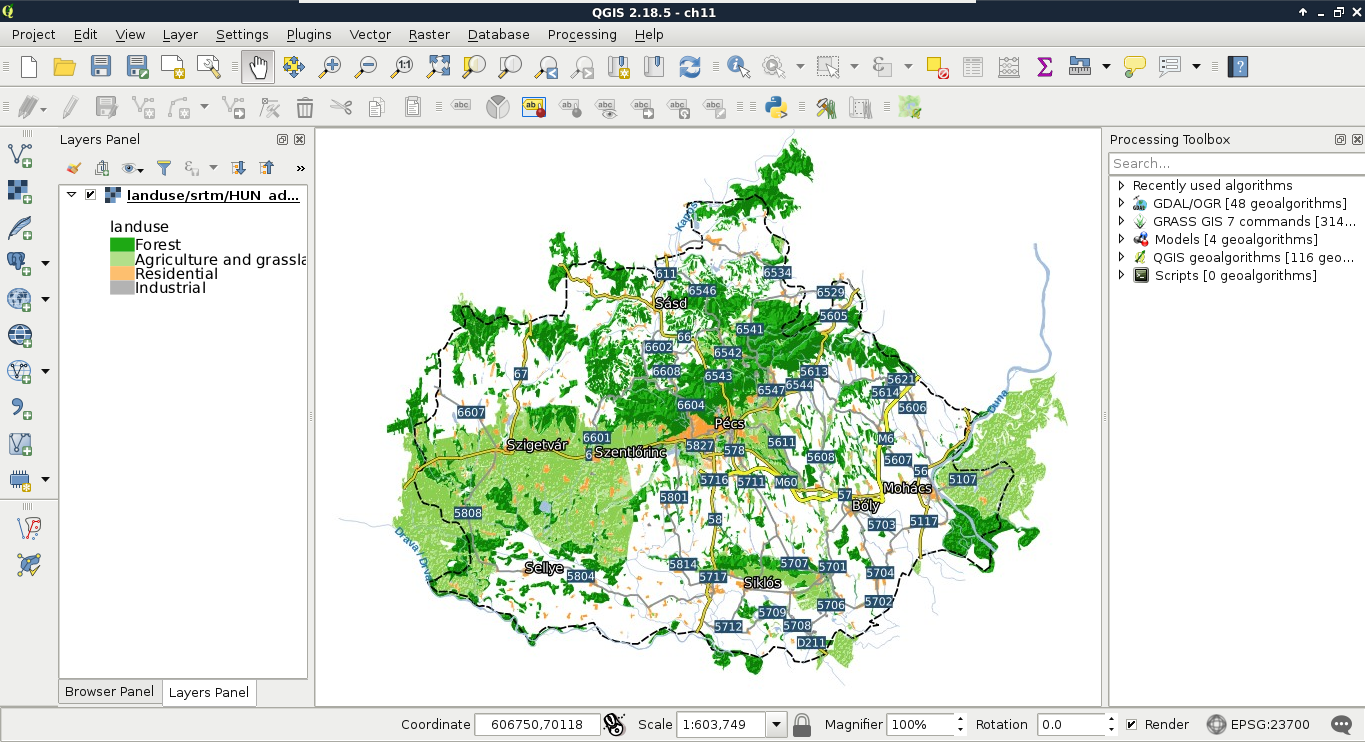
The image we see is the same as we will see on our webpage if we use the layers with web-mapping software. This is the greatest benefit of using QGIS Server--as it uses the same libraries as QGIS, the served images will be the same as we can see in the project's styled layers in QGIS.
