We have two additional tasks to complete in order to match the common preferences of our customers. If you do not remember the exact preferences, here they are again:
- They should be less than 500 meters away from a park with a playground
- They should be less than 500 meters away from a restaurant
- They should be less than 500 meters away from a bar or a pub
- There should be at least two markets within their 500 meters vicinity
The first three criteria can be easily matched building on the queries of the previous section. We only have to create three CTE tables or subqueries; one for the parks with playgrounds in their 200 meters vicinity, one for the restaurants, and one for the bars and pubs. After that, we only have to match our houses by using distance checks. Such a query can be formulated as follows:
WITH parks_with_playgrounds AS (
SELECT ST_Collect(l.geom) AS geom FROM spatial.landuse l,
spatial.pois p
WHERE l.fclass = 'park' AND p.fclass = 'playground' AND
ST_DWithin(l.geom, p.geom, 200)),
restaurants AS (
SELECT ST_Collect(geom) AS geom FROM spatial.pois p
WHERE p.fclass = 'restaurant'),
bars AS (
SELECT ST_Collect(geom) AS geom FROM spatial.pois p
WHERE p.fclass = 'bar' OR p.fclass = 'pub')
SELECT h.* FROM spatial.vw_quiethouses h,
parks_with_playgrounds pwp, restaurants r, bars b
WHERE ST_DWithin(h.geom, pwp.geom, 500) AND ST_DWithin(h.geom,
r.geom, 500) AND ST_DWithin(h.geom, b.geom, 500);
The final expression works as the ones formulated before. We filter the raw tables by attributes and distances, and use some distance checks in the final query. The only difference is that as we do not need the exact distances, we used ST_DWithin instead of ST_Distance. ST_DWithin is a simple filtering function for selecting features based on a proximity. It has almost no performance penalty over ST_Distance, but offers a more concise way to formulate our query. It needs three arguments: two geometries, and a distance in the units of the input layers' SRID.
If we load the result as a layer, we can see our constrained quiet houses, which match the results created in QGIS at a first glance:
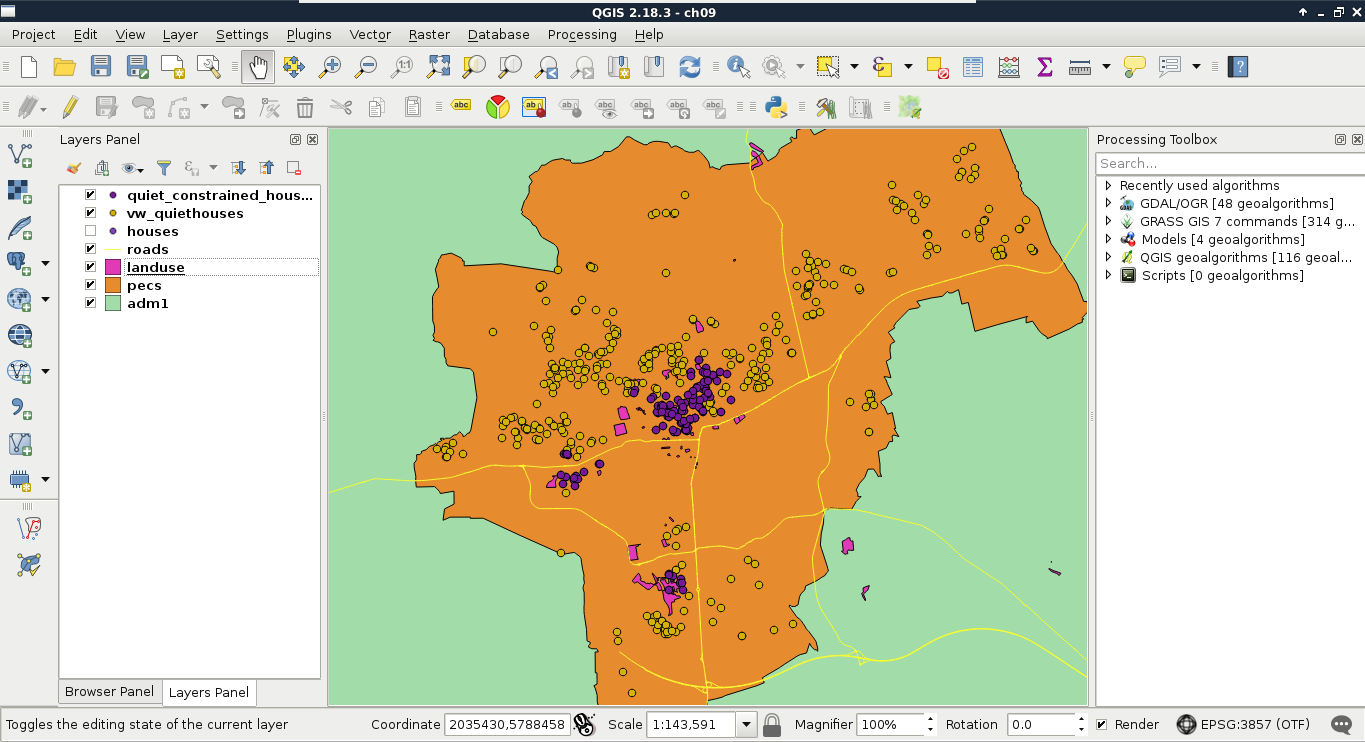
For the sake of simplicity and clarity, let's create another view from the result of this query. We just have to prefix our query with CREATE VIEW AS and the view's name:
CREATE VIEW spatial.vw_quietconstrainedhouses AS WITH
parks_with_playgrounds AS (
SELECT ST_Collect(l.geom) AS geom FROM spatial.landuse l,
spatial.pois p
WHERE l.fclass = 'park' AND p.fclass = 'playground' AND
ST_DWithin(l.geom, p.geom, 200)),
restaurants AS (
SELECT ST_Collect(geom) AS geom FROM spatial.pois p
WHERE p.fclass = 'restaurant'),
bars AS (
SELECT ST_Collect(geom) AS geom FROM spatial.pois p
WHERE p.fclass = 'bar' OR p.fclass = 'pub')
SELECT h.* FROM spatial.vw_quiethouses h,
parks_with_playgrounds pwp, restaurants r, bars b
WHERE ST_DWithin(h.geom, pwp.geom, 500) AND ST_DWithin(h.geom,
r.geom, 500) AND ST_DWithin(h.geom, b.geom, 500);
