The VMware environment leaves many artifacts on the system, especially when VMware Tools is installed. Malware can use these artifacts, which are present in the filesystem, registry, and process listing, to detect VMware.
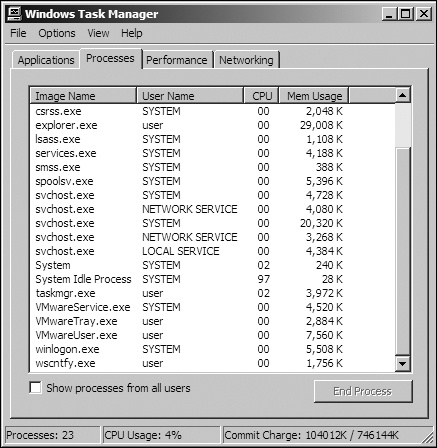
For example, Figure 17-1 shows the process
listing for a standard VMware image with VMware Tools installed. Notice that three VMware processes
are running: VMwareService.exe, VMwareTray.exe, and
VMwareUser.exe. Any one of these can be found by malware as it searches the
process listing for the VMware string.
VMwareService.exe runs the VMware Tools Service as a child of services.exe. It can be identified by searching the registry for services installed on a machine or by listing services using the following command:
C:\> net start | findstr VMware
VMware Physical Disk Helper Service
VMware Tools ServiceThe VMware installation directory C:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools may also contain artifacts, as can the registry. A quick search for “VMware” in a virtual machine’s registry might find keys like the following, which are entries that include information about the virtual hard drive, adapters, and virtual mouse.
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\HARDWARE\DEVICEMAP\Scsi\Scsi Port 0\Scsi Bus 0\Target Id 0\Logical Unit Id 0]
"Identifier"="VMware Virtual IDE Hard Drive"
"Type"="DiskPeripheral"
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Reinstall\0000]
"DeviceDesc"="VMware Accelerated AMD PCNet Adapter"
"DisplayName"="VMware Accelerated AMD PCNet Adapter"
"Mfg"="VMware, Inc."
"ProviderName"="VMware, Inc."
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Class\{4D36E96F-E325-11CE-BFC1-08002BE10318}\0000]
"LocationInformationOverride"="plugged into PS/2 mouse port"
"InfPath"="oem13.inf"
"InfSection"="VMMouse"
"ProviderName"="VMware, Inc."As discussed in Chapter 2, you can connect your virtual machine to a network in a variety of ways, all of which allow the virtual machine to have its own virtual network interface card (NIC). Because VMware must virtualize the NIC, it needs to create a MAC address for the virtual machine, and, depending on its configuration, the network adapter can also identify VMware usage.
The first three bytes of a MAC address are typically specific to the vendor, and MAC addresses starting with 00:0C:29 are associated with VMware. VMware MAC addresses typically change from version to version, but all that a malware author needs to do is to check the virtual machine’s MAC address for VMware values.
Malware can also detect VMware by other hardware, such as the motherboard. If you see malware checking versions of hardware, it might be trying to detect VMware. Look for the code that checks MAC addresses or hardware versions, and patch the code to avoid the check.
The most common VMware artifacts can be easily eliminated by uninstalling VMware Tools or by trying to stop the VMware Tools Service with the following command:
net stop "VMware Tools Service"You may also be able to prevent malware from searching for artifacts. For example, if you find
a single VMware-related string in malware—such as net start | findstr
VMware, VMMouse, VMwareTray.exe, or VMware Virtual IDE Hard
Drive—you know that the malware is attempting to detect VMware artifacts. You should
be able to find this code easily in IDA Pro using the references to the strings. Once you find it,
patch it to avoid detection while ensuring that the malware will function properly.
Defeating malware that searches for VMware artifacts is often a simple two-step process:
identify the check and then patch it. For example, say we run strings against the malware vmt.exe. We notice that the binary
contains the string "VMwareTray.exe", and we discover a
cross-reference from the code to this string. We follow this cross-reference to 0x401098, as shown
in the disassembly in Example 17-1 at ❶.
Example 17-1. Disassembly snippet from vmt.exe showing VMware artifact detection
0040102D call ds:CreateToolhelp32Snapshot00401033 lea ecx, [ebp+processentry32] 00401039 mov ebx, eax 0040103B push ecx ; lppe 0040103C push ebx ; hSnapshot 0040103D mov [ebp+processentry32.dwSize], 22Ch 00401047 call ds:Process32FirstW 0040104D mov esi, ds:WideCharToMultiByte 00401053 mov edi, ds:strncmp 00401059 lea esp, [esp+0] 00401060 loc_401060: ; CODE XREF: sub_401000+B7j 00401060 push 0 ; lpUsedDefaultChar 00401062 push 0 ; lpDefaultChar 00401064 push 104h ; cbMultiByte 00401069 lea edx, [ebp+Str1] 0040106F push edx ; lpMultiByteStr 00401070 push 0FFFFFFFFh ; cchWideChar 00401072 lea eax, [ebp+processentry32.szExeFile] 00401078 push eax ; lpWideCharStr 00401079 push 0 ; dwFlags 0040107B push 3 ; CodePage 0040107D call esi ; WideCharToMultiByte 0040107F lea eax, [ebp+Str1] 00401085 lea edx, [eax+1] 00401088 loc_401088: ; CODE XREF: sub_401000+8Dj 00401088 mov cl, [eax] 0040108A inc eax 0040108B test cl, cl 0040108D jnz short loc_401088 0040108F sub eax, edx 00401091 push eax ; MaxCount 00401092 lea ecx, [ebp+Str1] 00401098 push offset Str2 ; "VMwareTray.exe" ❶ 0040109D push ecx ; Str1 0040109E call edi ;strncmp❷ 004010A0 add esp, 0Ch 004010A3 test eax, eax 004010A5 jz short loc_4010C0 004010A7 lea edx, [ebp+processentry32] 004010AD push edx ; lppe 004010AE push ebx ; hSnapshot 004010AF call ds:Process32NextW004010B5 test eax, eax 004010B7 jnz short loc_401060 ... 004010C0 loc_4010C0: ; CODE XREF: sub_401000+A5j 004010C0 push 0 ; Code 004010C2 call ds:exit
Analyzing this code further, we notice that it is scanning the process listing with
functions like CreateToolhelp32Snapshot, Process32Next, and so on. The strncmp at ❷ is comparing the VMwareTray.exe string with the result of converting processentry32.szExeFile to ASCII to determine if the process name is in the process
listing. If VMwareTray.exe is discovered in the process listing,
the program will immediately terminate, as seen at 0x4010c2.
There are a couple of ways to avoid this detection:
Patch the binary while debugging so that the jump at 0x4010a5 will never be taken.
Use a hex editor to modify the
VMwareTray.exestring to readXXXareTray.exeto make the comparison fail since this is not a valid process string.Uninstall VMware Tools so that VMwareTray.exe will no longer run.
VMware leaves many artifacts in memory as a result of the virtualization process. Some are critical processor structures, which, because they are either moved or changed on a virtual machine, leave recognizable footprints.
One technique commonly used to detect memory artifacts is a search through physical memory for
the string VMware, which we have found may detect several hundred
instances.