The major code construct is an
ifstatement located at 0x401000.printfis the subroutine located at 0x40105F.The program checks for an active Internet connection. If an active connection is found, it prints “Success: Internet Connection.” If a connection is not found, it prints “Error 1.1: No Internet.” This program can be used by malware to check for a connection before attempting to connect to the Internet.
We begin by performing basic static analysis on this executable. Looking at the imports, we
see that the DLL WININET.dll and the function InternetGetConnectedState are imported. The Windows Internet (WinINet) API enables
applications to interact with HTTP protocols to access Internet resources.
Using MSDN, we learn this Windows API function checks the status of the Internet connection
for the local system. The strings Error 1.1: No Internet and
Success: Internet Connection hint that this program may check for
an active Internet connection on the system.
Next, we perform basic dynamic analysis on this executable. Nothing overly exciting happens when this executable is run from the command line. It simply prints “Success: Internet Connection” and then terminates.
Finally, we load the file into IDA Pro for full analysis. Much of this disassembly is
generated by the compiler, so we need to be careful to avoid going down rabbit holes of irrelevant
code. Therefore, we start from the main function, which is
typically where the code written by the malware author begins. In this case, the main function starts at 0x401040. The main function calls the function at 0x401000, which appears to be a key function of interest because it is the
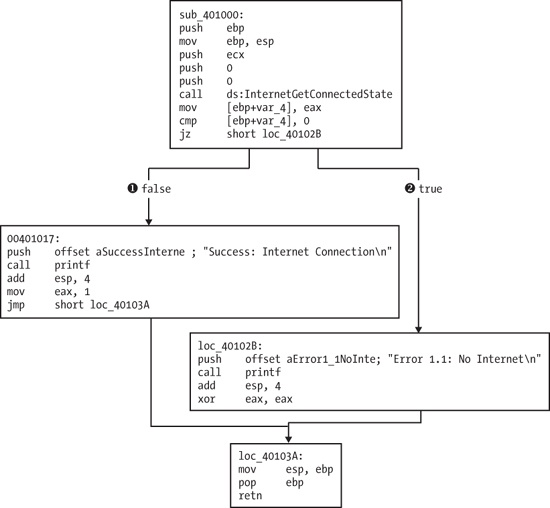
only one called by main. Figure C-18 shows a flow graph of this function.
Now we graph this function in IDA Pro using View ▸ Graphs
▸ Flow chart. Looking at this graph and code, we see a common code construct: two
different code paths depend on the result of the call to InternetGetConnectedState. The cmp instruction is used
to compare the result contained in EAX to 0, and then the jz
instruction is used to control the flow.
The MSDN page on InternetGetConnectedState further states
that the function returns 1 if there is an active Internet connection; otherwise it returns 0.
Therefore, the code will take the false branch at ❶ if
the result is 0 because the zero flag (ZF) will be clear; otherwise, it will take the true branch at
❷. The code construct used in this function is an
if statement.
The function calls the subroutine at 0x40105F in two locations, but if we dive into that
function, we will quickly get lost in a rabbit hole. This function is printf. Surprisingly, both the IDA Pro commercial and freeware versions will not always
recognize and label the printf function. Therefore, we must look
for certain signals that hint at an unlabeled call to printf. One
easy way to tell is by identifying parameters pushed onto the stack before the call to the
subroutine. Here, in both cases, a format string is pushed onto the stack. The \n at the end of a string denotes a line feed. Also, given the context and
the string itself, we can deduce that the function is printf. Therefore, we rename the function to printf,
so that it is marked as such throughout the code, as shown in Figure C-18. Once the printf function is called, we see that EAX is set to either 1 or 0 before the function
returns.
To summarize, this function checks for an active Internet connection, and then prints the result of its check, followed by returning a 1 if it is connected and 0 if it is not. Malware often performs a similar check for a valid Internet connection.