The simplest way to convert point data to polygon data would be to buffer the points by their known separation:
ST_Buffer(the_geom, 5)
We can imagine, however, that such a simplistic approach might look strange:
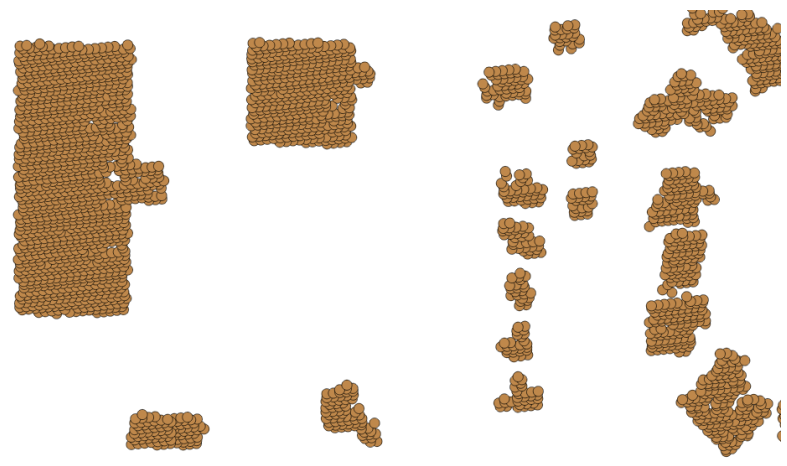
As such, it would be good to perform a union of these geometries in order to dissolve the internal boundaries:
ST_Union(ST_Buffer(the_geom, 5))
Now, we can see the start of some simple building footprints:
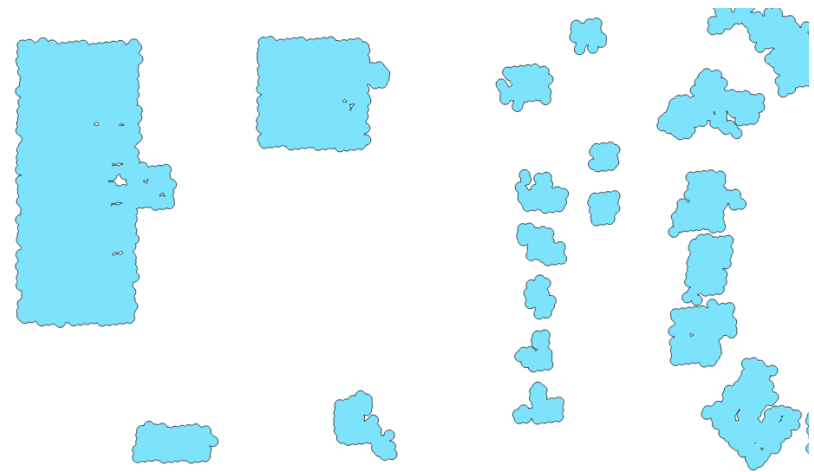
While this is marginally better, the result is quite lumpy. We will use the ST_Simplify_PreserveTopology function to simplify the polygons and then grab just the external ring to remove the internal holes:
CREATE TABLE chp04.lidar_buildings_buffer AS WITH lidar_query AS (SELECT ST_ExteriorRing(ST_SimplifyPreserveTopology(
(ST_Dump(ST_Union(ST_Buffer(the_geom, 5)))).geom, 10
)) AS the_geom FROM chp04.lidar_buildings) SELECT chp04.polygonize_to_multi(the_geom) AS the_geom from lidar_query;
Now, we have simplified versions of our buffered geometries:
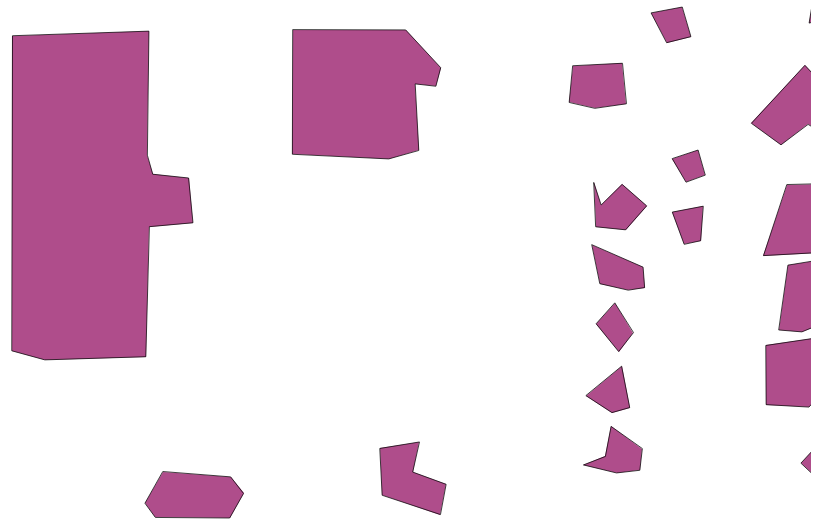
There are two things to note here. The larger the building, relative to the density of the sampling, the better it looks. We might query to eliminate smaller buildings, which are likely to degenerate when this approach is used, depending on the density of our LiDAR data.
