Carry out the following steps:
- Create the following table to host weather stations' data:
CREATE TABLE chp08.wstations
(
id bigint NOT NULL,
the_geom geometry(Point,4326),
name character varying(48),
temperature real,
CONSTRAINT wstations_pk PRIMARY KEY (id )
);
- Create an account at https://openweathermap.org to get an API key. Then, check the JSON response for the web service you are going to use. If you want the 10 closest weather stations from a point (the city centroid), the request you need to run is as follows (test it in a browser): http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/find?lat=55&lon=37&cnt=10&appid=YOURKEY
- You should get the following JSON response (the closest 10 stations and their relative data are ordered by their distance from the point coordinates, which in this case are lon=37 and lat=55):
{
"message": "accurate",
"cod": "200",
"count": 10,
"list": [
{
"id": 529315,
"name": "Marinki",
"coord": {
"lat": 55.0944,
"lon": 37.03
},
"main": {
"temp": 272.15,
"pressure": 1011,
"humidity": 80,
"temp_min": 272.15,
"temp_max": 272.15
}, "dt": 1515114000,
"wind": {
"speed": 3,
"deg": 140
},
"sys": {
"country": ""
},
"rain": null,
"snow": null,
"clouds": {
"all": 90
},
"weather": [
{
"id": 804,
"main": "Clouds",
"description": "overcast clouds",
"icon": "04n"
}
]
},
- Now, create the Python program that will provide the desired output and name it get_weather_data.py:
import sys
import requests
import simplejson as json
import psycopg2
def GetWeatherData(lon, lat, key):
"""
Get the 10 closest weather stations data for a given point.
"""
# uri to access the JSON openweathermap web service
uri = (
'https://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/find?
lat=%s&lon=%s&cnt=10&appid=%s'
% (lat, lon, key))
print 'Fetching weather data: %s' % uri
try:
data = requests.get(uri)
print 'request status: %s' % data.status_code
js_data = json.loads(data.text)
return js_data['list']
except:
print 'There was an error getting the weather data.'
print sys.exc_info()[0]
return []
def AddWeatherStation(station_id, lon, lat, name, temperature):
"""
Add a weather station to the database, but only if it does
not already exists.
"""
curws = conn.cursor()
curws.execute('SELECT * FROM chp08.wstations WHERE id=%s',
(station_id,))
count = curws.rowcount
if count==0: # we need to add the weather station
curws.execute(
"""INSERT INTO chp08.wstations (id, the_geom, name,
temperature) VALUES (%s, ST_GeomFromText('POINT(%s %s)',
4326), %s, %s)""",
(station_id, lon, lat, name, temperature)
)
curws.close()
print 'Added the %s weather station to the database.' % name
return True
else: # weather station already in database
print 'The %s weather station is already in the database.' % name
return False
# program starts here
# get a connection to the database
conn = psycopg2.connect('dbname=postgis_cookbook user=me
password=password')
# we do not need transaction here, so set the connection
# to autocommit mode
conn.set_isolation_level(0)
# open a cursor to update the table with weather data
cur = conn.cursor()
# iterate all of the cities in the cities PostGIS layer,
# and for each of them grap the actual temperature from the
# closest weather station, and add the 10
# closest stations to the city to the wstation PostGIS layer
cur.execute("""SELECT ogc_fid, name,
ST_X(the_geom) AS long, ST_Y(the_geom) AS lat
FROM chp08.cities;""")
for record in cur:
ogc_fid = record[0]
city_name = record[1]
lon = record[2]
lat = record[3]
stations = GetWeatherData(lon, lat, 'YOURKEY')
print stations
for station in stations:
print station
station_id = station['id']
name = station['name']
# for weather data we need to access the 'main' section in the
# json 'main': {'pressure': 990, 'temp': 272.15, 'humidity': 54}
if 'main' in station:
if 'temp' in station['main']:
temperature = station['main']['temp']
else:
temperature = -9999
# in some case the temperature is not available
# "coord":{"lat":55.8622,"lon":37.395}
station_lat = station['coord']['lat']
station_lon = station['coord']['lon']
# add the weather station to the database
AddWeatherStation(station_id, station_lon, station_lat,
name, temperature)
# first weather station from the json API response is always
# the closest to the city, so we are grabbing this temperature
# and store in the temperature field in cities PostGIS layer
if station_id == stations[0]['id']:
print 'Setting temperature to %s for city %s'
% (temperature, city_name)
cur2 = conn.cursor()
cur2.execute(
'UPDATE chp08.cities SET temperature=%s WHERE ogc_fid=%s',
(temperature, ogc_fid))
cur2.close()
# close cursor, commit and close connection to database
cur.close()
conn.close()
- Run the Python program:
(postgis-cb-env)$ python get_weather_data.py
Added the PAMR weather station to the database.
Setting temperature to 268.15 for city Anchorage
Added the PAED weather station to the database.
Added the PANC weather station to the database.
...
The KMFE weather station is already in the database.
Added the KOPM weather station to the database.
The KBKS weather station is already in the database.
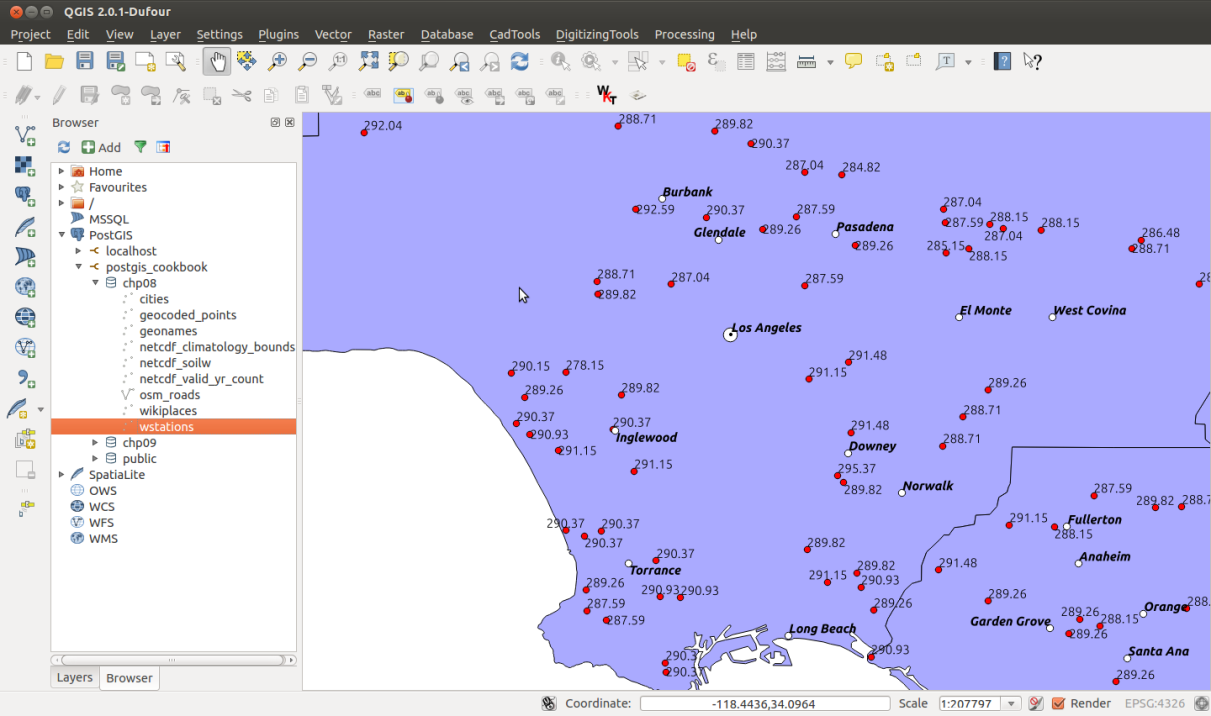
- Check the output of the Python program you just wrote. Open the two PostGIS layers, cities and wstations, with your favorite GIS desktop tool and investigate the results. The following screenshot shows how it looks in QGIS: