To use ST_MapAlgebra() on more than two bands, we must use the callback function variant. This means we need to create a callback function. Callback functions can be written in any PostgreSQL PL language, such as PL/pgSQL or PL/R. Our callback functions are all written in PL/pgSQL, as this language is always included with a base PostgreSQL installation.
Our callback function uses the following equation to compute the three-band EVI:
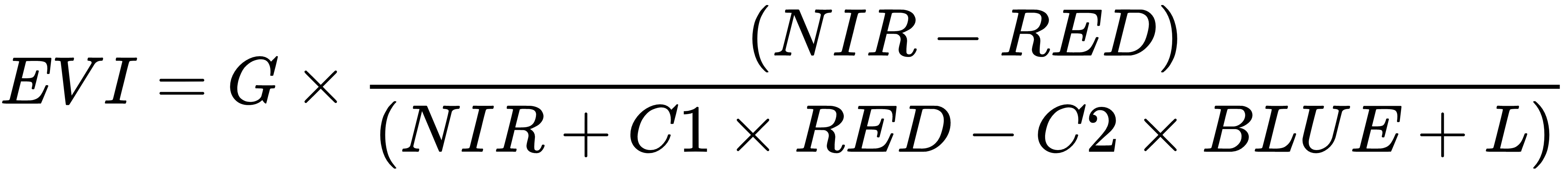
The following code implements the MODIS EVI function in SQL:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION chp05.modis_evi(value double precision[][][], "position" int[][], VARIADIC userargs text[])
RETURNS double precision
AS $$
DECLARE
L double precision;
C1 double precision;
C2 double precision;
G double precision;
_value double precision[3];
_n double precision;
_d double precision;
BEGIN
-- userargs provides coefficients
L := userargs[1]::double precision;
C1 := userargs[2]::double precision;
C2 := userargs[3]::double precision;
G := userargs[4]::double precision;
-- rescale values, optional
_value[1] := value[1][1][1] * 0.0001;
_value[2] := value[2][1][1] * 0.0001;
_value[3] := value[3][1][1] * 0.0001;
-- value can't be NULL
IF
_value[1] IS NULL OR
_value[2] IS NULL OR
_value[3] IS NULL
THEN
RETURN NULL;
END IF;
-- compute numerator and denominator
_n := (_value[3] - _value[1]);
_d := (_value[3] + (C1 * _value[1]) - (C2 * _value[2]) + L);
-- prevent division by zero
IF _d::numeric(16, 10) = 0.::numeric(16, 10) THEN
RETURN NULL;
END IF;
RETURN G * (_n / _d);
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql IMMUTABLE;
If you can't create the function, you probably do not have the necessary privileges in the database.
There are several characteristics required for all of the callback functions. These are as follows:
- All ST_MapAlgebra() callback functions must have three input parameters, namely, double precision[], integer[], and variadic text[]. The value parameter is a 3D array where the first dimension denotes the raster index, the second dimension the Y axis, and the third dimension the X axis. The position parameter is an array of two dimensions, with the first dimension indicating the raster index, and the second dimension consisting of the X, Y coordinates of the center pixel. The last parameter, userargs, is a 1D array of zero or more elements containing values that a user wants to pass to the callback function. If visualized, the parameters look like the following:
value = ARRAY[ 1 =>
[ -- raster 1 [pixval, pixval, pixval], -- row of raster 1 [pixval, pixval, pixval], [pixval, pixval, pixval] ], 2 => [ -- raster 2 [pixval, pixval, pixval], -- row of raster 2 [pixval, pixval, pixval], [pixval, pixval, pixval] ], ... N => [ -- raster N [pixval, pixval, pixval], -- row of raster [pixval, pixval, pixval], [pixval, pixval, pixval] ] ]; pos := ARRAY[ 0 => [x-coordinate, y-coordinate], -- center pixel o f output raster 1 => [x-coordinate, y-coordinate], -- center pixel o f raster 1 2 => [x-coordinate, y-coordinate], -- center pixel o f raster 2 ... N => [x-coordinate, y-coordinate], -- center pixel o f raster N ]; userargs := ARRAY[ 'arg1', 'arg2', ... 'argN' ];
- All ST_MapAlgebra() callback functions must return a double-precision value.
If the callback functions are not correctly structured, the ST_MapAlgebra() function will fail or behave incorrectly.
In the function body, we convert the user arguments to their correct datatypes, rescale the pixel values, check that no pixel values are NULL (arithmetic operations with NULL values always result in NULL), compute the numerator and denominator components of EVI, check that the denominator is not zero (prevent division by zero), and then finish the computation of EVI.
Now we call our callback function, modis_evi(), with ST_MapAlgebra():
SELECT ST_MapAlgebra(rast, ARRAY[1, 3, 4]::int[], -- only use the red, blue a nd near infrared bands 'chp05.modis_evi(
double precision[], int[], text[])'::regprocedure,
-- signature for callback function '32BF',
-- output pixel type 'FIRST', NULL, 0, 0, '1.', -- L '6.', -- C1 '7.5', -- C2 '2.5' -- G ) AS rast FROM modis m;
In our call to ST_MapAlgebra(), there are three criteria to take note of, which are as follows:
- The signature for the modis_evi() callback function. When passing the callback function to ST_MapAlgebra(), it must be written as a string containing the function name and the input-parameter types.
- The last four function parameters ('1.', '6.', '7.5', '2.5') are user-defined arguments that are passed for processing by the callback function.
- The order of the band numbers affects the order of the pixel values passed to the callback function.
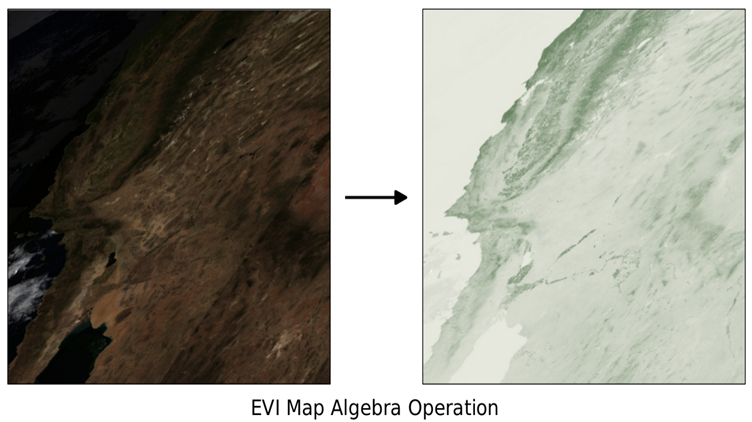
The following images show the MODIS raster before and after running the EVI operation. The EVI raster has a pale white to dark green colormap applied for highlighting areas of high vegetation:
For the two-band EVI, we will use the following callback function. The two-band EVI equation is computed with the following code:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION chp05.modis_evi2(value1 double precision, value2 double precision, pos int[], VARIADIC userargs text[])
RETURNS double precision
AS $$
DECLARE
L double precision;
C double precision;
G double precision;
_value1 double precision;
_value2 double precision;
_n double precision;
_d double precision;
BEGIN
-- userargs provides coefficients
L := userargs[1]::double precision;
C := userargs[2]::double precision;
G := userargs[3]::double precision;
-- value can't be NULL
IF
value1 IS NULL OR
value2 IS NULL
THEN
RETURN NULL;
END IF;
_value1 := value1 * 0.0001;
_value2 := value2 * 0.0001;
-- compute numerator and denominator
_n := (_value2 - _value1);
_d := (L + _value2 + (C * _value1));
-- prevent division by zero
IF _d::numeric(16, 10) = 0.::numeric(16, 10) THEN
RETURN NULL;
END IF;
RETURN G * (_n / _d);
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql IMMUTABLE;
Like ST_MapAlgebra() callback functions, ST_MapAlgebraFct() requires callback functions to be structured in a specific manner. There is a difference between the callback function for ST_MapAlgebraFct() and the prior one for ST_MapAlgebra(). This function has two simple pixel-value parameters instead of an array for all pixel values:
SELECT ST_MapAlgebraFct( rast, 1, -- red band rast, 4, -- NIR band 'modis_evi2(double precision, double precision, int[], text[])'::regprocedure,
-- signature for callback function '32BF', -- output pixel type 'FIRST', '1.', -- L '2.4', -- C '2.5' -- G) AS rast FROM chp05.modis m;
Besides the difference in function names, ST_MapAlgebraFct() is called differently than ST_MapAlgebra(). The same raster is passed to ST_MapAlgebraFct() twice. The other difference is that there is one less user-defined argument being passed to the callback function, as the two-band EVI has one less coefficient.
