Step one is to actually print the error out to the screen so we can see what we're working with. We're going to catch the error and we're going to print the error, console.log(e):
convertCurrencyAlt('USD', 'CAD', 100).then((status) => {
console.log(status);
}).catch((e) => {
console.log(e);
});
Now let's go ahead and start making some things fail. We're going to kick things off by making getCountries fail; that's the first call.
Now, this one only uses to, so all we have to do to get that to fail is to send in a bad to countryCode. I'm going to use MMM:
convertCurrencyAlt('USD', 'MMM', 100).then((status) => {
console.log(status);
}).catch((e) => {
console.log(e);
});
Save the file and we'll see what we get over inside the browser. Now what we're going to get back is a whole bunch of junk:
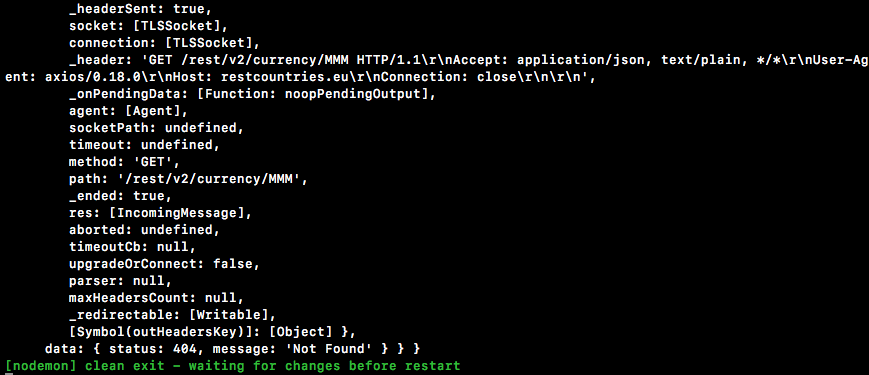
What's coming back here is actually the axios response. This has the error information; it has things like that status code. You can see it was a 404. We have a message saying not found. This is letting us know that countryCode we provided was not found by that endpoint. Now this is not particularly useful.
We want to come up with something that is a little more useful, like a message: Unable to get countries that use MMM. That'd be great. So, to do that, we're going to tweak getCountries. We're going to go ahead and use a regular old try catch block and set it up like this:
const getCountries = async (CurrencyCode) => {
try{
} catch (e){
}
If the code in the try block throws an error, the catch block will run, otherwise catch will never run. All we're going to do is take const response and return statement code and move it inside of try:
const getCountries = async (currencyCode) => {
try {
const response = await axios.get(`https://restcountries.eu/rest/v2/current/${currencyCode}`);
return response.data.map((country) => country.name);
} catch(e){
}
};
So, what we're doing is saying anytime either of these lines throw an error, run the code in the catch block and provide the error. Now we know what the error is. It doesn't contain much of anything, so what we're going to do is just throw our own error; something that is human-readable: throw new Error. In this case, we're going to stick with a template string and we're going to go ahead and set it up: Unable to get countries that use. Then we'll inject, right before the period, the currencyCode:
const getCountries = async (currencyCode) => {
try {
const response = await axios.get(`https://restcountries.eu/rest/v2/current/${currencyCode}`);
return response.data.map((country) => country.name);
} catch(e){
throw new Error(`Unable to get countries that use
${currencyCOde}.`);
}
};
Now, if we go ahead and save the currency-convert application with a bad to countryCode, we're going to see Unable to get countries that use MMM as the error. We could access the message directly using e.message.
convertCurrencyAlt('USD', 'MMM', 100).then((status) =>{
console.log(status);
}).catch((e) => {
console.log(e.message);
});
That'll improve the output even more. Now we just have a string. We could do anything we want with that string. It's very clear: Unable to get the countries that use MMM.
