Tables in Bootstrap 4 are largely unchanged from the previous version of the framework. However, there are a few new things, like inverse color table options and responsive tables. Let's start with the basics and we will build in the new features as we go.
The basic table structure in Bootstrap takes advantage of almost all the available HTML table tags. The header is wrapped in <thead> and the body <tbody> tags. This will allow additional styling as we get into the inverse table layout. For now, let's see how we put together a basic table in Bootstrap:
<table class="table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>first name</th>
<th>last name</th>
<th>twitter</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>john</td>
<td>smtih</td>
<td>@jsmtih</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>steve</td>
<td>stevens</td>
<td>@stevens</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>mike</td>
<td>michaels</td>
<td>@mandm</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
As you can see, the syntax is fairly straightforward. The only class being applied is the root table class on the <table> tag. This needs to be applied to any table variation you are using in Bootstrap. This will produce a table that looks like the following in the browser:
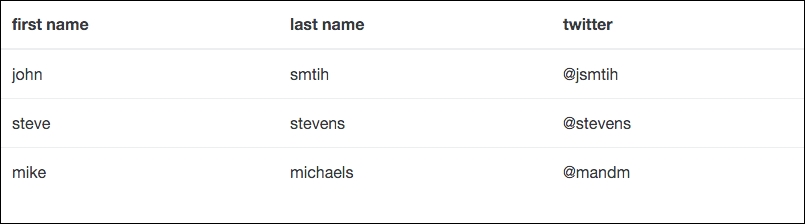
As you can see, the syntax is fairly straightforward. The only class being applied is the root table class on the <table> tag. This needs to be applied to any table variation you are using in Bootstrap.
Let me quickly show you one of the new table classes in Bootstrap 4. If we add the class table-inverse to the <table> tag, the table colors will flip to be a dark background with light text. Here's the code you need to change:
<table class="table table-inverse"> ... </table>
This slight variation in code will produce a table that looks like this:
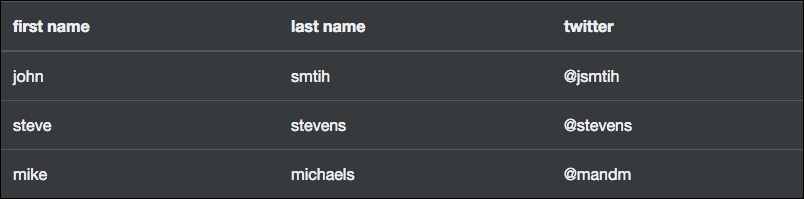
That's a pretty handy trick to know if you need to get a quick variation of the basic table styles going.
Perhaps you don't want to inverse the entire table? If that is the case, you can use the thead-inverse class on the <thead> tag to only inverse that row:
<table class="table"> <thead class="thead-inverse"> ... </thead> ... </table>
If this variation is applied, then your table will look like this:
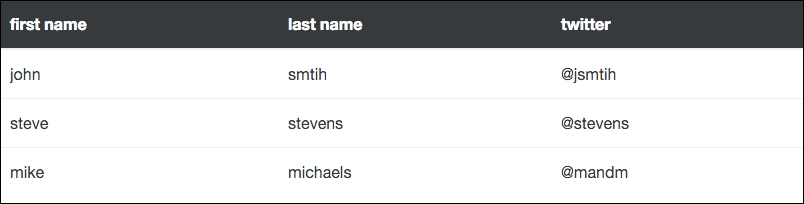
If you're looking for a more subtle design for your project, this approach may be more appealing to you.
Although not new to Bootstrap 4, the table-striped class is one that I use all the time. Applying this class to the <table> tag will add zebra striping to your table, starting with the first row in the body and applying a light grey background color on all the odd numbered rows:
<table class="table table-striped">
Using this class will produce a table that looks like this:
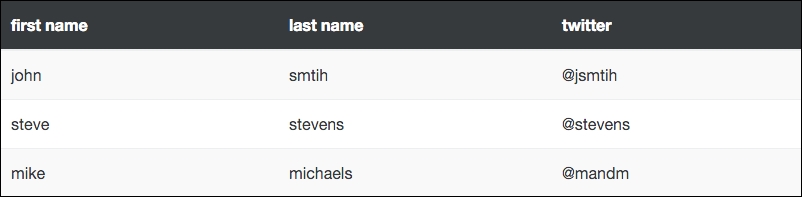
Now our table is starting to come together. With a few classes, we can get an attractive-looking layout. Let's see what else we can do with tables.
Another style that is regularly used is to add borders to your table. This can be done in the same way as stripes. Just change or add another class to the <table> tab called table-bordered. For this example, I'll remove the stripes and add the borders:
<table class="table table-bordered">
Now that we've added the borders and taken away the stripes, our table should look like this:
<table class="table table-bordered table-striped">
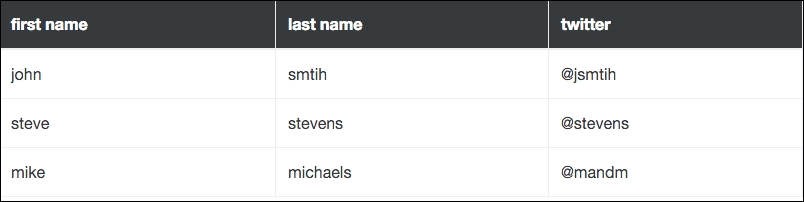
It's important to know that you can combine the table classes and use more than one. What if you wanted a table with stripes and borders? You can do that easily, by including both of the corresponding classes.
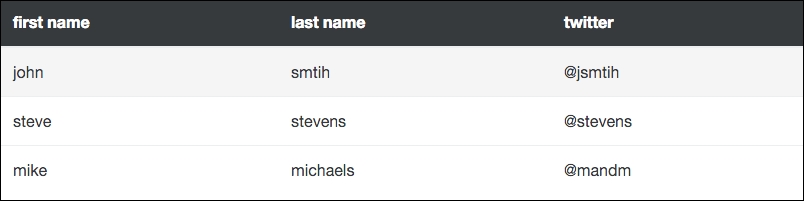
It's possible and easy to add a hover state to each of your table rows. To do so, you just need to add the table-hover class to the <table> tag. When used, if you hover over a row in the table, its background color will change to indicate a state change:
<table class="table table-hover">
Here I've removed the other table classes to show you the basic hover table option. When viewed in the browser, the table should look like the following when a row is hovered over with the mouse:
In some cases you may require a table with smaller text and compressed height. This can be done by adding the table-sm class to the <table> tag. This will make the look of the table more compact when viewing it:
<table class="table table-sm">
If you choose to use this class, your table should look like this:
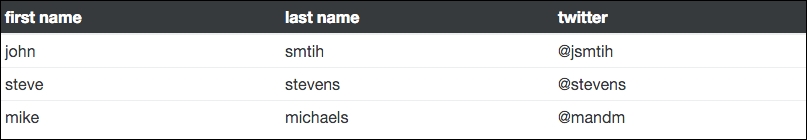
Creating smaller tables
That concludes the core table variations that you can apply through a simple CSS class. Before we move on, there are a couple more important points on tables that we should go over.
In some cases, you may want to color the background of a table row in a different color. This can easily be achieved through the use of some included contextual classes. There are five different color variations you can choose from:
table-activeis the hover color, light grey by defaulttable-successis green for a positive actiontable-infois blue for an informational highlighttable-warningis yellow to call out something that needs attentiontable-dangeris red for a negative or error action
The preceding classes can be applied to either a <tr> or <td> tag. If I apply all of these color variations to a single table, they look like this:
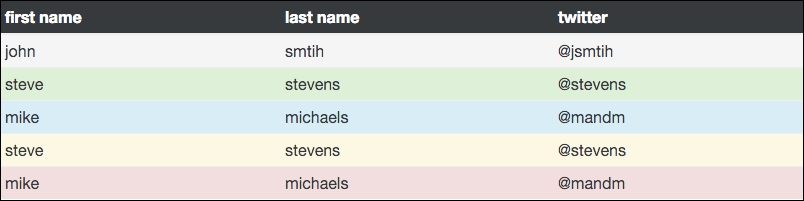
As you can see, these classes can be useful for validation or just highlighting a particular row that needs to stand out more.
Adding responsiveness to tables has never been very easy to do with CSS. Thankfully, Bootstrap 4 comes with some support built right in that you can easily take advantage of. To make a table responsive, you simply need to wrap a <div> around your <table> that has a class of table-responsive on it:
<div class="table-responsive">
<table class="table">
...
</table>
</div>
If you view the table on a viewport that is smaller than 768px, then the table cells will scroll horizontally, so they can all be viewed. If the viewport is larger, you will see no difference in the table compared to a regular one.
