At this point, you can be called a Bootstrap master around the world! You nailed the framework as few people do these days—you should be proud of that!
Now, you are about to face a challenge to overpass the boundaries of learning. In this chapter, we will see how to create and customize your own Bootstrap plugin. This could be tough, but if you reached this point you can go a step further to become a true Bootstrap master.
The topics covered are as follows:
- Customizing Bootstrap components
- Customizing Bootstrap plugins
- Creating a Bootstrap plugin
When we finish this chapter, we will also reach the end of the book. I hope this last chapter will help you empower yourself with all the Bootstrap framework skills.
To follow this chapter, create a sandbox.html file and just place the default template that we are using all over the book. We will place all the code snippets of this chapter in this file.
In my years of experience of using Bootstrap, one of the major issues that I received is how can I change a Bootstrap component to appear like I need?
Most of the time, the answer is to take a look at the CSS and see how you can override the style. However, this orientation can be obscure sometimes and the developer will be unable to find a solution.
In this section, we will customize some Bootstrap components. We did some of that in previous chapters, but now we will go a step further into this subject. Let's start customizing a single button.
We must start with a button, because of two factors. First, it is a quite simple component and second we have to customize a button very often.
Let's assume we have a simple button placed in a page that already has the Bootstrap fully loaded. We will call it as the sandbox page. The HTML for it should be like this:
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" aria-pressed="false" autocomplete="off"> This is a simple button </button>
As we saw so many times, this button is a simple one with the .btn and .btn-default classes that will make the button blue, as shown in the next screenshot:

If you want a different color for the button, you can use one of the others contextual classes provided by Bootstrap (.btn-success, .btn-info, .btn-warning, .btn-danger, and so on) by using them together with the base class .btn class.
If you want to define a new color, the suggestion is to create a new class and define the necessary pseudo-class. Let's assume we want a purple button defined by a class .btn-purple. Define a CSS for it:
.btn-purple {
color: #fff;
background-color: #803BDB;
border-color: #822FBA;
}This is the base CSS. Now we must define all the pseudo-classes for the button:
.btn-purple:hover,
.btn-purple:focus,
.btn-purple:active,
.btn-purple.active {
color: #ffffff;
background-color: #6B39AD;
border-color: #822FBA;
}Now, for every interaction with the button (such as hovering over it), the button will have a background color a little darker. Not all same pseudo-classes can have the same style; you can customize it as per your choice.
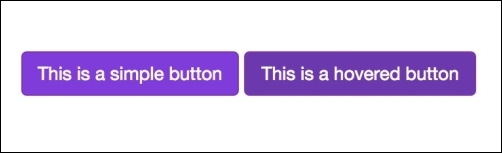
The next screenshot represents our new button. What we did was replace the .btn-default for the class .btn-purple. The one on the left is .btn-purple and the one on the right is .btn-purple:hover:
Bootstrap has a nice feature for button toggle. It is native from the framework and can be used in different ways. We will take a look at the single toggle button. For that, create a normal button in the sandbox page:
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" autocomplete="off"> Single toggle </button>
To make this button turn into a single toggle, we have to add the data attribute data-toggle="button" and the attribute aria-pressed="true". This will turn the button into a toggle button. Now when you click on the button, Bootstrap will add a class .active to it, making it appear pressed. The code is as follows:
<button type="button" class="btn btn-default" data-toggle="button" aria-pressed="false" autocomplete="off"> Single toggle </button>
The toggle buttons can turn into buttons checkbox or buttons radio. At first, we need to remember the concept of button group. So let's create a simple .btn-group in the HTML:
<div class="btn-group">
<button class="btn btn-default">
Laika
</button>
<button class="btn btn-default">
Jonny
</button>
<button class="btn btn-default">
Doge
</button>
</div>The concept of using button groups is to create a div with the class .btn-group and insert a bunch of button elements inside it. However, we want a bunch of checkboxes, so let's substitute the button element for a label and input elements with type checkbox:
<div class="btn-group">
<label class="btn btn-default">
<input type="checkbox" autocomplete="off"> Laika
</label>
<label class="btn btn-default">
<input type="checkbox" autocomplete="off"> Jonny
</label>
<label class="btn btn-default">
<input type="checkbox" autocomplete="off"> Doge
</label>
</div>Refresh the page and you will see that the button list now has a checkbox input on each label, as shown in the following screenshot:

To change it to toggle and hide the checkboxes, we just need to simple add the data attribute data-toggle="buttons".
There is an option to preselect a checkbox, just need to add the .active class to the label and add the attribute checked="checked" to the input:
<div class="btn-group" data-toggle="buttons">
<label class="btn btn-default">
<input type="checkbox" autocomplete="off"> Laika
</label>
<label class="btn btn-default active">
<input type="checkbox" autocomplete="off" checked="checked"> Jonny
</label>
<label class="btn btn-default">
<input type="checkbox" autocomplete="off"> Doge
</label>
</div>The next image shows the final output of the checkbox with the second checkbox selected on the page reload:

The other option for the toggle button is to become a radio button. The procedure is very similar to the checkbox. We just need to change the input from type="checkbox" to type="radio":
<div class="btn-group" data-toggle="buttons"> <label class="btn btn-default"> <input type="radio" autocomplete="off"> Laika </label> <label class="btn btn-default active"> <input type="radio" autocomplete="off" checked="checked"> Jonny </label> <label class="btn btn-default"> <input type="radio" autocomplete="off"> Doge </label> </div>
This will create a .btn-group formed by radio button, been just one selected at once.
Buttons can be customized using JavaScript as well. For instance, any toggle button can be toggled by calling:
$('button selector').button('toggle')This will toggle the state of the button from active to not active.
Before Version 3.3.6, it was possible to change the text of a button via JavaScript by calling the button passing a string. First, you should define a state text. For instance, let's define a button with the attribute data-statesample-text="What a sample":
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" autocomplete="off" data-statesample-text="What a sample"> Single toggle </button>
Using JavaScript, you can change the text with the value or the data text by calling:
$('button').button('statesample');Reset the text to original with the following function:
$('button').button('reset');However, this feature is deprecated after Version 3.3.6 and will be removed in Version 4 of Bootstrap.
