Having vector data without topology errors is important for further analysis, as these errors may lead to incorrect results.
This recipe shows you how to use the built-in GRASS tools to fix various topology errors in vector layers.
QGIS has very good integration with GRASS GIS; there is a GRASS plugin that provides access to the GRASS GIS database and functionality. GRASS algorithms are also available from the Processing plugin. The latter is simpler because you don't need to bother with setting up GRASS locations and mapsets and importing and exporting data.
To follow this recipe, load the nonbreak.shp, dangles.shp, and nosnap.shp layers from the sample data. Additionally, make sure that the Processing plugin is enabled in Plugin Manager.
The following steps show you how to fix various topology errors with the GRASS v.clean toolset using the Processing toolbox:
First, we will learn how to remove dangling lines. Dangling lines are lines that have no connection with other lines on one or either end nodes:
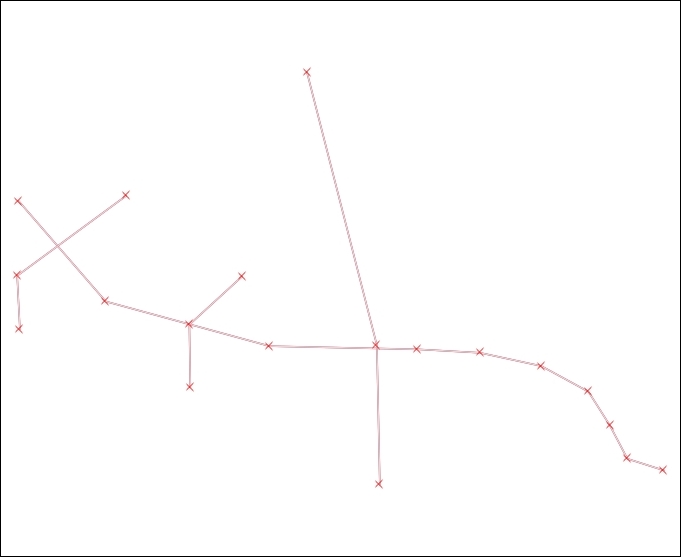
To remove them, perform the following steps:
- In the Processing Toolbox menu, find the v.clean algorithm by typing its name in the filter field at the top of the toolbox. Double-click on the algorithm name to open its dialog.
- In the Layer to clean combobox, select the
danglinglayer. - In the Cleaning tool combobox, select rmdangle—a tool for the removal of dangles.
- The Threshold field is used to define the maximum length of the dangling line. For our example, enter 6.000000:
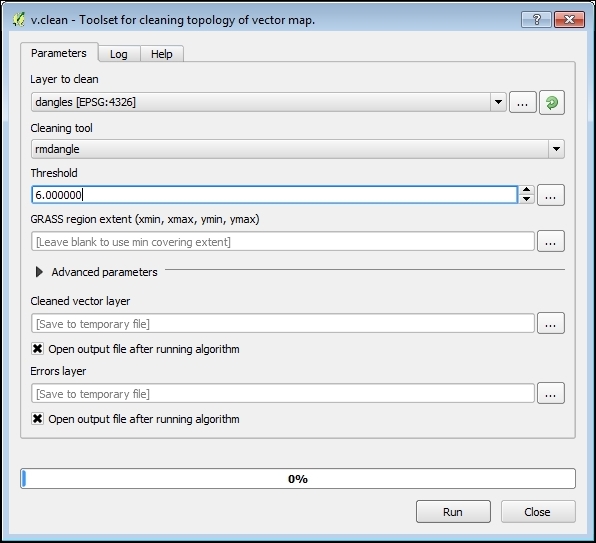
- Click on the Run button to remove dangles. When the algorithm is finished, two new layers will be added to QGIS: the
Cleanedlayer contains cleaned geometries (shown in green) and theErrorslayer contains dangles that were removed (shown in red):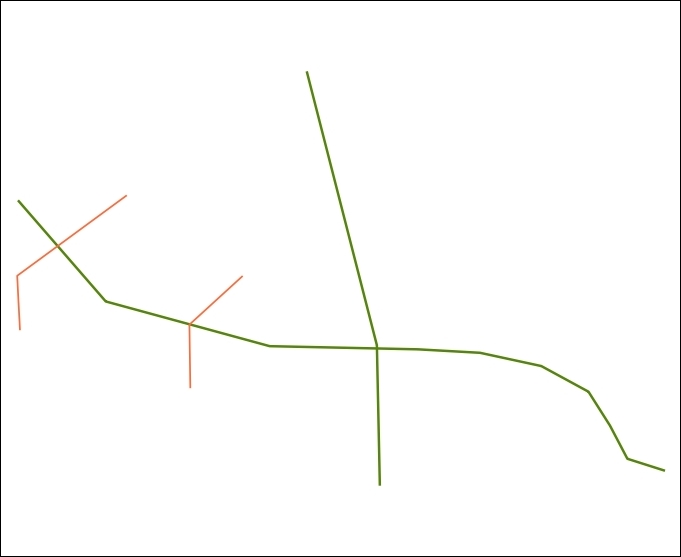
Another topology issue is missed line breaks in the intersection nodes. To add break at intersections, perform the following steps:
- In the Processing Toolbox menu, find the v.clean algorithm by typing its name in the filter field at the top of the toolbox. Double-click on the algorithm name to open its dialog.
- In the Layer to clean combobox, select the
nobreakslayer. - In the Cleaning tool combobox, select break.
- Leave all other parameters unchanged and click on the Run button to break lines on intersections. When the algorithm is finished, a new layer will be added to QGIS. You can easily verify that now lines are split at the intersection point.
Another very common topology issue is undershots, which happen when the line feature is not connected with another one at the intersection point and overshoots, which happens when the line ends beyond another line instead of connecting to it. Such errors often appear after inaccurate digitizing. To fix them, perform the following steps:
- In the Processing Toolbox menu, find the v.clean algorithm by typing its name in the filter field at the top of the toolbox. Double-click on the algorithm name to open its dialog.
- In the Layer to clean combobox, select the
nosnaplayer. - In the Cleaning tool combobox, select snap.
- The Threshold field is used to define the snapping tolerance in map units. For our example, you can leave this unchanged.
- Click on the Run button to remove overshoots and undershots. When the algorithm is finished, two new layers will be added to QGIS: the
Cleanedlayer contains features with fixed errors and theErrorslayer contains original invalid features.
The rmdangle tool simply sequentially removes all dangling lines with length less than the given threshold. If the threshold is less than 0, then all dangles will be removed.
The break tool breaks lines at intersections, so all lines will have a common node. This tool does not need a threshold value to be specified.
The snap tool tries to snap vertices to another one within the given threshold, if no appropriate vertices are found, then no snapping is done. It is worth mentioning that large threshold values may break the topology of polygonal features.
If you need more control over the topology cleaning process, try to use v.clean.advanced from the Processing Toolbox menu or consider using the GRASS plugin.
Also, there are other ways to clean vector topology, for example, using the lwgeom functions or external tools such as prepair and pprepair. Both tools are available as Processing plugins, and they can be installed via Plugin Manager.
- More information about the GRASS v.clean toolset can be found at http://grass.osgeo.org/grass64/manuals/v.clean.html
