QGIS supports PostGIS, SpatiaLite, MSSQL, and Oracle Spatial databases. We will cover two open source options: SpatiaLite and PostGIS. Both are available cross-platform, just like QGIS.
SpatiaLite is the spatial extension for SQLite databases. SQLite is a self-contained, server-less, zero-configuration, and transactional SQL database engine (www.sqlite.org). This basically means that a SQLite database, and therefore also a SpatiaLite database, doesn't need a server installation and can be copied and exchanged just like any ordinary file.
You can download an example database from www.gaia-gis.it/spatialite-2.3.1/test-2.3.zip (4 MB). Unzip the file; you will be able to connect to it by going to Layer | Add Layer | Add SpatiaLite Layer, using the Add SpatiaLite Layer toolbar button, or by pressing Ctrl + Shift + L. Click on New to select the test-2.3.sqlite database file. QGIS will save all the connections and add them to the drop-down list at the top. After clicking on Connect, you will see a list of layers stored in the database, as shown in this screenshot:
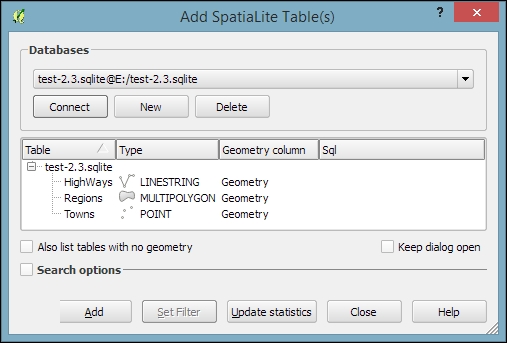
As with files, you can select one or more tables from the list and click on Add to load them into the map. Additionally, you can use Set Filter to only load specific features.
Tip
Filters in QGIS use SQL-like syntax, for example,
"Name" = 'EMILIA-ROMAGNA' to select only the region called
EMILIA-ROMAGNA or "Name" LIKE 'ISOLA%' to select all regions whose names start with ISOLA. The filter queries are passed on to the underlying data provider (for example, SpatiaLite or OGR). The provider syntax for basic filter queries is consistent over different providers but can vary when using more exotic functions. You can read the details of OGR SQL at http://www.gdal.org/ogr_sql.html.
In Chapter 4, Spatial Analysis, we will use this database to explore how we can take advantage of the spatial analysis capabilities of SpatiaLite.
PostGIS is the spatial extension of the PostgreSQL database system. Installing and configuring the database is out of the scope of this book, but there are installers for Windows and packages for many Linux distributions as well as for Mac (for details, visit http://www.postgresql.org/download/). To load data from a PostGIS database, go to Layers | Add Layer | Add PostGIS Layer, use the Add PostGIS Layer toolbar button, or press Ctrl + Shift + D.
When using a database for the first time, click on New to establish a new database connection. This opens the dialog shown in the following screenshot, where you can create a new connection, for example, to a database called postgis:
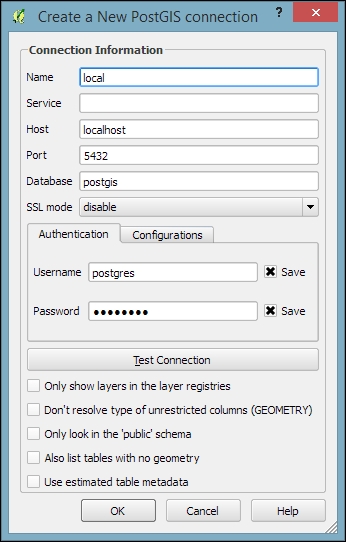
The fields that have to be filled in are as follows:
- Name: Insert a name for the new connection. You can use any name you like.
- Host: The server's IP address is inserted in this field. You can use
localhostif PostGIS is running locally. - Port: The PostGIS default port is
5432. If you have trouble reaching a database, it is recommended that you check the server's firewall settings for this port. - Database: This is the name of the PostGIS database that you want to connect to.
- Username and Password: For convenience, you can tell QGIS to save these.
After the connection is established, you can load and filter tables, just as we discussed for SpatiaLite.
