QGIS and the Web is not all about consuming data, it can also be used to serve data over the Web for others to view online or consume in other web clients (such as QGIS). Keep in mind that setting up your own web service is not the easiest way to make a web map (refer to the Hooking up web clients recipe in this chapter). This is, however, a great way to transition all the hard work that you've put into a QGIS project file into something other people can see and use.
For this recipe, you need a working installation of the QGIS server. This involves running a standard web server (such as Apache or Nginx). There are many ways to set up the server, so please see the official documentation at http://hub.qgis.org/projects/quantum-gis/wiki/QGIS_Server_Tutorial.
Once you have the QGIS server running, then you just need a QGIS project with the configuration outlined in this recipe.
- Open QGIS.
- Load up and style some layers:
- You need at least one vector layer to offer a WFS.
- You need at least one raster layer to offer a WCS.
- WMS can be any combination of layers, you can choose to server each as an independent layer or as a combined layer.
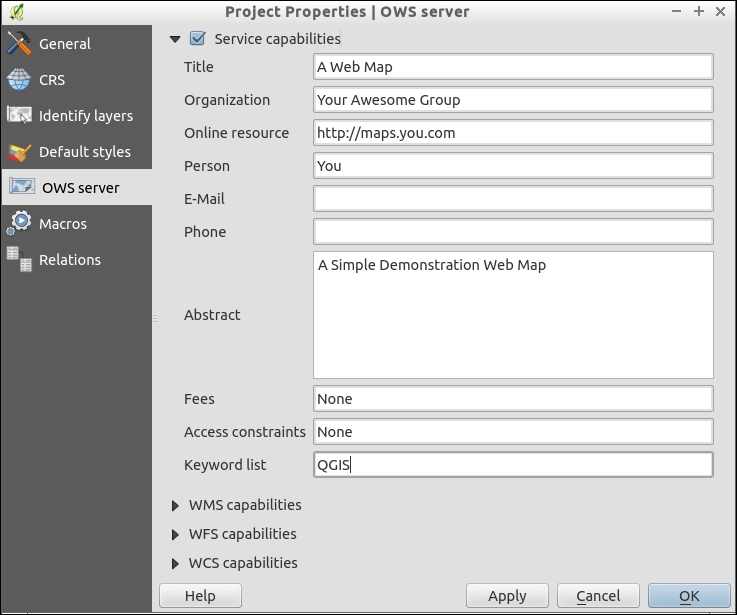
- Edit the Project properties in File | Project Properties:
- Now examine the WMS capabilities section:
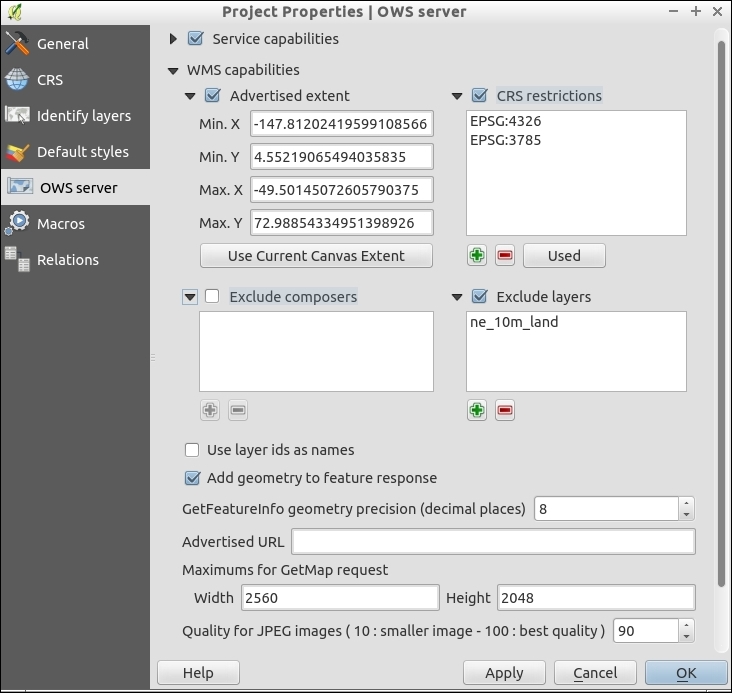
- Here, you can set the maximum extent that clients should expect.
- The CRS restrictions option lets you limit what projections are allowed.
- Exclude Layers allows you to have layers in your project that don't show up on the web.
- Add geometry to feature response is an optional enhancement if you are building a web map and you want to be able to work with the actual vectors (if it is a vector to begin with).
- GetFeatureInfo precision is about how close a user has to click to query a location. If you have a lot of data, you probably want this number to be small; but if you have only a few features, making this bigger makes it easier for end users.
- Set Maximums for GetMap request if you want to reduce the load on your server by limiting how much data a user can request at once. This is a good idea for a public server. 2560 x 2048, as shown in the screenshot, is enough pixels for an HD-resolution screen to be filled in a single request.
- Next, take a look at the WFS capabilities section:
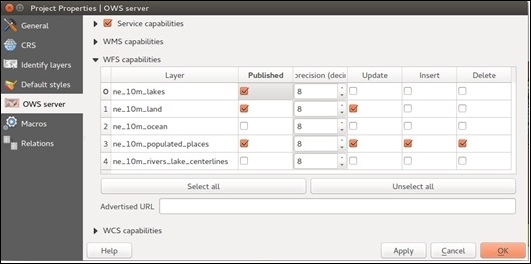
- Check the Published box next to any vector layers that you want to be usable over WFS.
- To enable WFS-T, check the Update, Insert, and Delete checkboxes. As they are separate, you can choose to only allow new data (Insert), only allow edits to existing data (Update), or only allow removal of data (Delete). Insert would be the safest option as it prevents editing or deletion of existing data.
- Finally, take a look at WCS capabilities:
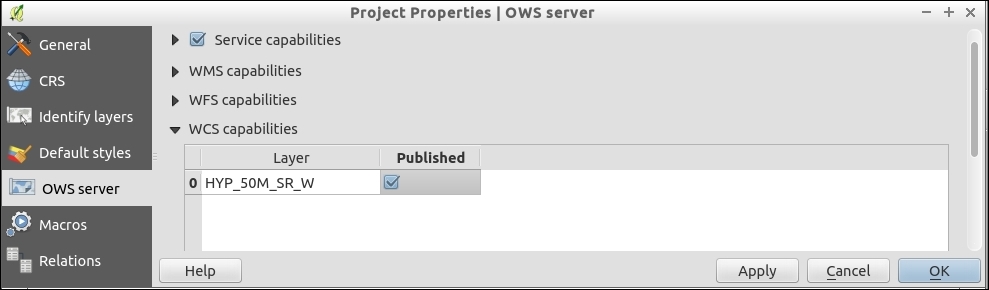
- When you are done setting options, click on the OK button.
- Now, save the project in a place where the QGIS server has access to it.
- Once saved, you can test access from any OGC-compliant web client:
The QGIS server is a middleman that takes in web service requests and translates them into QGIS internal calls, returning the requested data or rendered images, which are delivered to the end user via the web server.
The QGIS server contains many options that allow you to control which types of service to offer, which layers to offer over each service, and how to style these services. Alternatives to the QGIS server include MapServer and GeoServer (refer to the Managing GeoServer from QGIS section in this chapter).
- For more details, refer to the main documentation for the QGIS server at http://hub.qgis.org/projects/quantum-gis/wiki/QGIS_Server_Tutorial.
- Once you create a service, test it by adding your service to a QGIS project. Refer to the previous recipes in this chapter for how to add WMS, WFS, or WCS services.