In this recipe, we will look at the different layer and feature blending modes. Using these tools, we can achieve special rendering effects, which you may already know from other graphics programs.
To follow this recipe, you just need to load stamen.png and effect.png from our sample data. Make sure that stamen (left-hand side in the following screenshot) is the lower layer and effect (right-hand side in the following screenshot) is the upper layer. To test the feature blending modes, load blending.shp:
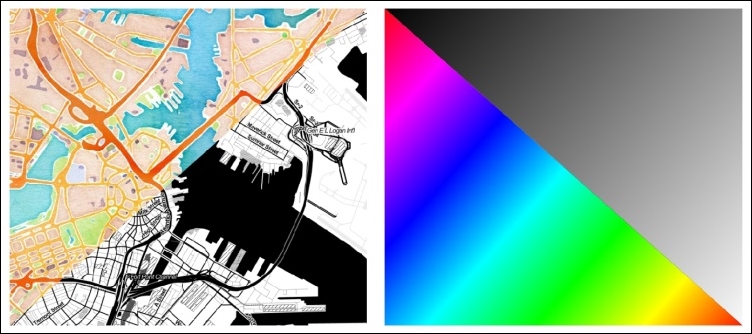
(Background maps "Watercolor" and "Toner" by Stamen Design, under CC BY 3.0. Data by OpenStreetMap, under CC BY SA).
Using the two raster layers, we can try the different blending modes. Of course, this works for vector layers, as well:
- Double-click on the
effectslayer to open Layer Properties. - You can find the blending settings by going to Layer Properties | Style | Color Rending together with other helpful controls for Brightness, Contrast, Saturation, and more, as shown in the next screenshot:
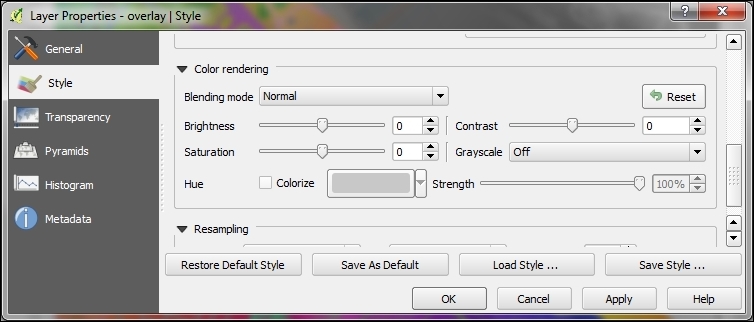
- Change the Blending mode and click on Apply to see the results.
- Similarly, for vector layers, such as our blending layer, we find the blending mode settings by going to Layer Properties | Style | Layer rendering, as shown in the following screenshot:
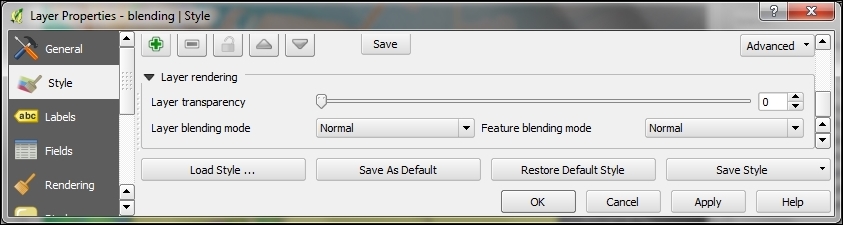
The main difference is that, for vector layers, we can control how features are blended together, and how the result is then blended to the underlying layers using the Feature blending and Layer blending modes, respectively. The feature blending mode is applied on a per-feature-basis.
The following screenshot shows the differences between feature and layer blending:
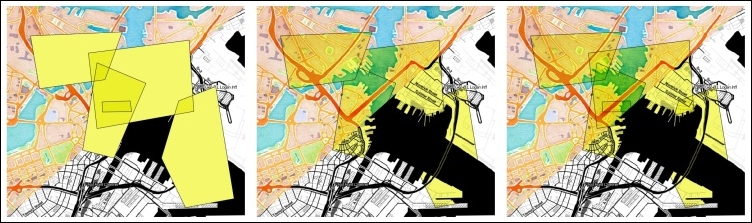
Feature and/or layer blending in action (from left to right): feature blending only, layer blending only, feature and layer blending combined (background maps "Watercolor" and "Toner" by Stamen Design, under CC BY 3.0. Data by OpenStreetMap, under CC BY SA).
The following is an explanation of the preceding screenshots:
- The leftmost image shows that Feature blending mode is set to Multiply, while Layer blending mode is set to default, Normal. This results in a map where the vector features are rendered on top of each other using the Multiply mode before the whole layer is overlaid on top of the lower layer(s).
- The center image instead shows Normal Feature blending mode combined with Multiply Layer blending mode. You can see how the features can block each other out because they are drawn on top of each other.
- Finally, the rightmost image shows both Layer blending mode and Feature blending modes being set to Multiply. In this combination, the Multiply rule is applied on both the feature and the layer level and, therefore, we can see features and the underlying background layer(s) shining through the features in the upper layer.
Based on the selected blending mode, the pixel colors (in the RGB mode) of the lower and upper layers are mixed as described next. For illustration and quick reference, the following figure shows the results of all 12 blending modes (from left to right and top to bottom), except for the Normal setting, which does not mix the colors but only uses the alpha channel of the upper layer to blend with the layer below it:
- Lighten: The Lighten mode selects the maximum of each RGB component from the foreground and background pixels. Be aware that the results tend to be jagged and harsh.
- Screen: The Screen mode paints light pixels from the upper layer over the lower layer, but it skips the dark pixels.
- Dodge: The Dodge mode will brighten and saturate the lower layer based on the lightness of the upper layer. This means that brighter colors in the upper layer cause the saturation and brightness of the lower layer to increase. This works best if the top pixels aren't too bright; otherwise, the effect is quite extreme.
- Addition: The Addition mode adds the pixel values of both layers. If the result exceeds 1 (in the case of RGB), the respective areas are displayed in white.
- Darken: The Darken mode creates a result that retains the smallest RGB components of both layers. Therefore, this is the opposite of the Lighten mode and, just as with Lighten, the results tend to be jagged and harsh.
- Multiply: The Multiply mode multiplies the values of both layers, thus resulting in a darker picture.
- Burn: The Burn mode causes darker colors in the upper layer to darken the lower layer. Burn can be used to tweak and colorize underlying layers.
- Overlay: The Overlay mode combines the Multiply and Screen blending modes. As a result, light parts become lighter and dark parts become darker.
- Soft light: The Soft light mode is very similar to Overlay, but it uses a combination of Burn and Dodge. This is supposed to emulate shining a soft light on an image.
- Hard light: The Hard light mode is also very similar to Overlay. It is supposed to emulate projecting a very intense light on an image.
- Difference: The Difference mode subtracts the values of the upper layer from the lower layer (or the other way around) to always get a positive value. Blending with black (which has an RGB value of 0,0,0) produces no change.
- Subtract: The Subtract mode subtracts the values of one layer from the other. In the case of negative values, black is displayed:
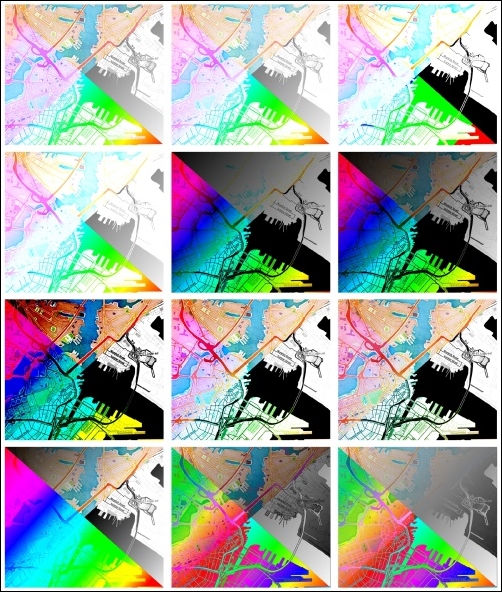
Overview of the 12 blending modes (background maps "Watercolor" and "Toner" by Stamen Design, under CC BY 3.0. Data by OpenStreetMap, under CC BY SA): first row: Lighten, Screen, and Dodge; second row: Addition, Darken, and Multiply; third row: Burn, Overlay, and Soft light; fourth row: Hard light, Difference, and Subtract.
