Besides print maps, web maps are another popular way of publishing maps. In this section, we will use different QGIS plugins to create different types of web map.
To create web maps from within QGIS, we can use the qgis2web plugin, which we have to install using the Plugin Manager. Once it is installed, go to Web | qgis2web | Create web map to start it. qgis2web supports the two most popular open source web mapping libraries: OpenLayers 3, and Leaflet.
The following screenshot shows an example of our airports dataset. In this example, we are using the Leaflet library (as configured in the bottom-left corner of the following screenshot) because at the time of writing this book, only Leaflet supports SVG markers:
- In the top-left corner, you can configure which layers from your project should be displayed on the web map, as well as the Info popup content, which is displayed when the user clicks on or hovers over a feature (depending on the Show popups on hover setting).
- In the bottom-right corner, you can pick a background map for your web map. Pick one and click on the Update preview button to see the result.
- In the bottom-left corner, you can further configure the web map. All available settings are documented in the Help tab, so the content is not reproduced here. Again, don't forget to click on the Update preview button when you make changes.
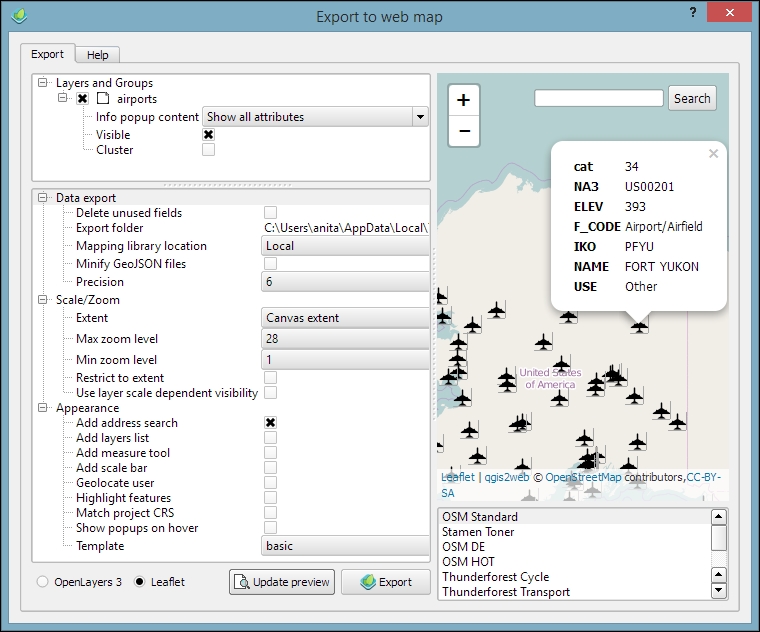
When you are happy with the configuration, click on the Export button. This will save the web map at the location specified as the Export folder and open the resulting web map in your web browser. You can copy the contents in the Export folder to a web server to publish the map.
Another popular way to share maps on the Web is map tiles. These are basically just collections of images. These image tiles are typically 256 × 256 pixels and are placed side by side in order to create an illusion of a very large, seamless map image. Each tile has a z coordinate that describes its zoom level and x and y coordinates that describe its position within a square grid for that zoom level. On zoom level 0 (z0), the whole world fits in one tile. From there on, each consecutive zoom level is related to the previous one by a power of 4. This means z0 contains 1 tile, z1 contains 4 tiles, and z2 contains 16 tiles, and so on.
In QGIS, we can use the QTiles plugin, which has to be installed using the Plugin Manager, to create map tiles for our project. Once it is installed, you can go to Plugins | QTiles to start it. The following screenshot shows the plugin dialog where we can configure the Output location, the Extent of the map that we want to export as tiles, as well as the Zoom levels we want to create tiles for.
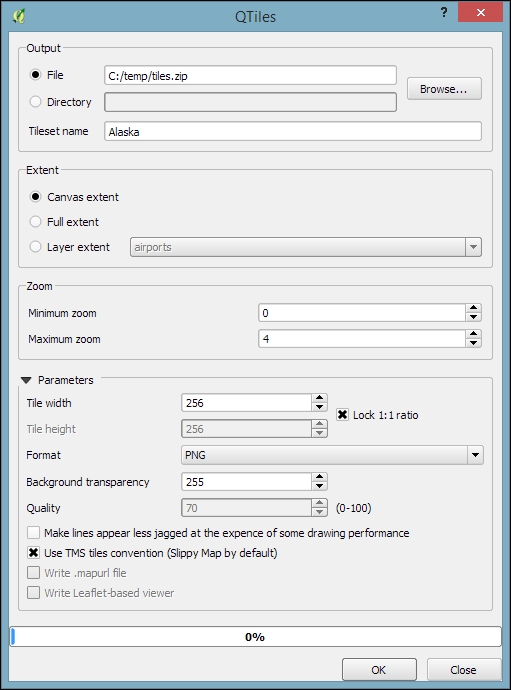
When you click on OK, the plugin will create a .zip file containing all tiles. Using map tiles in web mapping libraries is out of the scope of this book. Please refer to the documentation of your web mapping library for instructions on how to embed the tiles. If you are using Leaflet, for example, you can refer to https://switch2osm.org/using-tiles/getting-started-with-leaflet for detailed instructions.
To create stunning 3D web maps, we need the Qgis2threejs plugin, which we can install using the Plugin Manager.
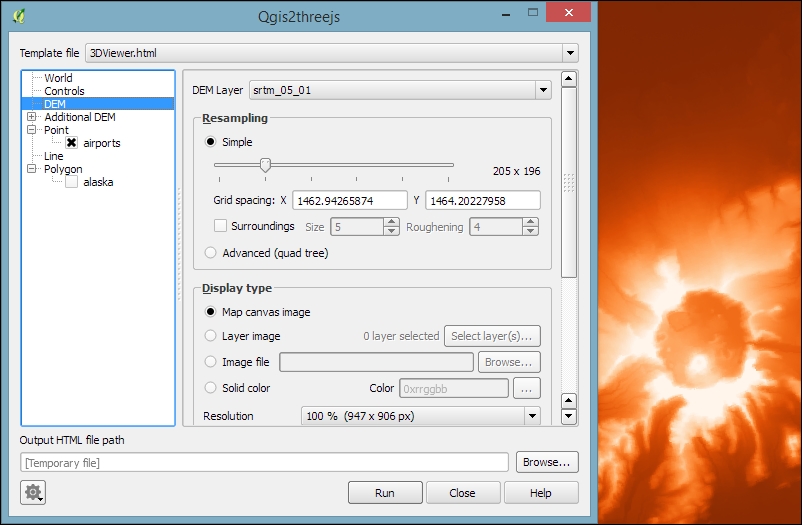
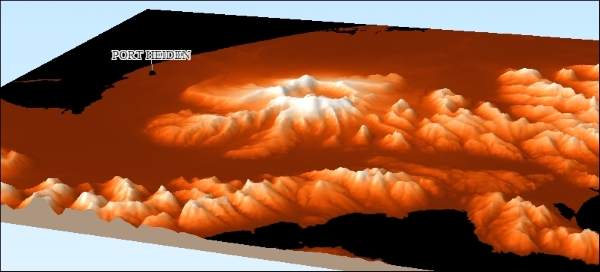
For example, we can use our srtm_05_01.tif elevation dataset to create a 3D view of that part of Alaska. The following screenshot shows the configuration of DEM Layer in the Qgis2threejs dialog. By selecting Display type as Map canvas image, we furthermore define that the current map image (which is shown on the right-hand side of the dialog) will be draped over the 3D surface:
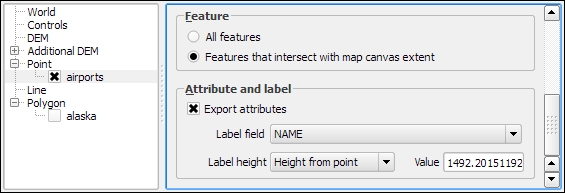
Besides creating a 3D surface, this plugin can also label features. For example, we can add our airports and label them with their names, as shown in the next screenshot. By setting Label height to Height from point, we let the plugin determine automatically where to place the label, but of course, you can manually override this by changing to Fixed value or one of the feature attributes.
If you click on Run now, the plugin will create the export and open the 3D map in your web browser. On the first try, it is quite likely that the surface looks too flat. Luckily, this can be changed easily by adjusting the Vertical exaggeration setting in the World section of the plugin configuration. The following example was created with a Vertical exaggeration of 10:
Qgis2threejs exports all files to the location specified in the Output HTML file path. You can copy the contents in that folder on a web server to publish the map.
