Optimum site selection is a pretty common problem, for example, when planning shop or warehouse locations or when looking for a new apartment. In this recipe, you will learn how to perform optimum site selection manually using tools from the Processing Toolbox option, but you will also see how to automate this workflow by creating a Processing model.
In the optimum site selection in this recipe, we will combine different vector analysis tools to find potential locations in Wake County that match the following criteria:
- Locations are near a big lake (up to 500 m)
- Locations are close to an elementary school (up to 500 m)
- Locations are within a reasonable distance (up to 2 km) from a high school
- Locations are at least 1 km from a main road
To follow this exercise, load the following datasets, lakes.shp, schools_wake.shp, and roadsmajor.shp.
As all datasets in our test data already use the same CRS, we can get right to the analysis. If you are using different data, you may have to get all your datasets into the same CRS first. In this case, please refer to Chapter 1, Data Input and Output.
The following steps show you how to perform optimum site selection using the Processing Toolbox option:
- First, we have to filter the lakes layer for big lakes. To do this, we use the Select by expression tool from the Processing toolbox, select the lakes layer, and enter
"AREA" > 1000000 AND "FTYPE" = 'LAKE/POND'in the Expression textbox, as shown in the following screenshot: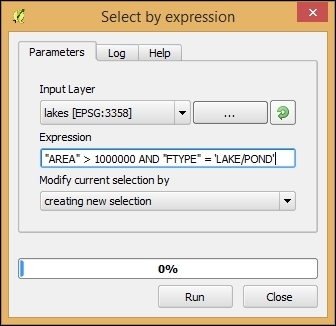
- Next, we create the buffers that will represent the proximity areas around lakes, schools, and roads. Use Fixed distance buffer from the Processing Toolbox option to create the following buffers:
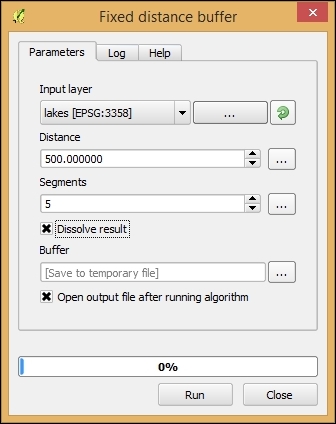
- For the lakes, select Distance of 500 meters and set Dissolve result by checking the box as shown in the following screenshot. By dissolving the result, we can make sure that the overlapping buffer areas will be combined into one polygon. Otherwise, each buffer will remain as a separate feature in the resulting layer:
- To create the elementary school buffers, first select only the schools with
"GLEVEL" = 'E'using the Select by Expression tool like we did for the lakes buffer. Then, use the buffer tool like we just did for the lakes buffer. - Repeat the process for the high schools using
"GLEVEL" = 'H'and a buffer distance of 2,000 meters. - Finally, for the roads, create a buffer with a distance of 1,000 meters.
- For the lakes, select Distance of 500 meters and set Dissolve result by checking the box as shown in the following screenshot. By dissolving the result, we can make sure that the overlapping buffer areas will be combined into one polygon. Otherwise, each buffer will remain as a separate feature in the resulting layer:
- With all these buffers ready, we can now combine them to fulfill these rules:
- Use the Intersection tool from the Processing Toolbox option on the buffers around elementary and high schools to get the areas that are within the vicinity of both school types.
- Use the Intersection tool on the buffers around the lakes and the result of the previous step to limit the results to lakeside areas. Use the Difference tool to remove areas around major roads (that is, the buffered road layer) from the result of the previous (Intersection) steps.
- Check the resulting layer to view the potential sites that fit all the criteria that we previously specified. You'll find that there is only one area close to WAKEFIELD ELEMENTARY and WAKEFIELD HIGH that fits the bill, as shown in the following screenshot:
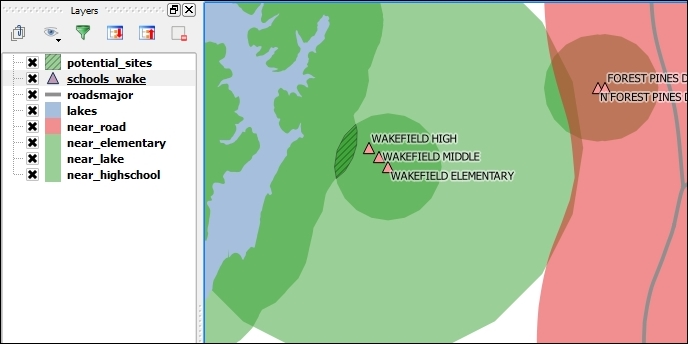
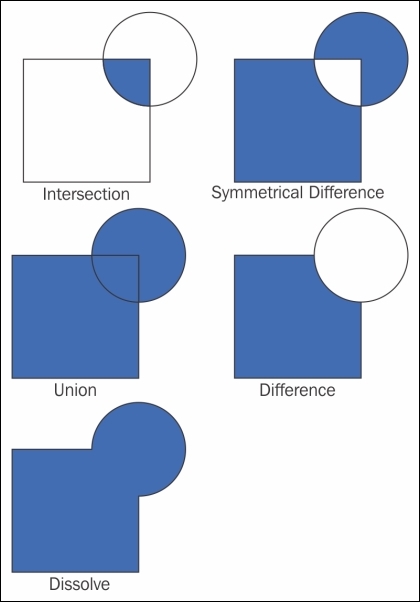
In step 1, we used Intersection to model the requirement that our preferred site would be near both an elementary and a high school. Later, in step 3, the Difference tool enabled us to remove areas close to major roads. The following figure gives us an overview of the available vector analysis tools that can be useful for similar analyses. For example, Union could be used to model requirements, such as "close to at least an elementary or a high school". Symmetrical Difference, on the other hand, would result in "close to an elementary or a high school but not both", as illustrated in the following figure:
We were lucky and found a potential site that matched all criteria. Of course, this is not always the case, and you will have to try and adjust your criteria to find a matching site. As you can imagine, it can be very tedious and time-consuming to repeat these steps again and again with different settings. Therefore, it's a good idea to create a Processing model to automate this task.
The model (as shown in the following screenshot) basically contains the same tools that we used in the manual process, as follows:
- Use two select by expression instances to select elementary and high schools. As you can see in the following screenshot, we used the descriptions Select "GLEVEL" = 'E' and Select "GLEVEL" = 'H' to name these model steps.
- For elementary schools, compute fixed distance buffers of 500 meters. This step is called Buffer "GLEVEL" = 'E'.
- For high schools, compute fixed distance buffers of 2,000 meters. This step is called Buffer "GLEVEL" = 'H'.
- Select the big lakes using
Select byexpression (refer to the Select big lakes step) and buffer them using fixed distance buffer of 500 meters (refer to the Buffer lakes step). - Buffer the roads using Fixed distance buffer (refer to the Buffer roads step). The buffer size is controlled by the number model input called road_buffer_size. You can extend this approach of controlling the model parameters using additional inputs to all the other buffer steps in this model. (We chose to show only one example in order to keep the model screenshot readable.)
- Use Intersection to get areas near schools (refer to the Intersection: near schools step).
- Use Intersection to get areas near schools and lakes (refer to the Intersection: schools and lakes step).
- Use Difference to remove areas near roads (refer to the Difference: avoid roads step).
This is how the final model looks like:
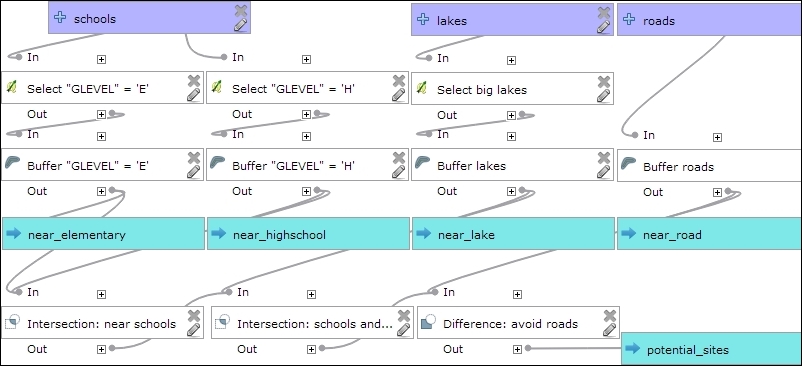
You can run this model from the Processing Toolbox option, or you can even use it as a building block in other models. It is worth noting that this model produces intermediate results in the form of buffer results (near_elementary, near highschool, and so on). While these intermediate results are useful while developing and debugging the model, you may eventually want to remove them. This can be done by editing the buffer steps and removing the Buffer <OutputVector> names.
