This recipe shows you how to use the built-in Road graph plugin to calculate the shortest paths in a network.
To follow this recipe, load network_pgr.shp from the sample data. Additionally, make sure that the Road graph plugin is enabled in Plugin Manager.
The Road graph plugin enables us to route between two points that are selected on the map. Before we can use this, we have to configure it first, as follows:
- Enable the Shortest path panel by navigating to View | Panels. This should add the plugin panel to the user interface.
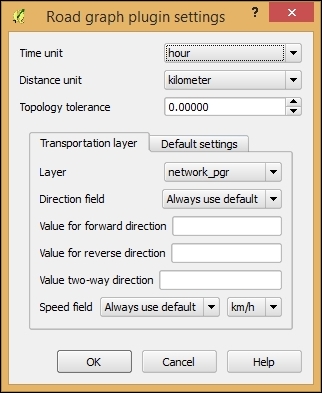
- Go to Vector | Road graph | Settings to get to the configuration dialog. For now, the default settings, as shown in the following screenshot, should be fine. Note that the network layer is selected as Transportation layer. Click on OK to confirm the settings:
- Once the settings are configured, we can calculate our first route. Select the Start and Stop locations using the buttons marked with crosshair icons. Activate the crosshair button and then click in the map to select a location. This location will be marked on the map, and the coordinates will be automatically inserted into the Start or Stop input field.
- Click on Calculate to initiate route computation. Depending on the size of the network used, this step will either be very fast or it can take much more time. The route will be highlighted in the map, and the route length and travel time will be displayed, as shown in the following screenshot:
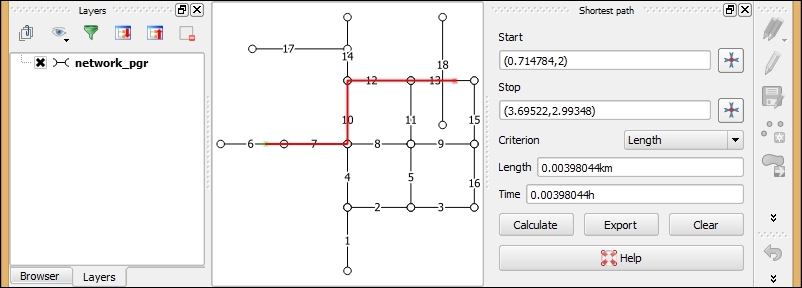
- If you want to store the computed shortest path, click on Export and you will be able to choose whether you want to create a new layer for the path or add the route to an existing line layer.
- To compute a new route, simply change the start and stop locations and click on Calculate again.
- Click on Clear to remove the route highlights when you are done.
The Road graph plugin uses the QGIS network analysis library, which implements Dijkstra's algorithm. For a given starting node, the algorithm finds the path with the lowest cost (that is, the shortest path if the cost criterion is length or the fastest path if the cost criterion is time) between this node and every other node in the network. This can also be used to find costs of the shortest paths from a start node to a destination node by stopping the algorithm once the shortest path to the destination node has been determined.
In contrast to many simple routing tools, the Road graph plugin builds the network topology automatically. As our network dataset is topologically sound (that is, there are no tiny gaps where network edges meet), we can set up Road graph plugin settings with Topology tolerance as 0. If you are using a network from a different source, it may not have been created with the same attention to detail, and you may have to increase Topology tolerance to get routing to work.
- If you are interested in learning more about this algorithm, you can start at http://wiki.gis.com/wiki/index.php/Dijkstra's_algorithm
