A topological network, which specifies the formal relationships between geometric objects, requires real geographic data for it to be useful in an actual physical space. So next, we will acquire some geographic data in order to construct a network providing the shortest path between points in a physical space, following certain rules embedded in the network. A great source of data for this, and many other purposes, is OpenStreetMap.
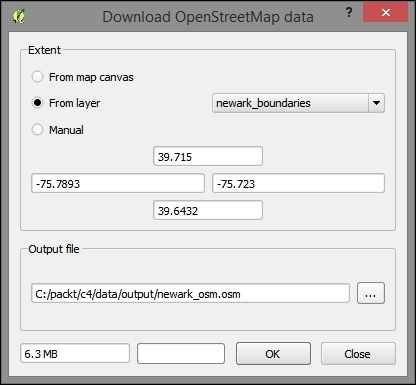
Now, let's move back to QGIS to acquire the OpenStreetMap data from which we will create a topological network:
The downloaded data must be added to the QGIS project to verify that it has been downloaded and to further work on the data from within QGIS. Perform the following steps:
We will project the OSM data onto the projection used by the other data to be added to the project, which is the location of the students. We want these two datasets to use the same projection system; otherwise, we will run into trouble while building our topological network and analyzing the network. Perform the following steps:
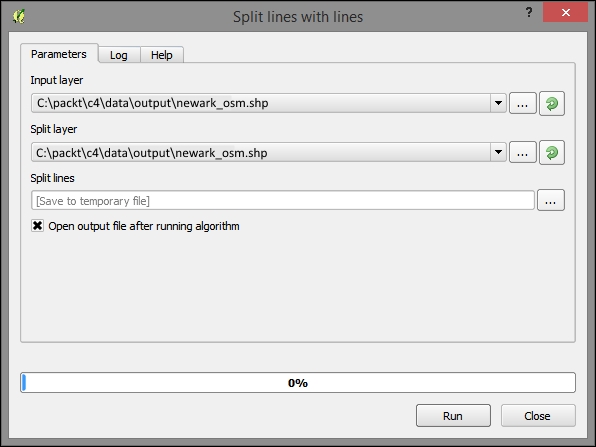
It is necessary that the topological edges to be created are coterminous with the geographic data vertices. This is called a topologically correct dataset. We will use Split lines with lines to fulfill this requirement. Perform the following steps:
- Search for Split lines with lines in the Processing Toolbox panel.
- Select the projected OSM lines file,
c4/data/output/newark_osm.shp, as both the Input layer and Split layer. - Click on Run, as shown in the following screenshot: