While QGIS itself is a great and functional program, sometimes it is better to use more suitable tools to perform some simple or complex actions. This recipe shows you how to use some of these third-party tools.
To follow this recipe, you will need a btnmeatrack_2014-05-22_13-35-40.nmea file from the book dataset. We will also use the cookbook.db SpatiaLite database that we created in the Loading vector layers into SpatiaLite recipe in Chapter 1, Data Input and Output, and the PostgreSQL database, which we developed in Chapter 6, Network Analysis.
Besides this, don't forget to install GPSBabel (usually this comes with QGIS), spatialite-gui, and pgAdmin (these should be installed manually).
First we will convert NMEA data to GPX format with GPSBabel, then learn how to use SpatiaLite GUI tools and pgAdmin to work with databases.
GPSBabel is a command-line tool to manipulate, convert, and process GPS data (waypoints, tracks, and routes) in different formats.
To convert a file from the NMEA format to more common GPX, follows these steps:
- Open the command prompt and go to the directory where the
btnmeatrack_2014-05-22_13-35-40.nmeafile is located. Usually, this can be done with thecdcommand, for example, if the file is located in thedatadirectory on theC:drive, use this command:cd c:\data - In the command prompt, enter the following command to convert the NMEA file to the GPX file:
gpsbabel -i nmea -f btnmeatrack_2014-05-22_13-35-40.nmea -o gpx -F 2014-05-22_13_35-40.gpx
spatialite-gui is a GUI tool supporting SpatiaLite. This is lightweight and very useful when you need to quickly perform some queries or just check contents of the SQLite/SpatiaLite database.
To explore spatial or nonspatial tables in the SpatiaLite database, perform these steps:
- Start
spatialite-guiby double-clicking on its executable file. - Connect to the database that you want to explore by navigating to Files | Connecting an existing SQLite DB or clicking on the corresponding button on the toolbar.
- Select the table you want to explore in the table tree on the left-hand side of the spatialite-gui dialog, open its context menu by clicking on the right mouse button, and select the Edit table rows menu entry.
- If your table contains spatial data, it is possible to view geometry in different representations. Select the field with the geometry information in the row, open the context menu by clicking the right mouse button and select the BLOB Explore menu entry:
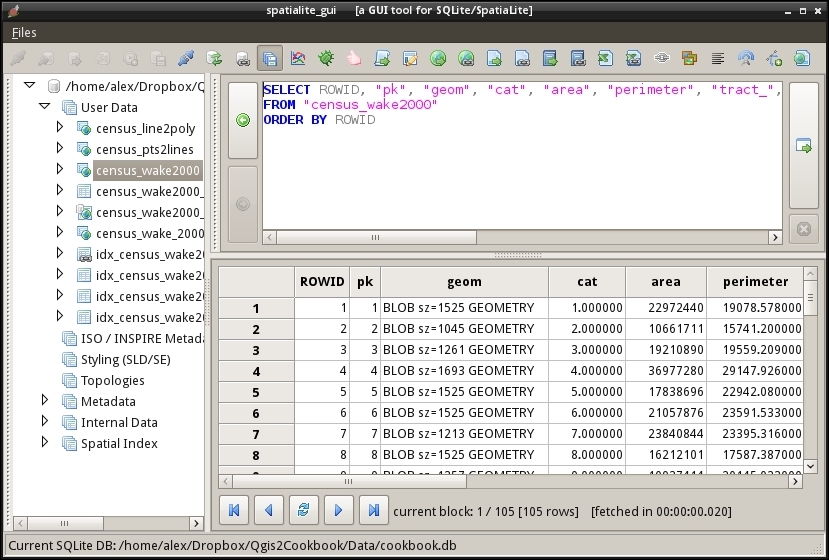
After massive edits, especially when tables were altered or deleted, it is recommended to run VACUUM command to rebuild the database. To do this, perform these steps:
- Start
spatialite-guiby double-clicking on its executable file. - Connect to the database that you want to explore by navigating to Files | Connecting an existing SQLite DB or clicking on the corresponding button on the toolbar.
- Navigate to Files | Optimizing current SQLite DB [VACUUM] or click on the corresponding button on the toolbar.
pgAdmin is an administration tool and development platform for PostgreSQL databases. It allows you to perform administrative tasks (such as backup and restore), run simple queries as well as develop new databases from scratch.
To create a backup of the database with pgAdmin, follow these steps:
- Start pgAdmin by clicking on its desktop shortcut or by finding it in the Start menu.
- Create a connection to your database server if it does not exist by navigating to File | Add Server… or clicking on the corresponding button on the toolbar.
- Connect to the database server where your database is located by double-clicking on its name in Object Browser on the left-hand side of the pgAdmin window.
- Select the database that you want to back up, open its context menu by clicking the right mouse button, and select Backup. A backup settings dialog will be opened, as shown in the following screenshot:
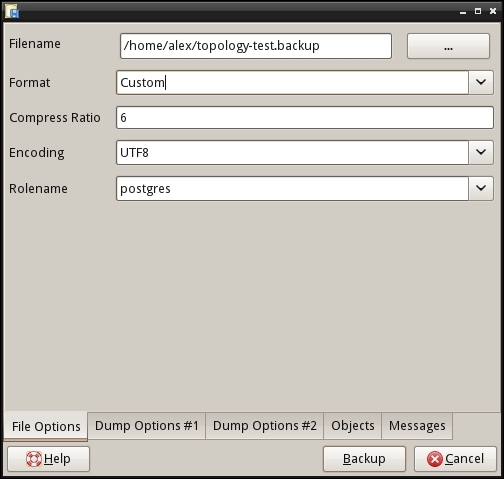
- Choose a location where your backup will be saved, adjust the backup options according to your needs, and click on the Backup button to start the backup process. The progress will be displayed in the Messages tab.
To restore the database from the backup, perform the following steps:
- Start pgAdmin by clicking on its desktop shortcut or by finding it in the Start menu.
- Create a connection to your database server if it does not exist by navigating to File | Add Server... or clicking on the corresponding button on the toolbar.
- Connect to the database server where you want to restore the backup and double-click on its name in Object Browser on the left-hand side of the pgAdmin window.
- Select database that should be restored, open its context menu by clicking the right mouse button, and select Restore. A restore options dialog will be opened, as shown in the following screenshot:
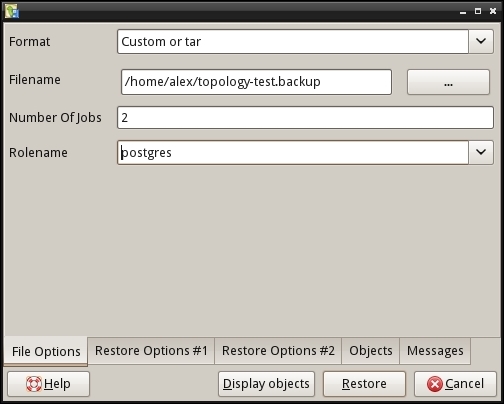
- Select the location of the backup file and adjust the restore options according to your needs.
- Click on the Restore button to start restoring. The progress will be displayed in the Messages tab.
