Date and time data get stored in all sorts of ways. One of the more frustrating issues is that some common GIS formats (Shapefiles) can't store date and time in the same field without making it a string. This is fine for visual display but terrible for use with tools that use DateTime for their functionality, such as the TimeManager Plugin (refer to Chapter 4, Data Exploration).
Use datetime-example.shp, which contains a variety of date and time representations to play with.
- Load
datetime-example.shp. - Open the attribute table of
datetime-example. - Create a new field. As this is a shapefile, we'll need to use a String of length 30 (or you can use the empty field called
calculated). - Turn on layer editing (this is the pencil icon, which is the first icon to the left of the window toolbar).
- From the drop-down list, select Calculated.
- Now press the Calculation button.
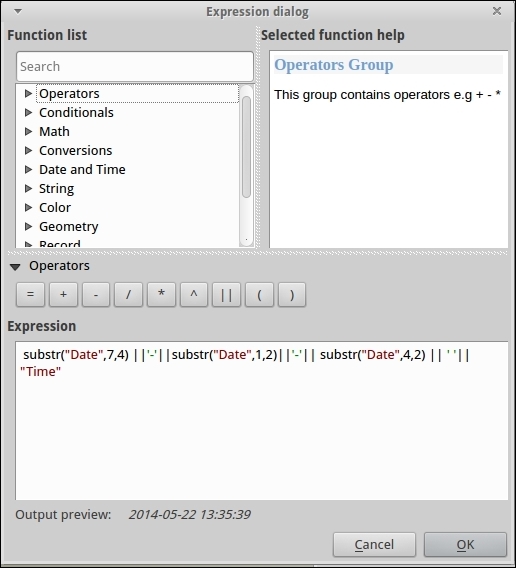
- In the calculator, we'll use the
substrString operation (that is, Substring) in combination with the||concatenation to rearrange the values from existing fields into a validDateTime:- The simplest variant is just to combine
shpDatewithTimeand put a space in between:"shpdate" || ' '|| "Time"
- For a bit more of a challenge, use
Date:substr("Date",7,4) ||'-'||substr("Date",1,2)||'-'|| substr("Date",4,2) || ' '|| "Time"
- The simplest variant is just to combine
- Experiment with the formulas, checking the results with the calculator preview at the bottom. When satisfied, select OK, and then click on the Update All button:
- If you're happy with the results, save the edits; if not, toggle editing off and choose Close without saving.
Substr takes three arguments: the field name, the starting position, and the number of characters after this to include. The position index starts at 1.
Using string manipulation, we've combined multiple fields into an ISO standard format for DateTime, which other tools will recognize and be able to utilize.
The fields included in this example data are as follows:
|
Field |
Type |
Explanation |
|---|---|---|
|
|
String |
This is time in a 24 hour format: hours:minutes:seconds. |
|
|
String |
This is a |
|
|
String |
This is a String that is long enough to hold date and time with padding characters and a timezone UTC offset. |
|
|
String |
This is a typical date format coming out of a spreadsheet. |
|
|
Date |
This is a date format in the |
- If using database layers, this can all be performed with SQL in SpatiaLite or PostGIS. The ISO date time standard is 8601, and can be found at http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ISO_8601.
