Sometimes, you may not need to load a whole layer into QGIS, but only some subset of it, or perform some calculations on the fly. In such situations, the ability to run complex SQL queries and display their results in QGIS will be very useful.
This recipe shows you how to execute SQL code with the QspatiaLite plugin and load data in QGIS.
To follow this recipe, you need to create connection to the cookbook.db database created in the Loading vector layers into SpatiaLite recipe in Chapter 1, Data Input and Output. Alternatively, you can use your own SpatiaLite database, but be aware that you might have to alter some of the following SQL statements to match your tables.
Additionally, install the QspatiaLite plugin from Plugin Manager.
Make sure that you created a connection to cookbook.db. Start the QspatiaLite plugin by navigating to Database | SpatiaLite | QspatiaLite:
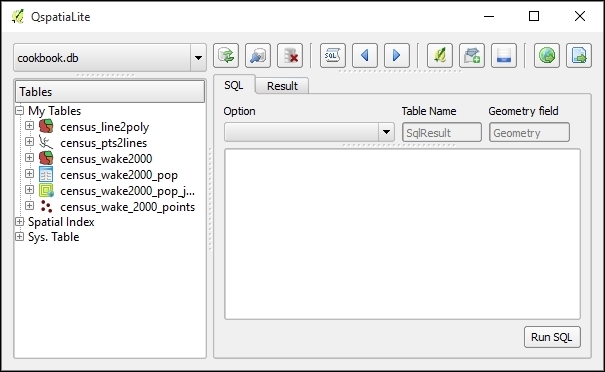
To execute the SQL query, perform the following steps:
- Select database you want to use from the combobox in the top-left corner of the plugin dialog.
- In the SQL tab, enter following query:
SELECT "census_wake2000".'pk' AS id, "census_wake2000".'geom' AS Geometry, "census_wake2000".'area', "census_wake2000".'perimeter' FROM "census_wake2000" WHERE "census_wake2000".'perimeter > 100000;
You can easily insert the table and column names by double-clicking on them in the Tables tree on the left-hand side of the dialog.
- Click on the Run button at the bottom of the dialog to execute the query. The Result tab will open automatically and you can examine the query results in the table representation, as follows:
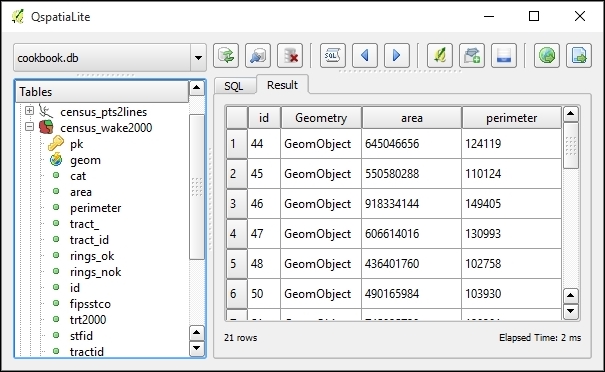
If the query results contain geometry information (the so-called geometry column), you can display them in QGIS. To do this, perform the following steps:
- Switch back to the SQL tab.
- In the Option combobox, select the action that you want to perform, for example, Create Spatial View & Load in QGIS.
- In the Table field, enter name of the resulting view, for example,
above100k. - Ensure that you entered the correct name of the geometry column in the Geometry field.
- Click on the Run button at the bottom of the dialog.
- A dialog will pop up asking for the source geometry table. Select table that you used in the query and click on OK.
- A new view will be created and added to the QGIS as a new layer.
When we click on the Run button, the query is passed to the SpatiaLite database engine for execution, and the results are returned to the plugin and displayed in the table. If you want to store results permanently, you can export them in a text file or in an OGR-compatible format using the corresponding buttons in the plugin dialog.
You can also use the DB Manager plugin (which is bundled with QGIS) to execute SQL-queries directly and load them as layers.
- A very good introduction to SpatiaLite and SQL can be found at https://www.gaia-gis.it/fossil/libspatialite/wiki?name=misc-docs. Also, a full list of the supported spatial SQL functions is available at http://www.gaia-gis.it/gaia-sins/spatialite-sql-4.3.0.html.
