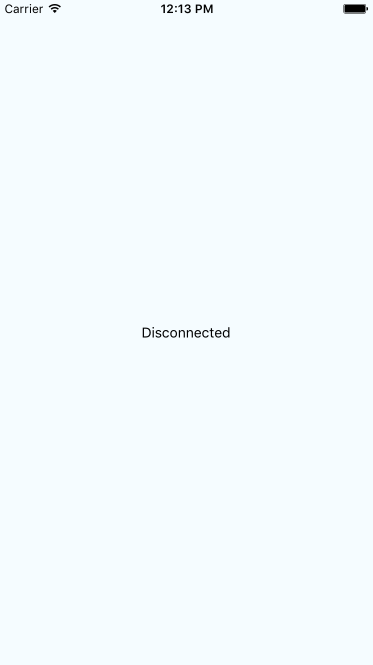
If your code tries to make a request over the network while disconnected, using fetch(), for example, an error will occur. You probably have error-handling code in place for these scenarios already, since the server could return some other type of error. However, in the case of connectivity trouble, you might want to detect this issue before the user attempts to make network requests.
There are two potential reasons for proactively detecting the network state. You might display a friendly message to the user stating that, since the network is disconnected, they can't do anything. You would then prevent the user from performing any network requests until you detect that it's back online. The other possible benefit of early network state detection is that you can prepare to perform actions offline and sync the app state when the network is connected again.
Let's look at some code that uses the NetInfo utility to handle changes in network state:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Text, View, NetInfo } from 'react-native';
import { fromJS } from 'immutable';
import styles from './styles';
// Maps the state returned from "NetInfo" to
// a string that we want to display in the UI.
const connectedMap = {
none: 'Disconnected',
unknown: 'Disconnected',
wifi: 'Connected',
cell: 'Connected',
mobile: 'Connected'
};
export default class NetworkState extends Component {
// The "connected" state is a simple
// string that stores the state of the
// network.
state = {
data: fromJS({
connected: ''
})
};
// Getter for "Immutable.js" state data...
get data() {
return this.state.data;
}
// Setter for "Immutable.js" state data...
set data(data) {
this.setState({ data });
}
// When the network state changes, use the
// "connectedMap" to find the string to display.
onNetworkChange = connection => {
this.data = this.data.set(
'connected',
connectedMap[connection.type]
);
};
// When the component is mounted, we add a listener
// that changes the "connected" state when the
// network state changes.
componentDidMount() {
NetInfo.addEventListener(
'connectionChange',
this.onNetworkChange
);
}
// Make sure the listener is removed...
componentWillUnmount() {
NetInfo.removeEventListener(
'connectionChange',
this.onNetworkChange
);
}
// Simply renders the "connected" state as
// it changes.
render() {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text>{this.data.get('connected')}</Text>
</View>
);
}
}
This component will render the state of the network, based on the string values in connectedMap. The connectionChange event of the NetInfo object will cause the connected state to change. For example, when you first run this app, the screen might look like this:
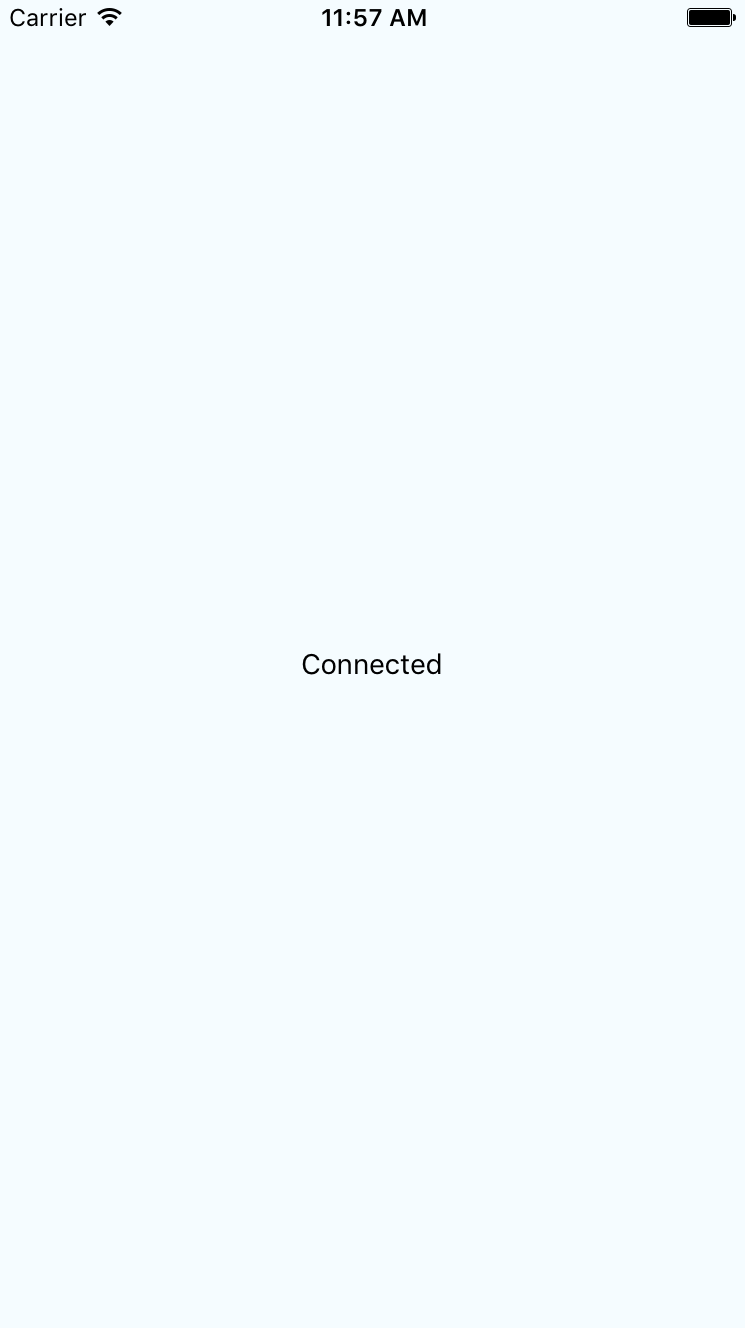
Then, if you turn off networking on your host machine, the network state will change on the emulated device as well, causing the state of our application to change as follows: