The Expo mobile app is a tool that you can use to assist with React Native development. The npm start command launches the React Native package, which integrates seamlessly with Expo (provided the device is on the same network as the packager). This enables you to view and interact with your application on real mobile devices during development. It even supports live reloading as you make changes to your source.
Expo is set apart from the mobile device emulators in that it enables you to experience the application the same way your users will experience it. Virtual device emulators give you a rough approximation, but it isn't the same thing as holding a device in your hand. Furthermore, not everyone has a Macbook, which is a requirement for simulating iOS devices.
You can find the Expo app by searching the Play Store on Android devices or the App Store on iOS devices:

When you launch Expo, you'll see an option to scan a QR code:
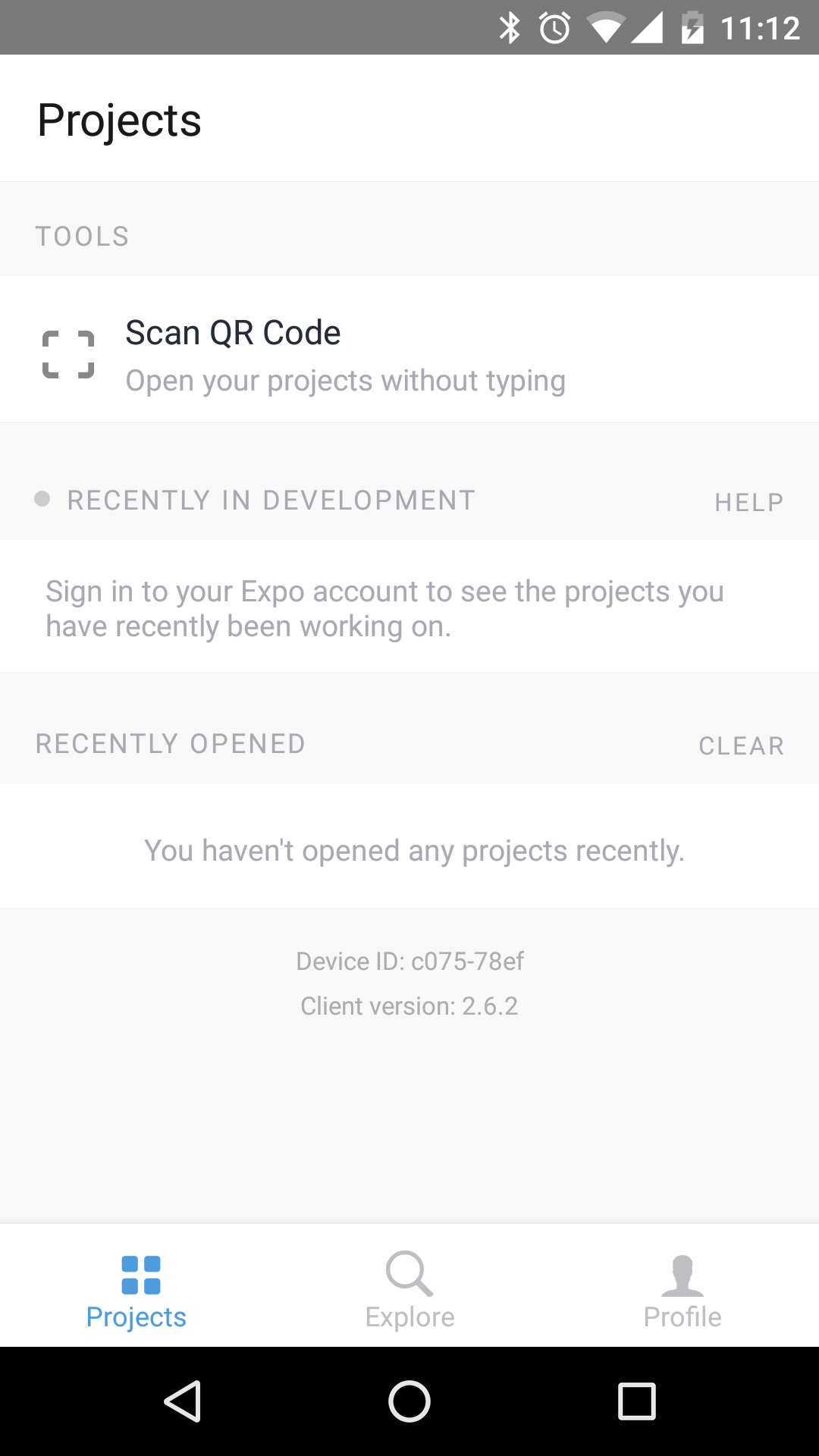
When you select Scan QR Code, your phones camera can scan the QR code that's printed in your terminal. This is how you connect the React Native packager running on your computer with your device. If you can't scan the QR code, you can open the app in Expo by emailing the Expo link to your phone. Clicking on it from your phone is the same thing as scanning the QR code.
Here's what the my-project app should look like when opened in Expo:
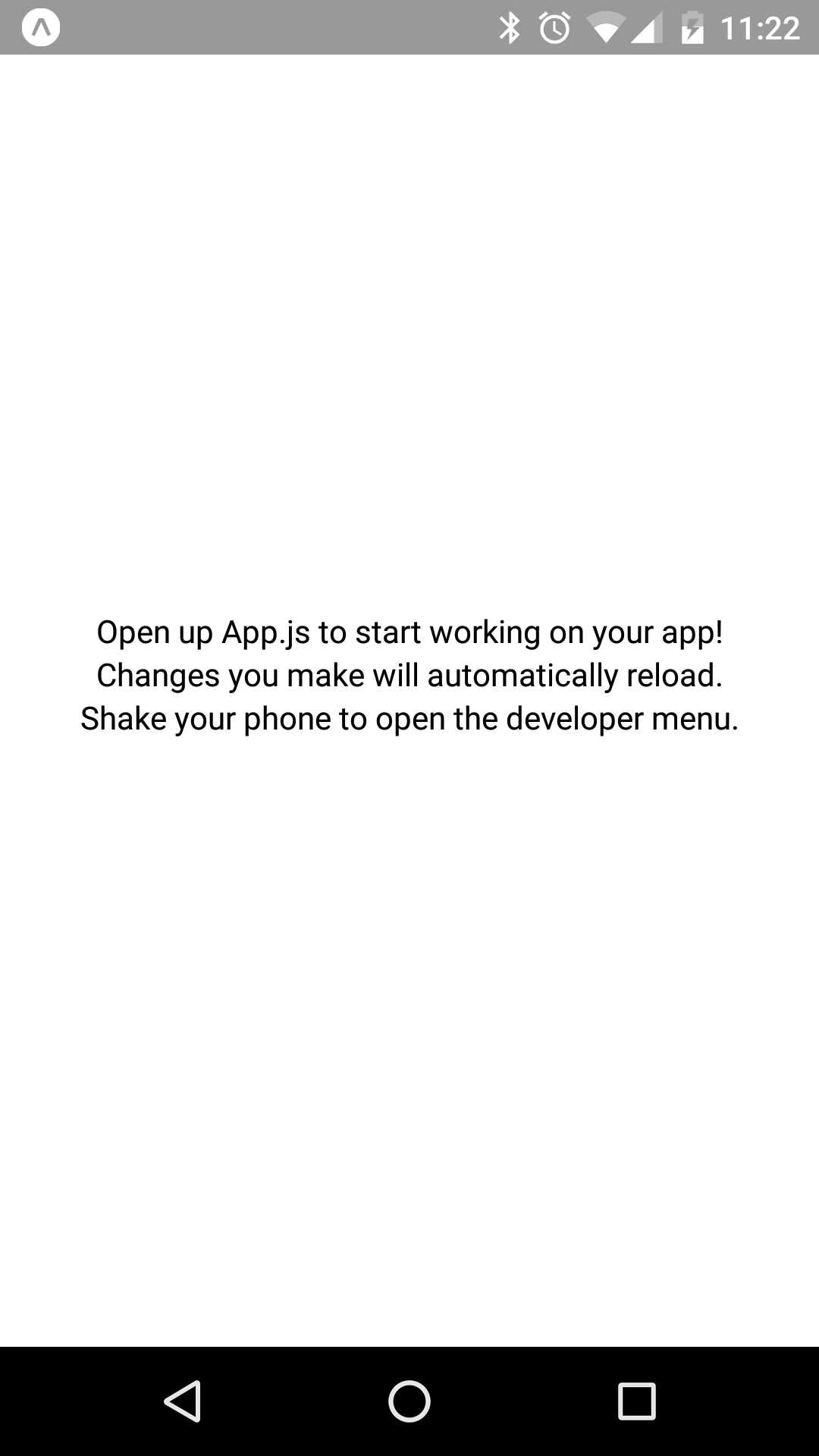
Let's take a look at the App.js module that was created by create-react-native-app for you:
import React from 'react';
import { StyleSheet, Text, View } from 'react-native';
export default class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text>Open up App.js to start working on your app!</Text>
<Text>Changes you make will automatically reload.</Text>
<Text>Shake your phone to open the developer menu.</Text>
</View>
);
}
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
backgroundColor: '#fff',
alignItems: 'center',
justifyContent: 'center'
}
});
This App component will render three lines of text on the screen, with some styles applied to the View component. Let's make a change to the first line to make the text bold:
import React from 'react';
import { StyleSheet, Text, View } from 'react-native';
export default class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text style={styles.bold}>
Open up App.js to start working on your app!
</Text>
<Text>Changes you make will automatically reload.</Text>
<Text>Shake your phone to open the developer menu.</Text>
</View>
);
}
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
backgroundColor: '#fff',
alignItems: 'center',
justifyContent: 'center'
},
bold: {
fontWeight: 'bold'
}
});
There's now a bold style in the styles and this is applied to the style property of the first Text component. If you look at your phone again, you'll notice that the application is updated:
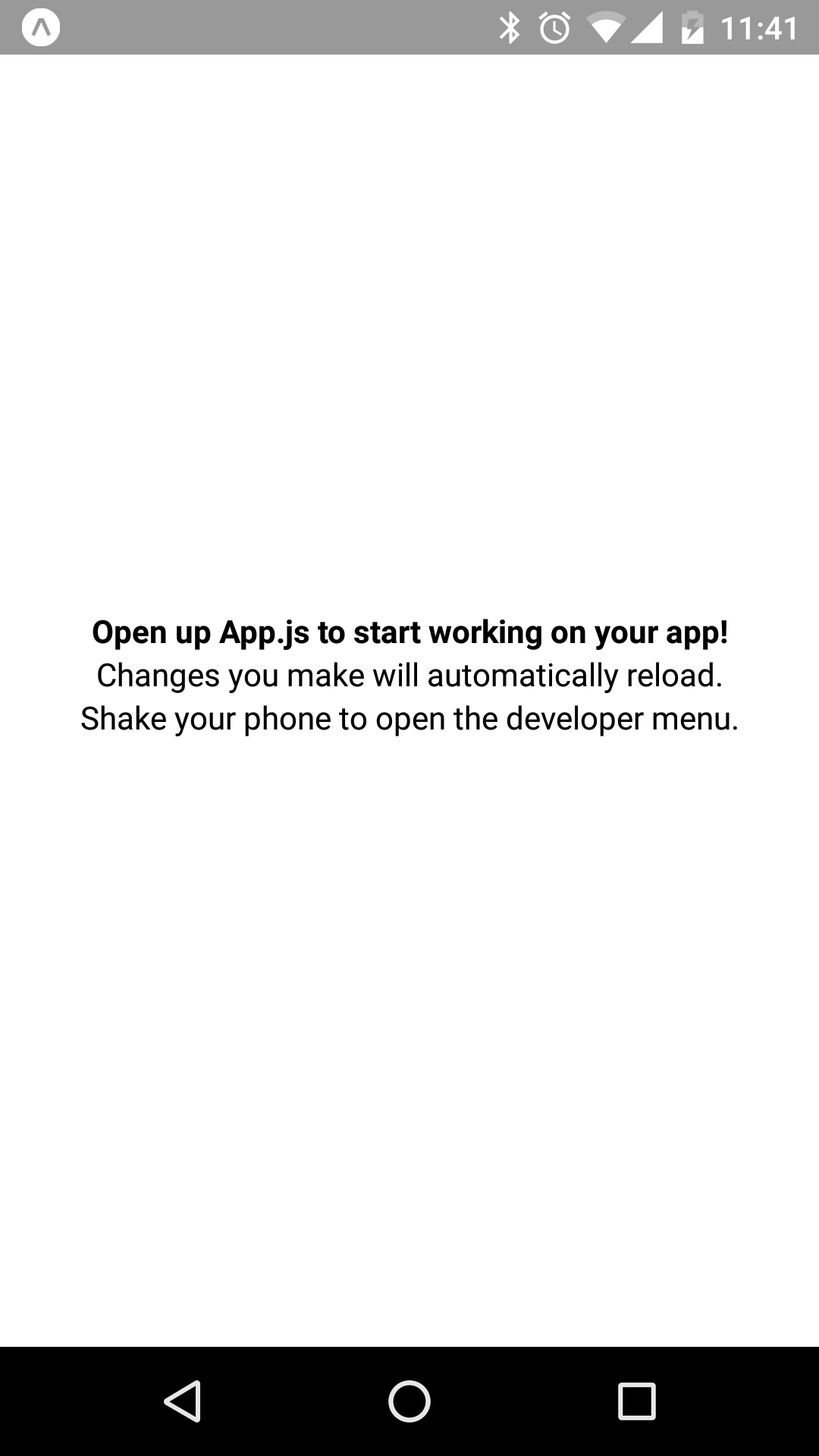
The change is immediately reflected in the app on your device.
