Just as in a wired LAN, on WLAN, we have the ability to sniff network traffic. The following sniffing technique requires that you have been properly authenticated to the wireless network you are testing and have received a valid IP address from the router. This type of sniffing will make use of the Ettercap tool to conduct an ARP poisoning attack and sniff out credentials:
- Start Ettercap by going to Applications | Sniffing and Spoofing | Ettercap-gui or by entering ettercap-gui into command prompt. Navigate to Sniff and click on Unified Sniffing. Once there, you will be given a drop-down list of network interfaces. Choose your wireless interface, in our case, WLAN0:
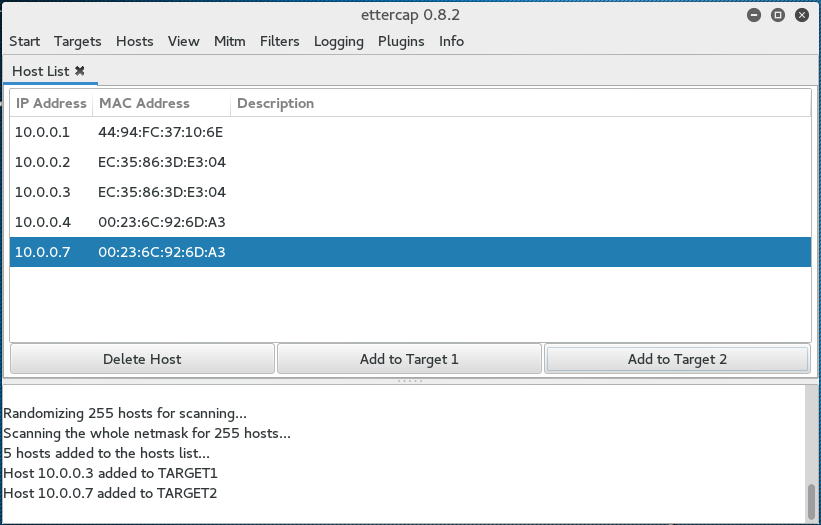
- Click on Hosts and click Scan for Hosts. After the scanning is complete, hit Hosts List. If it is an active wireless network, you should see a few hosts on there.
- Click on MiTM and then ARP Poisoning. On the next screen, choose one IP address and click on Target 1, and then a second IP address and click on Target 2:
- Click on the Sniff Remote Connections radio button and click OK:
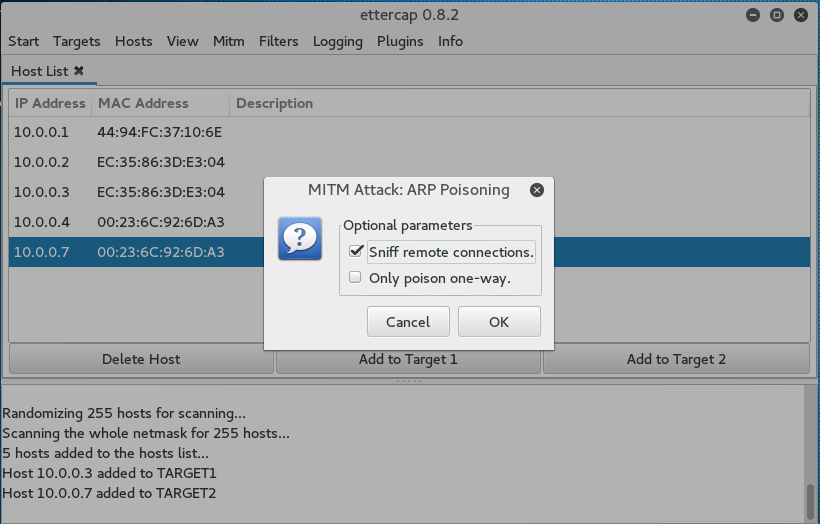
This will start the ARP Poisoning attack whereby we will be able to see all the traffic between the two hosts that we have chosen.
- Start a Wireshark capture. When you are brought to the first screen, make sure you choose the wireless interface, in this case, WLAN0:
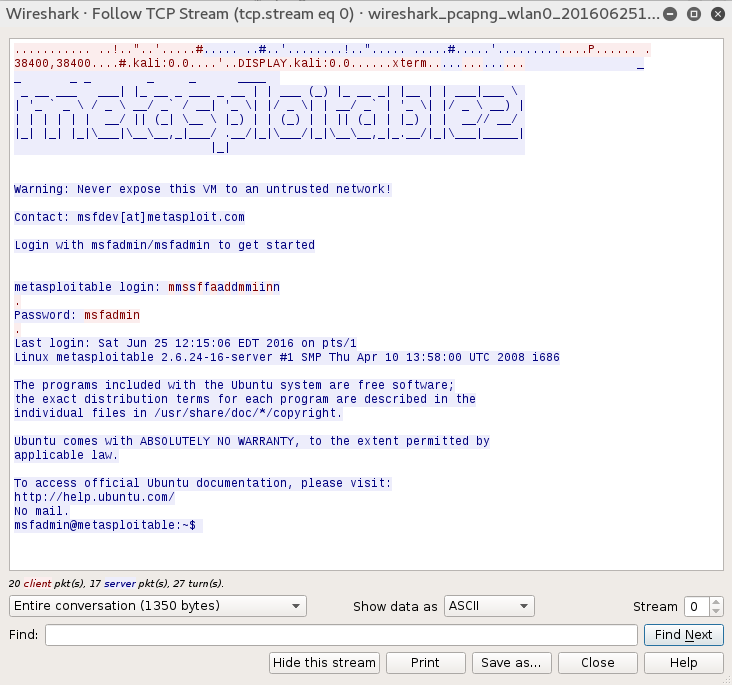
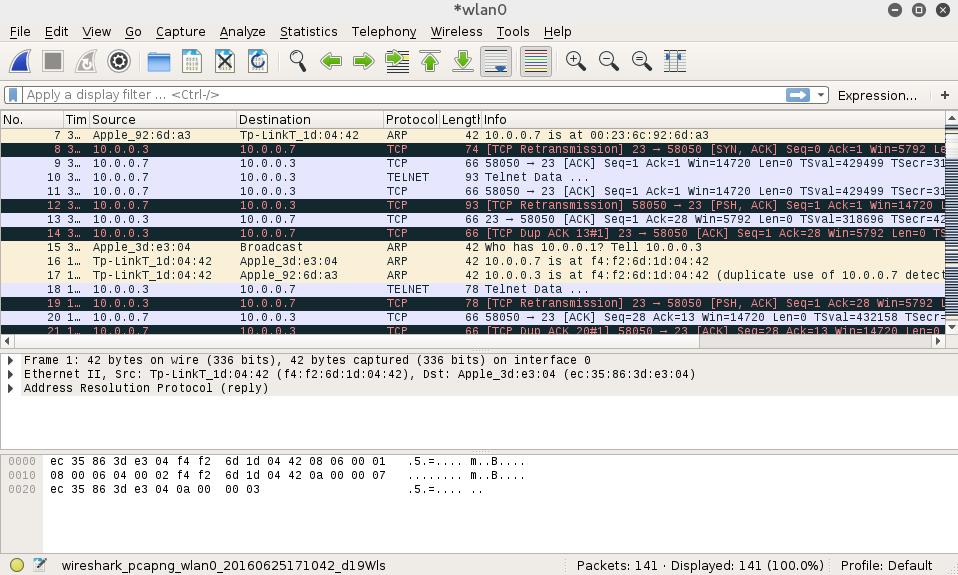
When you examine the traffic, we can see a number of types of traffic being captured. Most notable is a Telnet session that has been opened between our two hosts:
If we right-click on the Telnet session and choose Follow TCP Stream, we are able to see the credentials for a Metasploitable instance with the Telnet credentials in cleartext: