The p0f tool is used to fingerprint an operating system passively. It can be used to identify an operating system on the following machines:
- Machines that connect to your box (SYN mode; this is the default mode)
- Machines you connect to (SYN + ACK mode)
- Machines you cannot connect to (RST+ mode)
- Machines whose communications you can observe
The p0f tool works by analyzing the TCP packets sent during the network activities. Then, it gathers the statistics of special packets that are not standardized by default by any corporations. An example is that the Linux kernel uses a 64-byte ping datagram, whereas the Windows operating system uses a 32-byte ping datagram or the Time To Live (TTL) value. For Windows, the TTL value is 128, while for Linux this TTL value varies among Linux distributions. This information is then used by p0f to determine the remote machine's operating system.
To access p0f, open a console and type p0f -h. This will display its usage and options description. Let's use p0f to identify the operating system used in a remote machine we are connecting to. Just type the following command in your console:
p0f -f /etc/p0f/p0f.fp -o p0f.log
This will read the fingerprint database from the file and save the log information to the p0f.log file. It will then display the following information:
--- p0f 3.07b by Michal Zalewski <lcamtuf@coredump.cx> ---
[+] Closed 1 file descriptor.
[+] Loaded 320 signatures from '/usr/share/p0f/p0f.fp'.
[+] Intercepting traffic on default interface 'eth0'.
[+] Default packet filtering configured [+VLAN].
[+] Log file 'p0f.log' opened for writing.
[+] Entered main event loop.
Next, you need to generate network activities involving a TCP connection, such as browsing the remote machine or letting the remote machine connect to your machine. For the purposes of this demonstration, a connection to the HTTP site on the 2 machine was established.
The following is the abridged information displayed to the console:
.-[ 172.16.43.150/41522 -> 172.16.43.156/80 (syn+ack) ]-
|
| server = 172.16.43.156/80
| os = Linux 2.6.x
| dist = 0
| params = none
| raw_sig = 4:64+0:0:1460:mss*4,5:mss,sok,ts,nop,ws:df:0
The following screenshot shows the content of the log file:
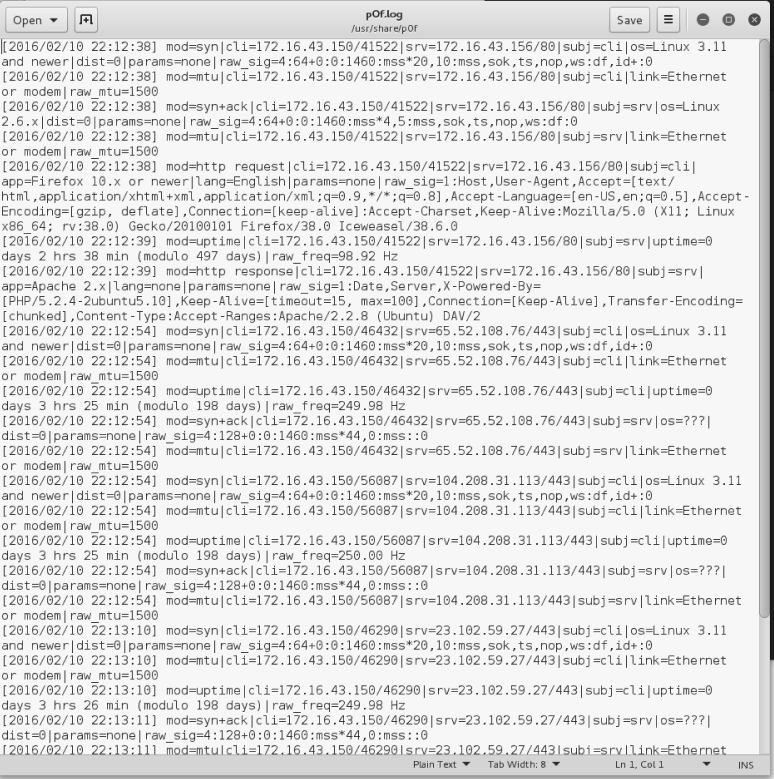
Based on the preceding result, we know that the target is a Linux 2.6 machine.
The following screenshot shows the information from the target machine:
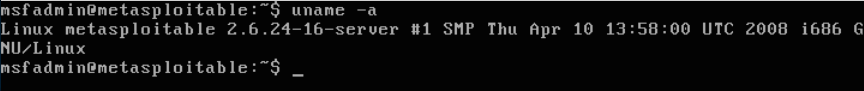
By comparing this information, we know that p0f got the OS information correctly. The remote machine is using Linux Version 2.6.
You can stop p0f by pressing the Ctrl + C key combination.
