Aside from the process of adding new products to your store, there are a number of configurations you should review that affect how products are managed and presented. The goal of any Magento store is to sell, and the ease with which customers can shop, as well as the presentation of the categories and products, greatly affects the success of any e-commerce venture.
Therefore, this section of the checklist may be a lengthy, yet necessary, process. There are no set recommendations, either, for most of these settings, as we find different intentions for each site we build. As with all Magento configurations, don't assume each setting's purpose is clear.
Some product categories lend themselves to long listings of products, each on its own line. Other products may be better suited to a grid layout of no more than six products to a page. Magento's immense flexibility means you not only have a variety of presentation options; it also means you have to be willing to experiment and test. And that, my friend, is one of the exciting aspects of configuring a Magento store.
The Stores | Configuration | Catalog | Catalog configuration section has, perhaps, the most panels of any section in Magento. I'm going to break each panel down into its own subsection in order to address the many configuration choices.
This is one panel with which we encourage you to experiment, as it dictates how products are to be displayed when a customer views a category in your store.
- List Mode: Set the default category view to Grid Only, List Only, Grid by default, or List by default.
- Products per Page on Grid Allowed Values: On grid view pages, there will be a drop-down menu to allow customers to select how many products should appear. The values you use here should be a multiple of how many products appear on each row. For the default of three products in each row, use values that are evenly divisible by three to avoid having an incomplete last row.
- Products per Page on Grid Default Value: Set the default number of products to display on a grid layout category page.
- Products per Page on List Allowed Values: This uses the same methodology as for the Grid Allowed Values, except that you're not concerned with multiples of products per row, since each row only contains one product.
- Products per Page on List Default Value: As you can imagine, this is the default number of products that appear in a list view. As with any view default value, this can be a number larger than the smallest number in your list of allowed values.
- Allow All Products per Page: If your categories don't contain a very large number of products, you may want to allow customers to select All as one of the allowed values. Setting this value to Yes will automatically add All to the drop-down menu of allowed values.
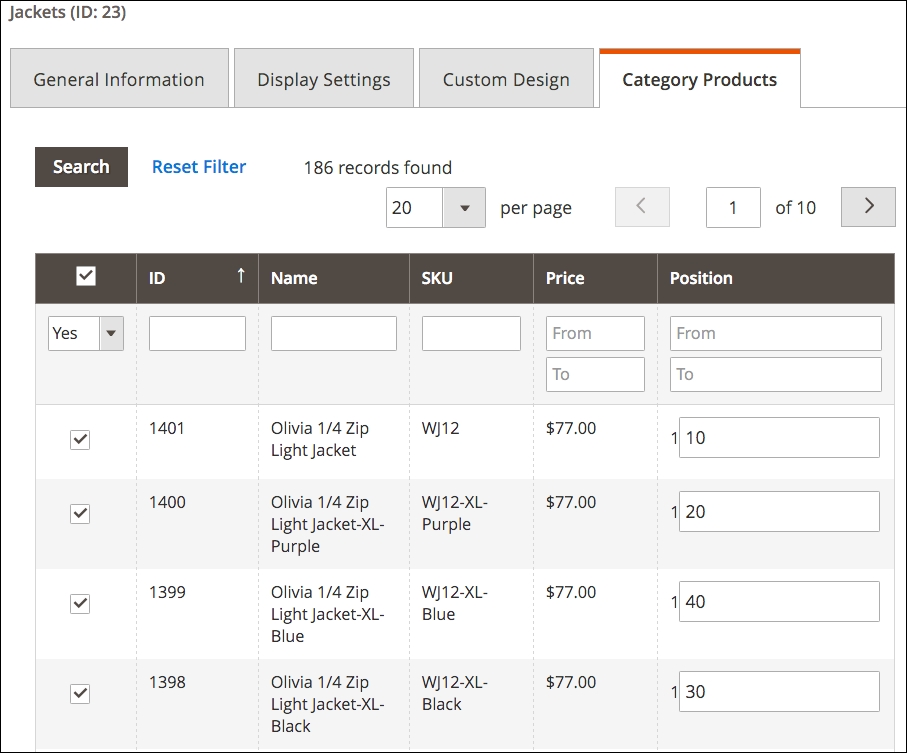
- Product Listing Sort by: Customers can sort views by Best Value, Name, or Price. This selection determines the default sorting of views. Position is one of the more misunderstood concepts of Magento configurations, so allow me to explain. If you go to a category detail screen under Products | Categories, you'll find under the Category Products tab a list of products assigned to that category. The last column is labeled Position. By entering values into these fields, you dictate a manual sorting order for those products, in ascending order of the position value. For instance, if you want to feature products in a special order, you might enter position values of 10, 20, 30, and so on. The following screenshot shows how we can dictate the sorting order for the Jackets category so that the items are in ascending order according to the values entered into the last column.
- Use Flat Catalog Category and Use Flat Catalog Product: As discussed in Chapter 8, Marketing Tools, flattening category and product records can speed up database lookups, thus decreasing page generation times.
- Allow Dynamic Media URLs in Products and Categories: If you want to insert images into product and category descriptions, you may want Magento to use dynamic URLs to preserve the image link regardless of changes you make to design themes. If you're set on your theme and where you want to store images, set this to No, as it can help reduce the amount of server processing time needed to render description content.
By default, Magento allows viewers to submit reviews for products. This panel determines whether non-registered customers — or guests — are allowed to submit reviews for products.
The alerts configured in this panel pertain to emails that can be sent to customers when product prices or stock availability changes. If you set Allow Alert When Product Price Changes to Yes, then customers will see a link labeled Sign up for price alert on each product page.
If you have activated your cron jobs, Magento will process any customer-subscribed pricing and stock availability alerts according to the schedule you specify in this panel. You can also receive email alerts if an error in the processing occurs.
See the section Placeholder Images earlier in this checklist for information on uploading placeholder images.
In this panel, you can set how customer-selected recently viewed and compared product lists are handled, especially if you are operating a multi-store installation.
How you choose product price sharing — globally or by website — affects how currency conversions are applied to prices.
In most cases, automatic calculation of price steps in the layered navigation sidebar will work fine. However, in some cases, you may want to set your own steps for each store.
If you want to limit the depth of your top menu category navigation, enter the maximum level you wish. Zero (0) means all levels will be displayed.
This panel contains several settings that can affect how well your site is indexed by search engines, such as Google, Yahoo! and Bing.
- Popular Search Terms: Enabling this feature adds a link to a page of search terms used in searches on your site. This helps search sites identify links generated by popular searches and can help in your rankings when those terms are used in the search engines.
- Product URL Suffix and Category URL Suffix: By default, product and catalog page URLs end in
.html. You can specify any suffix you wish, but you may also want to have no suffix, as is the common practice for many websites. - Use Categories Path for Products URLs: If you want URLs for products to contain the category name in the path, such as
http://www.storedomain.com/furniture/living-room/ottoman, set this to Yes. - Create Permanent Redirect for old URLs if URL key changed: During development and setup, I generally set this to No, as there is no reason to have Magento create a lot of redirects as you edit product URL keys. However, before launch, you should set this to Yes so that future updates will create redirects. These redirects mean that older links still showing in search engines will lead visitors to the correct pages.
- Page Title Separator: Enter the character you wish to use in URLs as a substitute for blank spaces. It is generally accepted that a hyphen (-) is better for SEO than an underscore (_).
- Use Canonical Link Meta Tag for Categories and Use Canonical Link Meta Tag for Products: Search engines — especially Google — can penalize you for duplicate content. In an e-commerce store, categories and products can be accessed through a variety of URLs. For instance,
http://www.storedomain.com/ottomanandhttp://www.storedomain.com/furniture/living-room/ottomantake the user to the very same page (Magento knows how to interpret both URLs). To Google, these are two different pages, both with the same content. Therefore, Google might penalize your site for having duplicate content, when, in fact, it's not. Canonical link meta tags are, as the name implies, meta tags in your page header that contain, for lack of a better term, the definitive link to the page. That is, if Google analyzes multiple URLs, but each one has the same value for the canonical link meta tag, then Google understands that these pages are really one in the same and treats them not as duplicate pages, but simply alternative link paths. An example of a canonical link meta tag, for our example ottoman, would be<link rel="canonical" href="http://www.storedomain.com/ottoman" />, and it would be the same regardless of the URL used to arrive at the ottoman page.
Your site will most likely have a site-wide search feature, with a search field somewhere on the page. Allowing your visitors to be able to search your site to find products is one more way you can increase the usability of your Magento site.
- Minimal Query Length: This represents the minimum number of characters that are required in order to do a search of your site. While the default value is 1, we usually set this to at least 3. Searching for one letter among all the possible categories and products of your site doesn't really make sense. Three may even be too small. Experiment and find the ideal minimum. In most Magento themes, the search field is auto complete, meaning that once the user starts typing into the field, Magento is immediately searching the database for possible matches, displaying them just below the field. This minimum value dictates how many letters are typed before Magento starts this searching process.
- Maximum Query Length: Enter the maximum number of characters you wish to allow for a query.
- Maximum Query Words Count: To keep searches fast and efficient, you should have some limit to the number of words that are used in a Like search.
