In today's online retailing world, most purchasers use credit cards (or debit cards) as payment currency. Nothing new there. However, the process of taking someone's credit card online, verifying the card for available purchasing limit, and drawing the amount of the purchase from the buyer's account and into your bank account is one that remains a mystery to many. Of all the components that comprise online commerce, the process of moving money – in this case from the credit card account of the buyer to your bank account – remains one of the most complex of them all.
Without the ease of credit cards, online e-commerce might well be growing at a much slower pace. However, the use of credit cards – and the potential for misuse – concerns your shoppers, particularly when the press relates stories of hackers breaking into retailer databases. What is important is that online purchases have never been "hacked." That is, no one has been prosecuted for stealing credit card information used to buy online as long as the store is using SSL encryption. To ease consumers' fears, several payment systems have evolved over the past decade, each designed to help you process the financial transactions for your store, while providing the increased security and processes necessary to give both you and your buyer a safer, easier transaction process.
As a Magento administrator, you have within Magento, several default payment systems available based on your own needs. Each one requires that the store owner enrolls and qualifies, but, having done so, allows the store to provide buyers with a convenient, secure means of paying for their purchase.
In this section, we will cover the most common, popular payment systems and how they work with Magento. This is intended to familiarize you with how each system interacts with Magento, the buyer, and the store owner. Once you understand how they work, you will be able to decide on which system(s) you want to employ, which also makes configuring Magento easier.
The protection of your customer's payment information is extremely important. Not only would a breach of security cause damage to your customer's credit and financial accounts, but the publicity of such a breach could be devastating to your business.
Merchant account providers will require that your store meet stringent guidelines for PCI compliance, a set of security requirements called Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). Your ability to be PCI compliant is based on the integrity of your hosting environment and by which methods you allow customers to enter credit card information on your site.
Magento 2 no longer offers a "stored credit card" payment method. It is highly unlikely that you could — or would want to — provide a server configuration secure enough to meet PCI DSS requirements for storing credit card information. You probably don't want the liability exposure, either.
You can, however, provide SSL encryption that could satisfy PCI compliance as long as the credit card information is encrypted before being sent to your server, and then from your server to the credit card processor. As long as you're not storing the customer's credit card information on your server, you can meet PCI compliance as long as your hosting provider can assure compliance for server and database security.
Therefore, you should decide whether to provide onsite or offsite credit card payments. In other words, do you want to take payment information within your Magento checkout page or redirect the user to a payment service, such as PayPal, to complete their transaction?
There are pros and cons of each method. Onsite transactions may be perceived as less secure and you do have to prove PCI compliance to your merchant account provider on an ongoing basis. However, onsite transactions mean that the customer can complete their transaction without leaving your website. This helps to preserve your brand experience for your customers.
Fortunately, Magento is versatile enough to allow you to provide both options to your customers. Personally, we feel that offering multiple payment methods means you're more likely to complete a sale, while also showing your customers that you want to provide the most convenience in purchasing.
Let's now review the various payment methods offered by default in Magento 2.
Tip
Magento 2 comes with a host of the most popular and common payment methods. However, you should review other possibilities, such as Amazon Payments, Stripe, and Moneybookers, depending on your target market. We anticipate that developers will be offering add-ons for these and other payment methods.
The determination of which payment system to utilize in your Magento store is driven by a comparison of pros and cons (isn't everything in life?). In terms of credit card sales, there are two basic classifications of payment systems: off-site and on-site.
Off-site systems allow buyers to make purchase choices, but pay for their order on another website which offers the buyer a sense of greater security and fraud protection. The buyer is actually paying the off-site payment provider, who in turn pays the store owner once there is sufficient verification that the order has been processed and shipped. Each system has different degrees of verification based on the type of products sold, the history of the merchant (for example, has there been previous problems with the merchant's reliability?), and the amount of the purchase.
The pros of this type of payment method are as follows:
- Provides extra layer of protection to buyers against unscrupulous merchants.
- Quick merchant approval. No credit report is required.
- No PCI compliance requirements.
- Easy integration into almost any e-commerce platform.
Many buyers prefer these systems because of the added layer of protection against merchants who fail to deliver the expected results.
Additionally, the off-site system qualifies the merchant as opposed to a merchant account provider or bank. For first-time e-commerce merchants, this qualification is usually easier to obtain, as no credit report is required.
The cons of this type of payment method are as follows:
- Takes buyers off your e-commerce site
- May require the buyer to enroll in a third-party payment system
- Merchant has limited access to buyer information, including e-mail addresses
The dominant off-site systems are PayPal Express, PayPal Standard, and Authorize.net Direct Post.
Almost any well-developed e-commerce store will allow buyers to pay directly on the site without having to go off-site to another payment system. While most will also provide off-site payment alternatives, by providing an on-site payment process, the merchant eliminates any reluctance the buyer may have to enroll in a third-party payment system.
The pros of this type of payment method are as follows:
- Keeps the buyer on the site, surrounded by the merchant's branding design
- Eliminates the need for the buyer to register or enroll with an outside payment system
- Gives the merchant access to all buyer information for follow-up, processing, and future marketing
In order to succeed with on-site payment systems, merchants need to consider design elements and payment system brands that will help buyers have confidence in the security of the payment process. Most buyers have no history with new merchants; therefore, merchants, if they wish to offer on-site payments, should pay special attention to methods of communicating the security of the buyer's information.
The cons of this type of payment method are as follows:
- Requires a merchant banking account, which can be difficult to obtain for new businesses
- Site may be subject to PCI compliance
- Integration with e-commerce platforms is more complex
Off-site payments are processed through gateways. Gateways accept the customer payment information, as well as the order total, by means of a secure connection between your store server and the gateway's servers. The gateway validates the buyer's information and returns a result of success or error, which your store platform processes accordingly.
Today, PayPal remains one of the most popular payment systems in the world because it does allow for global purchases. You can sell to buyers in other countries, as long as they have a PayPal account, knowing that you will receive payment. Most regular merchant accounts, such as those used by bricks and mortar retailers, restrict sales to only buyers with cards issued by US banks.
In the past, the downside to using PayPal was that buyers would have to sign up for PayPal if you, the merchant, offered it as a payment system. That changed some years ago: today your buyers don't have to sign up for PayPal. They can purchase using a credit card without enrolling.
While PayPal is commonly known for their quick and easy PayPal Express, PayPal can provide you with credit and debit card solutions that allow customers to use their cards without needing a PayPal account. To the customer, the Magento checkout appears no different than if they were using a normal credit card checkout process.
The big difference is that you have to set up a business account with PayPal before you can begin accepting non-PayPal account payments. Proceeds will go almost immediately into your PayPal account (you have to have a PayPal account), but your customers can pay by using a credit/debit card or their own PayPal account.
With the all-in-one solution, PayPal approves your application for a merchant account and allows you to accept all popular cards, including American Express, at a flat 2.9% rate, plus $0.30/transaction. PayPal payments incur normal per transaction PayPal charges.
PayPal provide two ways to incorporate credit card payment capture on your website:
- PayPal Payments Advanced inserts a form on your site that is actually hosted from PayPal's highly secure servers. The form appears as part of your store, but you don't have any PCI compliance concerns.
- PayPal Payments Pro allows you to obtain payment information using the normal Magento form, then submits it to PayPal for approval.
The difference to your customer is that for Advanced, there is a slight delay while the credit card form is inserted into the checkout page. You may also have some limitations in terms of styling.
PayPal Standard, also a part of the all-in-one solution, takes your customer to a PayPal site for payment. Unlike PayPal Express, however, you can style this page to better reflect your brand image. Plus, customers do not have to have a PayPal account in order to use this checkout method.
If you already have a merchant account for collecting online payments, you can still utilize the integration of PayPal and Magento by setting up a PayPal business account that is linked to your merchant account. Instead of paying PayPal a percentage of each transaction — you would pay this to your merchant account provider — you simply pay a small per transaction fee.
Offering PayPal Express is as easy as having a PayPal account. It does require some configurations of API credentials, but it does provide the simplest means of offering payment services without setting up a merchant account.
PayPal Express will add Buy Now buttons to your product pages and the cart page of your store, giving shoppers quick and immediate ability to checkout using their PayPal account.
PayPal recently acquired Braintree, a payment services company that adds additional services to merchants. While many of their offerings appear to overlap PayPal's, Braintree brings additional features to the marketplace such as Bitcoin, Venmo, Android Pay, and Apple Pay payment methods, recurring billing, and fraud protection. Like PayPal Payments, Braintree charges 2.9% + $0.30/transaction.
If you have customers for whom you will accept payment by check and/or money order, you can enable this payment method. Be sure to enter all the information fields, especially Make Check Payable to and Send Check to. You will most likely want to keep the New Order Status as Pending, which means the order is not ready for fulfillment until you receive payment and update the order as Paid.
As with any payment method, be sure to edit the Title of the method to reflect how you wish to communicate it to your customers. If you only wish to accept money orders, for instance, you might change Title to Money Orders (sorry, no checks).
As with check/money order, you can allow customers to wire money to your account by providing information to your customers who choose this method.
Likewise, you can offer COD payments. We still see this method being made available on wholesale shipments, but very rarely on B2C (business-to-consumer) sales. COD shipments usually cost more, so you will need to accommodate this added fee in your pricing or shipping methods. At present, there is no ability to add a COD fee using this payment method panel.
If your customer, by use of discounts or credits, or selecting free items, owes nothing at the checkout, enabling this method will cause Magento to hide payment methods during checkout. The content in the Title field will be displayed in these cases.
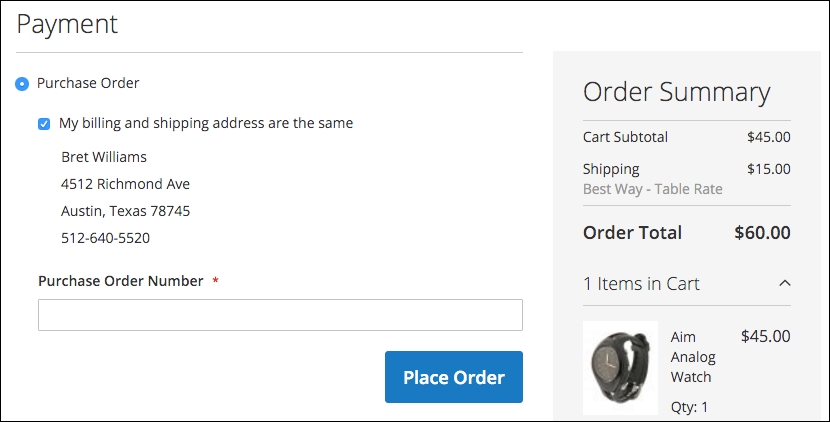
In B2B (business-to-business) sales, it's quite common to accept purchase orders (PO's) for customers with approved credit. If you enable this payment method, an additional field is presented to customers for entering their PO number when ordering.
Authorize.net — perhaps the largest payment gateway provider in the USA — provides an integrated payment capture mechanism that gives your customers the convenience of entering credit/debit card information on your site, but the actual form submission bypasses your server and goes directly to Authorize.net. This mechanism, as with PayPal Payments Advanced, lessens your responsibility for PCI compliance as the data is communicated directly between your customer and Authorize.net instead of passing through the Magento programming.
