We are at the end of the book, but this only the beginning of your walk through the Magento training. It's important to know some Magento extension options, but it is more important to build your own path in the Magento world by studying for a certification and achieving a new professional level.
The following topics will be covered in this chapter:
- Magento Connect extensions
- Installing a Magento extension
- Debugging Grunt.js styles
- Magento knowledge center
- Improving your Magento skills
The Magento 2.0 architecture allows a natural improvement of native resources and the addition of new ones. Magento 2.0 is built based on the best software development practices. Its architecture is modular, which allows the development of extensions, as we discussed in an earlier chapter.
Magento Commerce maintains a marketplace to provide Magento extensions known as Magento Connect (https://www.magentocommerce.com/magento-connect). Magento Connect includes extensions that provide new functionalities, such as modules, add-ons, language packs, design interfaces, and themes to extend the power of your store.
I strongly suggest that you visit Magento Connect to get some ideas for personal projects and follow the extension development tendency in the marketplace.
Besides the Magento Connect marketplace, to search for Magento extension solutions, you can access the extension options through your admin area. To access Magento extension options in your admin area, perform the following steps:
- Access your admin area at
http://localhost/admin_packt. - Navigate to Find Partners and Extensions | Visit Magento Marketplaces.
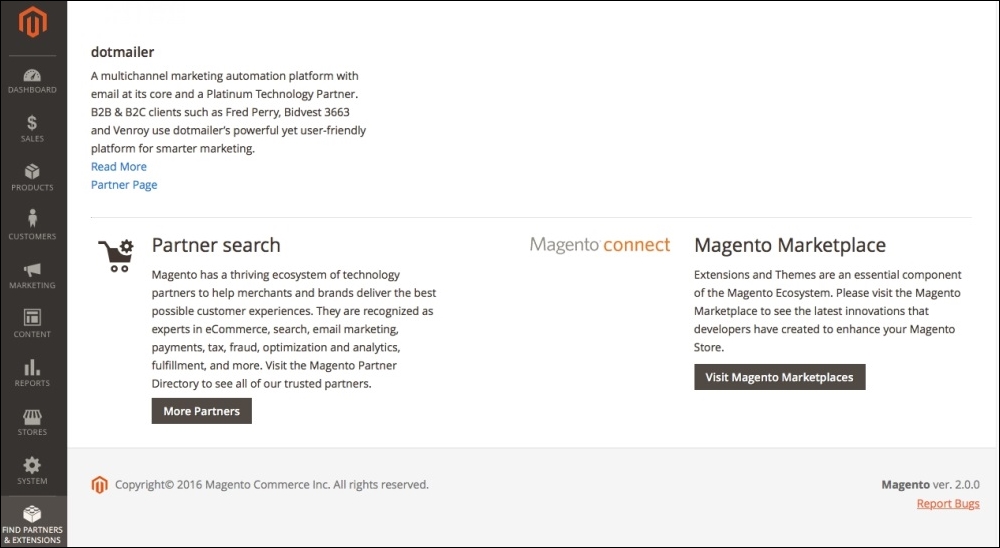
- Once you choose the extension to install, Magento 2.0 offers two options for extension installation:
- Installation via Composer
- Manual installation
To install the extensions via Composer, you need to configure composer.json to work with the Magento 2 Composer repository (http://packages.magento.com/) as a repository solution for Magento Core extensions. The composer already has the Packagist (https://packagist.org/) configuration. To proceed with this configuration, perform the following:
- Open the terminal or command prompt.
- Go to the root directory of your Magento installation.
- Run the
composer config repositories.magento composer http://packages.magento.comcommand.
To install a Magento extension via composer, do the following:
- Open the terminal or command prompt.
- Go to the root directory of your Magento installation.
- Run the
composer require <vendor>/<module>command. - An example of this is
composer require Packt/TweetsAbout. - Run the
composer updatecommand. - Then, run the
php bin/magento setup:upgradecommand. - In some cases, it is necessary to give write permissions again to the directories.
To install a Magento extension manually, perform the following steps:
- Download the
.zipfile of the module. - Extract it and move it under the
<magento_root_directory>/app/codedirectory. - Run the
php bin/magento setup:upgradecommand. - In some cases, it is necessary to give write permissions again to the directories (for example, the
vardirectory)
As you noted in the previous chapters, for every change that you apply in a Magento extension or theme styles, you need to clean the static files directory and deploy it to see the effect. This process takes time and unnecessary effort. So, what if you have a tool to automate this process?
Grunt.js (http://gruntjs.com/) is a task runner to automate tasks; for example, it provides productivity in Magento development by automating CSS changes. To install Grunt, follow these steps:
- Install Node.js (https://nodejs.org) in your machine.
- Open the terminal or command prompt.
- Run the
npm install -g grunt-clicommand to install the Grunt command-line interface. - Go to the
packt/Magento root directory and run thenpm install grunt --save-devcommand. - Still under the
packtdirectory, run thenpm installcommand. - Then, run the
npm updatecommand. - In your favorite code editor open, the
packt/dev/tools/grunt/configs/theme.jsfile, add the following code, and save it:'use strict'; module.exports = { blank: { area: 'frontend', name: 'Magento/blank', locale: 'en_US', files: [ 'css/styles-m', 'css/styles-l', 'css/email', 'css/email-inline' ], dsl: 'less' }, luma: { area: 'frontend', name: 'Magento/luma', locale: 'en_US', files: [ 'css/styles-m', 'css/styles-l' ], dsl: 'less' }, backend: { area: 'adminhtml', name: 'Magento/backend', locale: 'en_US', files: [ 'css/styles-old', 'css/styles' ], dsl: 'less' }, compstore: { area: 'frontend', name: 'Packt/compstore', locale: 'en_US', files: [ 'css/styles-m', 'css/styles-l', 'css/source/compstore' ], dsl: 'less' } };
Once the Grunt environment is configured, it's time to test Grunt. Perform the following steps:
- Open the terminal or command prompt.
- Run the
grunt exec:compstorecommand. - Then, run the
grunt less:compstorecommand. - Run the
grunt watchcommand.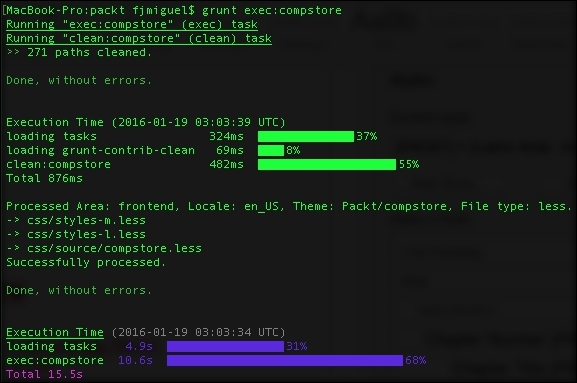
These commands will create a direct channel with the possibility to edit your .CSS files on the fly. The grunt watch command shows you the update in real time. With "grunt watch" still active in your terminal/prompt window, try to edit and save the body's background color in the app/design/frontend/Packt/compstore/web/css/source/compstore.less file to see the result in the browser by accessing your base URL: