When using database models, as explained in the previous recipe, the corresponding tables needs to be created during setup. These operations are placed in setup scripts and executed during the installation of an extension.
While running the installation of a module, there are four files executed to create schemas and insert data. To create schemas, the files used are as follows:
Setup/InstallSchema.php
Setup/UpgradeSchema.php
The installation file is executed only when there is no record in the setup_module table for the module. The upgrade file is executed only when the current version number in the setup_module table is lower than the version configured in your etc/module.xml file.
When it's necessary to insert default values into a table or new EAV attributes need to be created, these actions need to be configured in the following files:
Setup/InstallData.php
Setup/UpgradeData.php
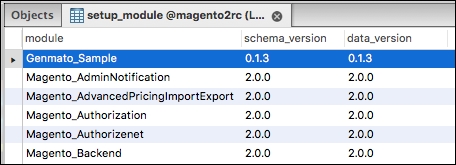
Magento keeps track of which version is installed for an extension in the setup_module table; here, the current installed version for the schema and data is stored:
Follow these steps to create your database tables:
- The following is the table schema installation:
Setup/InstallSchema.php<?php namespace Genmato\Sample\Setup; use Magento\Framework\Setup\InstallSchemaInterface; use Magento\Framework\Setup\ModuleContextInterface; use Magento\Framework\Setup\SchemaSetupInterface; use Magento\Framework\DB\Adapter\AdapterInterface; class InstallSchema implements InstallSchemaInterface { public function install(SchemaSetupInterface $setup, ModuleContextInterface $context) { $installer = $setup; $installer->startSetup(); /** * Create table 'genmato_demo' */ $table = $installer->getConnection()->newTable( $installer->getTable('genmato_demo') )->addColumn( 'demo_id', \Magento\Framework\DB\Ddl\Table::TYPE_SMALLINT, null, ['identity' => true, 'nullable' => false, 'primary' => true], 'Demo ID' )->addColumn( 'title', \Magento\Framework\DB\Ddl\Table::TYPE_TEXT, 255, ['nullable' => false], 'Demo Title' )->addColumn( 'creation_time', \Magento\Framework\DB\Ddl\Table::TYPE_TIMESTAMP, null, [], 'Creation Time' )->addColumn( 'update_time', \Magento\Framework\DB\Ddl\Table::TYPE_TIMESTAMP, null, [], 'Modification Time' )->addColumn( 'is_active', \Magento\Framework\DB\Ddl\Table::TYPE_SMALLINT, null, ['nullable' => false, 'default' => '1'], 'Is Active' )->addIndex( $setup->getIdxName( $installer->getTable('genmato_demo'), ['title'], AdapterInterface::INDEX_TYPE_FULLTEXT ), ['title'], ['type' => AdapterInterface::INDEX_TYPE_FULLTEXT] )->setComment( 'Demo Table' ); $installer->getConnection()->createTable($table); $installer->endSetup(); } } - Trigger the execution of the setup scripts:
bin/magento setup:upgrade
In Magento 2, the running of the setup scripts is no longer triggered by the first request after flushing the cache; to initiate the running of these scripts, run the command specified in step 2. When running the upgrade command, all modules are evaluated on their current version and module version in the configuration file. First, all schema installations/updates are executed, and next, the data installations/updates are processed.
The InstallData and InstallSchema files are executed only when there is no prior registration of the extension in the setup_module table. To run the installation files during testing, it is possible to remove the module row from the table and run the bin/magento setup:upgrade command.
The available methods to create a new table are defined in the Magento\Framework\DB\Adapter\AdapterInterface\Table class and are as follows:
addColumn: This adds a new column to the table; this method has the following parameters:name: This is the name of the tabletype: This is the table type; the available column types are defined as constants in theMagento\Framework\DB\Adapter\AdapterInterface\Tableclass asTYPE_*:TYPE_BOOLEANTYPE_SMALLINTTYPE_INTEGERTYPE_BIGINTTYPE_FLOATTYPE_NUMERICTYPE_DECIMALTYPE_DATETYPE_TIMESTAMPTYPE_DATETIMETYPE_TEXTTYPE_BLOBTYPE_VARBINARYsize: This specifies the size of the columnoptions: This is used to specify extra column options; the available options are as follows:unsigned: This is only for number types; allows True/False (default: False)precision: This is only for decimal and numeric types (default: calculated from size parameter or 0 if not set)scale: This is only for decimal and numeric types (default: calculated from size parameter or 10 if not set)default: The default value is used when creating a new recordnullable: In case a column is NULL (default: True)primary: This makes a column a primary keyprimary_position: This is only for primary keys and sets the sort order for the primary keysidentity/auto_increment: This auto-increments a column on inserting a new record (used to identify a unique record ID)comment: This is the description of the column
addForeignKey: This adds a foreign key relation to another table; the parameters allowed are as follows:fkName: This is the name of the foreign keycolumn: This is the column used as the foreign keyrefTable: This is the table where the key references torefColumn: This is the column name in the referenced tableonDelete: This sets the action to be performed when deleting a record; the available options are (constants as defined inMagento\Framework\DB\Adapter\AdapterInterface\Table):ACTION_CASCADEACTION_RESTRICTACTION_SET_DEFAULTACTION_SET_NULLACTION_NO_ACTION
addIndex: This adds a column to the search index; the available parameters are as follows:indexName: This is the name used for the indexfields: These are the column(s) used for the index (can be a single column or an array of columns)options: This is an array with extra options; currently, only the option type is used to specify the index type
When changing an existing table, it is possible to use the following methods; these are the methods that can be used directly on the $installer->getConnection() class:
dropTable: This removes a table from the database; the available parameters are as follows:tableName: This is the name of the table to deleteschemaName: This is the optional schema name used
renameTable: This renames a table from the database; the available parameters are as follows:oldTableName: This is the current name of the tablenewTableName: This is the new name for the tableschemaName: This is the optional schema name
addColumn: This adds an extra column to a table; the available parameters are as follows:tableName: This is the name of the table to altercolumnName: This is the name of the new columndefinition: This is an array with the following parameters:Type: Column typeLength: Column sizeDefault: Default valueNullable: If a column can be NULLIdentify/Auto_Increment: Used as an identity columnComment: Column descriptionAfter: Specify where to add the columnschemaName: This is the optional schema name
changeColumn: This changes the column name and definition; the available parameters are as follows:tableName: This is the name of the table to changeoldColumnName: This is the current column namenewColumnName: This is the new name for the columndefinition: This is the table definition; seeaddColumnfor available valuesflushData: This flushes the table cacheschemaName: This is the optional schema name
modifyColumn: This changes the column definition; the available parameters are as follows:dropColumn: This removes a column from the table; the available parameters are as follows:tableName: This is the name of the columncolumnName: This is the name of the column to removeschemaName: This is the optional schema name
addIndex: This adds a new index; the available parameters are as follows:tableName: This is the name of the table to changeindexName: This is the name of the index to addfields: These are the columns to be used as the indexindexType: This is the type of index; the available options (constants defined in (Magento\Framework\DB\Ddl\Table\AdapterInterface) are as follows:INDEX_TYPE_PRIMARYINDEX_TYPE_UNIQUEINDEX_TYPE_INDEXINDEX_TYPE_FULLTEXTschemaName: This is the optional schema name
dropIndex: This removes an index from a table; the available parameters are as follows:tableName: This is the name of the columnindexName: This is the name of the indexschemaName: This is the optional schema name
addForeignKey: This adds a new foreign key; the available parameters are as follows:fkName: This is the name of the foreign keytableName: This is the name of the tablecolumnName: This is the name of the column used in the foreign keyrefTableName: This is the name of the referenced tablerefColumnName: This is the name of the referenced columnonDelete: This is the action to perform on delete (see the precedingaddForeignKeydescription for available options)purge: This removes invalid data (default: false)schemaName: This is the optional schema namerefSchemaName: This is the option-referenced schema name
When, in a later version of the extension, there are extra fields necessary (or the current fields need to be changed), this is handled through the UpgradeSchema function, upgrade:
Setup/UpgradeSchema.php
<?php
namespace Genmato\Sample\Setup;
use Magento\Framework\DB\Ddl\Table;
use Magento\Framework\Setup\UpgradeSchemaInterface;
use Magento\Framework\Setup\ModuleContextInterface;
use Magento\Framework\Setup\SchemaSetupInterface;
class UpgradeSchema implements UpgradeSchemaInterface
{
public function upgrade(SchemaSetupInterface $setup, ModuleContextInterface $context)
{
$setup->startSetup();
if (version_compare($context->getVersion(), '0.1.1', '<')) {
$connection = $setup->getConnection();
$column = [
'type' => Table::TYPE_SMALLINT,
'length' => 6,
'nullable' => false,
'comment' => 'Is Visible',
'default' => '1'
];
$connection->addColumn($setup->getTable('genmato_demo'), 'is_visible', $column);
}
$setup->endSetup();
}
}As this file is run every time the module version is different than the currently installed version, it is necessary to check the current version that is installed to execute only the updates necessary:
if (version_compare($context->getVersion(), '0.1.1', '<')) {The preceding statement will make sure that the schema changes are executed only if the current version is less than 0.1.1.
In order to provide default content during installation (this can be records in a table or adding extra attributes to some entity), the data installation function is used:
Setup/InstallData.php
<?php
namespace Genmato\Sample\Setup;
use Genmato\Sample\Model\Demo;
use Genmato\Sample\Model\DemoFactory;
use Magento\Framework\Setup\InstallDataInterface;
use Magento\Framework\Setup\ModuleContextInterface;
use Magento\Framework\Setup\ModuleDataSetupInterface;
class InstallData implements InstallDataInterface
{
/**
* Demo factory
*
* @var DemoFactory
*/
private $demoFactory;
/**
* Init
*
* @param DemoFactory $demoFactory
*/
public function __construct(DemoFactory $demoFactory)
{
$this->demoFactory = $demoFactory;
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
* @SuppressWarnings(PHPMD.ExcessiveMethodLength)
*/
public function install(ModuleDataSetupInterface $setup, ModuleContextInterface $context)
{
$demoData = [
'title' => 'Demo Title',
'is_active' => 1,
];
/**
* Insert demo data
*/
$this->createDemo()->setData($demoData)->save();
}
/**
* Create demo
*
* @return Demo
*/
public function createDemo()
{
return $this->demoFactory->create();
}
}In this example, there is one record created in the table created during setup. For this, the DemoFactory class is injected through dependency injection into the constructor function of this class. DemoFactory is an automatically created class that allows you to instantiate a class (in this case, Genmato\Sample\Model\Demo) without injecting this directly into the constructor. Here, this is done in the createDemo function:
$this->demoFactory->create();
Similar to SchemaUpgrade, there is also a DataUpgrade option to insert data while upgrading to a newer version.
