- Let's create an Entity directory in our module's src folder. First, we will create an interface for our entity by creating a MessageInterface.php file:
- The MessageInterface will extend \Drupal\Core\Entity\ContentEntityInterface:
<?php
namespace Drupal\mymodule\Entity;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\ContentEntityInterface;
interface MessageInterface extends ContentEntityInterface {
/**
* Gets the message value.
*
* @return string
*/
public function getMessage();
}
This will be implemented by our entity and will provide the method requirements. It is best practice to provide an interface for entities. This allows you to provide required methods if another developer extends your entity or if you are doing advanced testing and need to mock an object. We also provide a method to return our main base field definition (to be defined).
- Then, let's create Message.php in our Entity directory in src. This file will contain the Message class, which extends \Drupal\Core\Entity\ContentEntityBase and implements our entity's interface:
<?php
namespace Drupal\mymodule\Entity;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\ContentEntityBase;
class Message extends ContentEntityBase implements MessageInterface {
}
- We will need to create an annotation document block on our class to provide information about our entity, such as its id, label, and entity keys:
<?php
namespace Drupal\mymodule\Entity;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\ContentEntityBase;
/**
* Defines the message entity class.
*
* @ContentEntityType(
* id = "message",
* label = @Translation("Message"),
* base_table = "message",
* fieldable = TRUE,
* entity_keys = {
* "id" = "message_id",
* "label" = "title",
* "langcode" = "langcode",
* "uuid" = "uuid"
* },
* )
*/
class Message extends ContentEntityBase implements MessageInterface {
}
The id is the internal machine name identifier for the entity type, and the label is its human-readable version. The entity keys definition tells Drupal the attributes that represent our identifier and label.
The base_table defines the database table in which the entity will be stored, and fieldable allows custom fields to be configured through the Field UI module.
- Next, we will add handlers to our entity. We will use the default handlers provided by Drupal:
/**
* Defines the message entity class.
*
* @ContentEntityType(
* id = "message",
* label = @Translation("Message"),
* handlers = {
* "list_builder" = "Drupal\mymodule\MessageListBuilder",
* "form" = {
* "default" = "Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityForm",
* "add" = "Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityForm",
* "edit" = "Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityForm",
* "delete" = "Drupal\Core\Entity\ContentEntityDeleteForm",
* },
* },
* base_table = "message",
* fieldable = TRUE,
* entity_keys = {
* "id" = "message_id",
* "label" = "title",
* "langcode" = "langcode",
* "uuid" = "uuid"
* },
* )
*/
The handlers array specifies classes that provide the interaction functionality with our entity. The list builder class will be created to show you a table of our entities. The form array provides classes for forms to be used when creating, editing, or deleting our content entity.
- An additional handler, the route_provider, can be added to dynamically generate our canonical (view), edit, add, delete, and collection (list) routes:
/**
* Defines the message entity class.
*
* @ContentEntityType(
* id = "message",
* label = @Translation("Message"),
* handlers = {
* "list_builder" = "Drupal\mymodule\MessageListBuilder",
* "form" = {
* "default" = "Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityForm",
* "add" = "Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityForm",
* "edit" = "Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityForm",
* "delete" = "Drupal\Core\Entity\ContentEntityDeleteForm",
* },
* "route_provider" = {
* "html" = "Drupal\Core\Entity\Routing\DefaultHtmlRouteProvider",
* },
* },
* base_table = "message",
* fieldable = TRUE,
* entity_keys = {
* "id" = "message_id",
* "label" = "title",
* "langcode" = "langcode",
* "uuid" = "uuid"
* },
* links = {
* "canonical" = "/messages/{message}",
* "edit-form" = "/messages/{message}/edit",
* "delete-form" = "/messages/{message}/delete",
* "collection" = "/admin/content/messages"
* },
* )
*/
There is a routing service for entities that will automatically provide Drupal a route with the proper controllers based on this annotation.
- We will then define an administration permission property in our entity's annotation, which the system checks, by default, for all create, update, and delete operations:
/**
* Defines the message entity class.
*
* @ContentEntityType(
* id = "message",
* label = @Translation("Message"),
* handlers = {
* "list_builder" = "Drupal\mymodule\MessageListBuilder",
* "form" = {
* "default" = "Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityForm",
* "add" = "Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityForm",
* "edit" = "Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityForm",
* "delete" = "Drupal\Core\Entity\ContentEntityDeleteForm",
* },
* "route_provider" = {
* "html" = "Drupal\Core\Entity\Routing\DefaultHtmlRouteProvider",
* },
* },
* admin_permission = "administer message",
* base_table = "message",
* fieldable = TRUE,
* entity_keys = {
* "id" = "message_id",
* "label" = "title",
* "langcode" = "langcode",
* "uuid" = "uuid"
* },
* links = {
* "canonical" = "/messages/{message}",
* "add-form" = "/messages/add",
* "edit-form" = "/messages/{message}/edit",
* "delete-form" = "/messages/{message}/delete",
* "collection" = "/admin/content/messages"
* },
* )
*/
- We will need to implement the baseFieldDefinitions method to satisfy the FieldableEntityInterface interface, which will provide our field definitions to the entity's base table. Add the following method to your class:
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public static function baseFieldDefinitions(EntityTypeInterface $entity_type) {
$fields = parent::baseFieldDefinitions($entity_type);
$fields['title'] = BaseFieldDefinition::create('string')
->setLabel(t('Title'))
->setRequired(TRUE)
->setTranslatable(TRUE)
->setRevisionable(TRUE)
->setSetting('max_length', 255)
->setDisplayOptions('view', array(
'label' => 'hidden',
'type' => 'string',
'weight' => -5,
))
->setDisplayOptions('form', array(
'type' => 'string_textfield',
'weight' => -5,
))
->setDisplayConfigurable('form', TRUE);
$fields['content'] = BaseFieldDefinition::create('text_long')
->setLabel(t('Content'))
->setDescription(t('Content of the message'))
->setTranslatable(TRUE)
->setDisplayOptions('view', array(
'label' => 'hidden',
'type' => 'text_default',
'weight' => 0,
))
->setDisplayConfigurable('view', TRUE)
->setDisplayOptions('form', array(
'type' => 'text_textfield',
'weight' => 0,
))
->setDisplayConfigurable('form', TRUE);
return $fields;
}
The FieldableEntityInterface is implemented by the ContentEntityBase class using the ContentEntityInterface. The method needs to return an array of BaseFieldDefinitions for typed data definitions. The parent class provides field definitions for most of the entity_keys value in our entity's annotation. We must provide the label field and any specific fields for our implementation.
The content base field definition will hold the actual text of the message.
- Next, we will implement the getMessage method in our class to satisfy our interface and provide a means to retrieve our message's text value:
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function getMessage() {
return $this->get('content')->value;
}
This method provides a wrapper around the defined base field's value and returns it.
- Create the MessageListBuilder class defined in our list_builder handler by creating a MessageListBuilder.php file and extending \Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityListBuilder. We will need to override the default implementation to display our base field definitions:
<?php
namespace Drupal\mymodule;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityListBuilder;
class MessageListBuilder extends EntityListBuilder {
public function buildHeader() {
$header['title'] = t('Title');
return $header + parent::buildHeader();
}
public function buildRow(EntityInterface $entity) {
$row['title'] = $entity->label();
return $row + parent::buildRow($entity);
}
}
In our list builder handler, we override the buildHeader and builderRow methods so that we can add our configuration entity's properties to the table.
- Before we move on, we must create a mymodule.permissions.yml file in the module's root directory. We will need to provide the permission definition for administer message, as provided in our annotation:
administer message:
title: 'Administer messages'
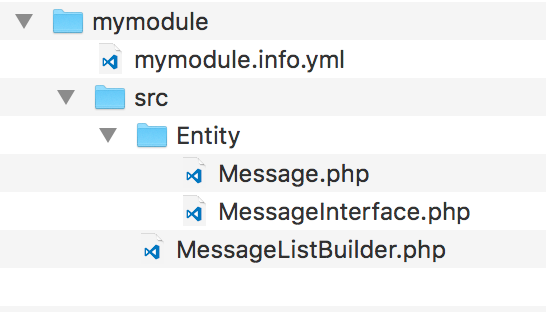
- Our module's structure should resemble the following screenshot:
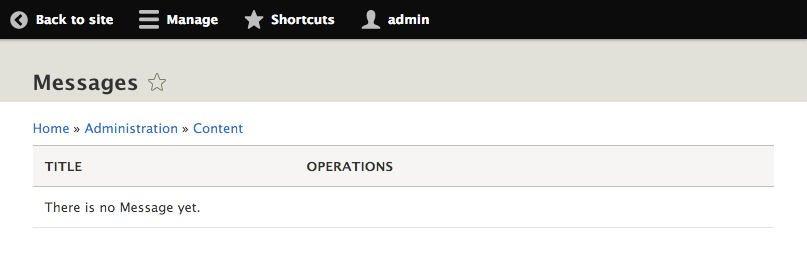
- Install the module. Go to /messages/add to create our first custom content entity entry and then view it on /admin/content/messages: