- Permissions are stored in a permissions.yml file. Add a mymodule.permissions.yml to the base directory of your module.
- First, we will need to define the internal string used to identify this permission, such as view mymodule pages:
view mymodule pages:
- Each permission is a YAML array of data. We will need to provide a title key that will be displayed on the permissions page:
view mymodule pages: title: 'View my module pages'
- Permissions have a description key to provide details of the permission on the permissions page:
view mymodule pages: title: 'View my module pages' description: 'Allows users to view pages provided by My Module'
- Save your permissions.yml and edit the module's routing.yml to use the permission for controlling access to a route.
- Modify the route's requirements key to have a _permission key that is equal to the defined permission:
mymodule.mypage: path: '/mypage' defaults: _controller: '\Drupal\mymodule\Controller\MyPageController::customPage' _title: 'My custom page' requirements: _permission: 'view mymodule pages'
- Go to Configuration and then to Performance in the DEVELOPMENT section and click on Clear all caches to rebuild Drupal's routes.
- Go to People and then to Permissions to add your permission as the authenticated user and anonymous user roles for My module!:
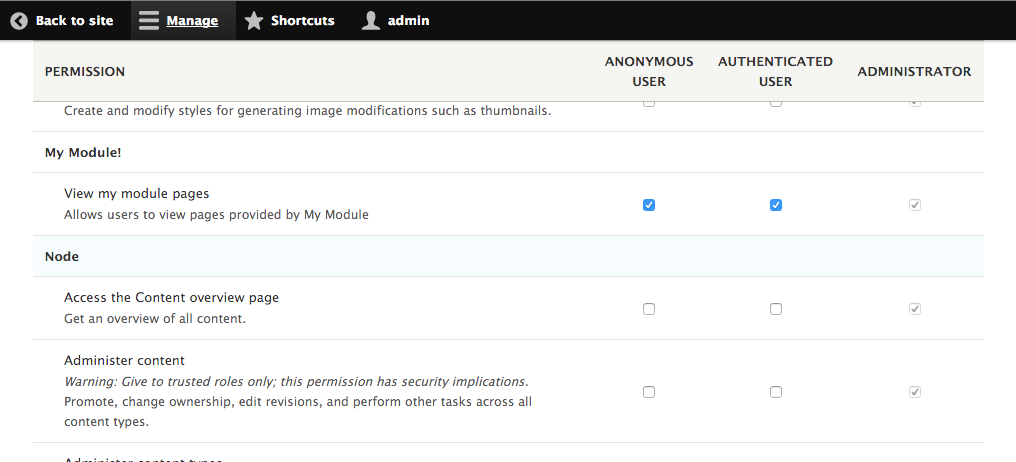
- Log out of your Drupal site and view the /mypage page. You will see the content, and will not receive an access denied page.
