Amap is a tool that can be used to check the application running on a specific port. Amap works by sending a trigger packet to the port and comparing the response with its database. It will print the application information if the application's response matches the database information.
In Kali Linux, the Amap trigger file is located in /etc/apmap/appdefs.trig, whereas the response file is available in /etc/amap/appdefs.resp.
To start Amap, go to the console and execute the following command:
amap
This will display a simple usage instruction and example on your screen.
For our exercise, we will analyze the application that runs on the target system's port 22. We will use the -b and -q options to get banner information without reporting the closed or unidentified ports, as given in the following command:
amap -bq 172.16.43.156 22
The following is the result of this command:

Using Amap, we can identify the application used on a specific port and the version information too.
To identify more than one port, define the ports on the command line separated by a space, as follows:
amap -bq 172.16.43.156445 6000
The following is the result of this command:
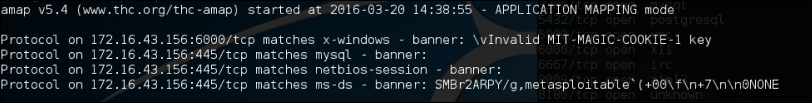
Amap is able to identify the service that is running on port 445, but it gives several matches when identifying the service running on port 22.
Amap is useful if you want a quick way to find out the application service information.
