Unicornscan is an information gathering and correlation engine tool. It is useful for introducing stimulus and measuring the response from a TCP/IP device. Unicornscan has the following features:
- Asynchronous stateless TCP port scanning
- Asynchronous stateless TCP banner grabbing
- Asynchronous UDP port scanning
- Active and passive remote OS and application identification
To start Unicornscan, use the console to execute the following command:
# unicornscan -h
This will display all the options with their descriptions.
The main difference between Unicornscan and other similar tools is that it is a very fast and scalable port scanner. From our experience, the scanning of UDP ports will take a long time to finish, especially if you want to test all the ports for a network. Unicornscan can help you with this problem.
In Unicornscan, you can define how many packets you want to send per second. The higher the packets per second (PPS) value, the faster the scan process; but this may cause an overload on the network, so be careful when using this capability. The default PPS is 300.
Let's scan the target using the default options in Unicornscan. To carry out a UDP scan (-m U) for the ports 1-65535 on machine 172.16.43.156, display the result immediately, and to be verbose (-Iv), the command is as follows:
# unicornscan -m U -Iv 172.16.43.156:1-65535
The following is the reply from Unicornscan:

From the preceding information, we know that by using the default PPS, this scan will take more than three minutes. To speed up the scanning process, let's change the packet sending rate to 10,000 (-r 10000):
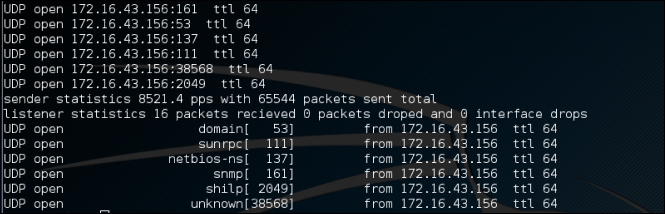
unicornscan -m U -Iv 172.16.43.156/24:1-65535 -r 10000
The following is the response from Unicornscan:

The scanning is much faster after we change the packet sending rate. Note that you may only use this rate in a fast network; if not, you may overwhelm the network with your UDP packets.
The following is the scan result: