The first thing to do before installing and using Kali Linux is to download it. You can get Kali Linux from the Kali Linux website (http://www.kali.org/downloads/).
On the download page, you can select the official Kali Linux image based on the following items, which are also shown in the next screenshot:
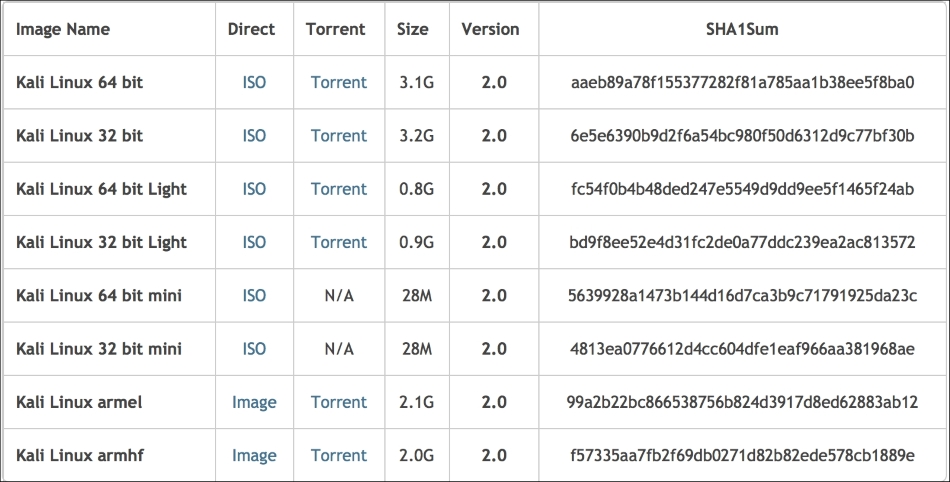
Machine architecture: i386, amd64, armel, and armhf
Image type: ISO image or VMware image
If you want to burn the image to a DVD or install Kali Linux to your machine, you might want to download the ISO image version. However, if you want to use Kali Linux for VMWare, you can use the VMWare image file to speed up the installation and configuration for a virtual environment.
After you have downloaded the image file successfully, you need to compare the SHA1 hash value from the downloaded image with the SHA1 hash value provided on the download page. The purpose of checking the SHA1 value is to ensure the integrity of the downloaded image is preserved. This prevents the user from either installing a corrupt image or an image file that has been maliciously tampered with.
In the Unix/Linux/BSD operating system, you can use the sha1sum command to check the SHA1 hash value of the downloaded image file. Remember that it might take some time to compute the hash value of the Kali Linux image file due to its size. For example, to generate the hash value of the kali-linux-2.0-i386.iso file, the following command is used:
sha1sum kali-linux-2.0-i386.iso 6e5e6390b9d2f6a54bc980f50d6312d9c77bf30b kali-linux-2.0-i386.iso
In the Windows world, there are many tools that can be used to generate the SHA1 hash value; one of them is sha1sum. It is available from http://www.ring.gr.jp/pub/net/gnupg/binary/sha1sum.exe.
We like it because of its small size, and it just works. If you want an alternative tool instead of sha1sum, there is HashMyFiles (http://www.nirsoft.net/utils/hash_my_files.html). HashMyFiles supports MD5, SHA1, CRC32, SHA-256, SHA-384, and SHA-512 hash algorithms.
After you have downloaded HashMyFiles, just run the HashMyFiles and select the file by navigating to File | Add Files to find out the SHA1 hash value of a file. Or, you can press F2 to perform the same function. Then, choose the image file you want.
The following screenshot resembles the SHA1 hash value generated by HashMyFiles for the Kali Linux v 2.0 i386.iso image file:
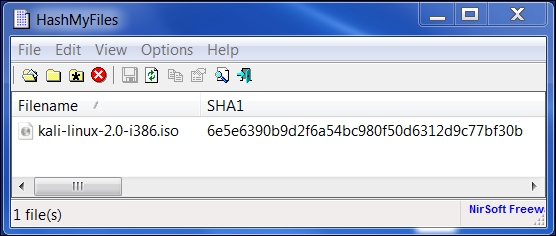
You need to compare the SHA1 hash value generated by sha1sum, HashMyFiles, or other similar tools with the SHA1 hash value displayed on the Kali Linux download page.
If both the values match, you can go straight to the Using Kali Linux section. However, if they do not match, it means that your image file is broken; you may want to download the file again from an official download mirror. When we run the hash of our downloaded file and compare it to the hash on the website, we see that they match, indicating that the package has been fully downloaded and is complete.
