However, the same-origin policy also limits legitimate use cases just like our own. Therefore, the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) came up with the Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) specification to deal with this. The CORS specification outlines the mechanism whereby browsers and servers can communicate with each other, through a set of HTTP headers, in order to determine which cross-origin requests are allowed.
CORS requires support from both the client (the browser) and the server. Almost all modern browsers support CORS:
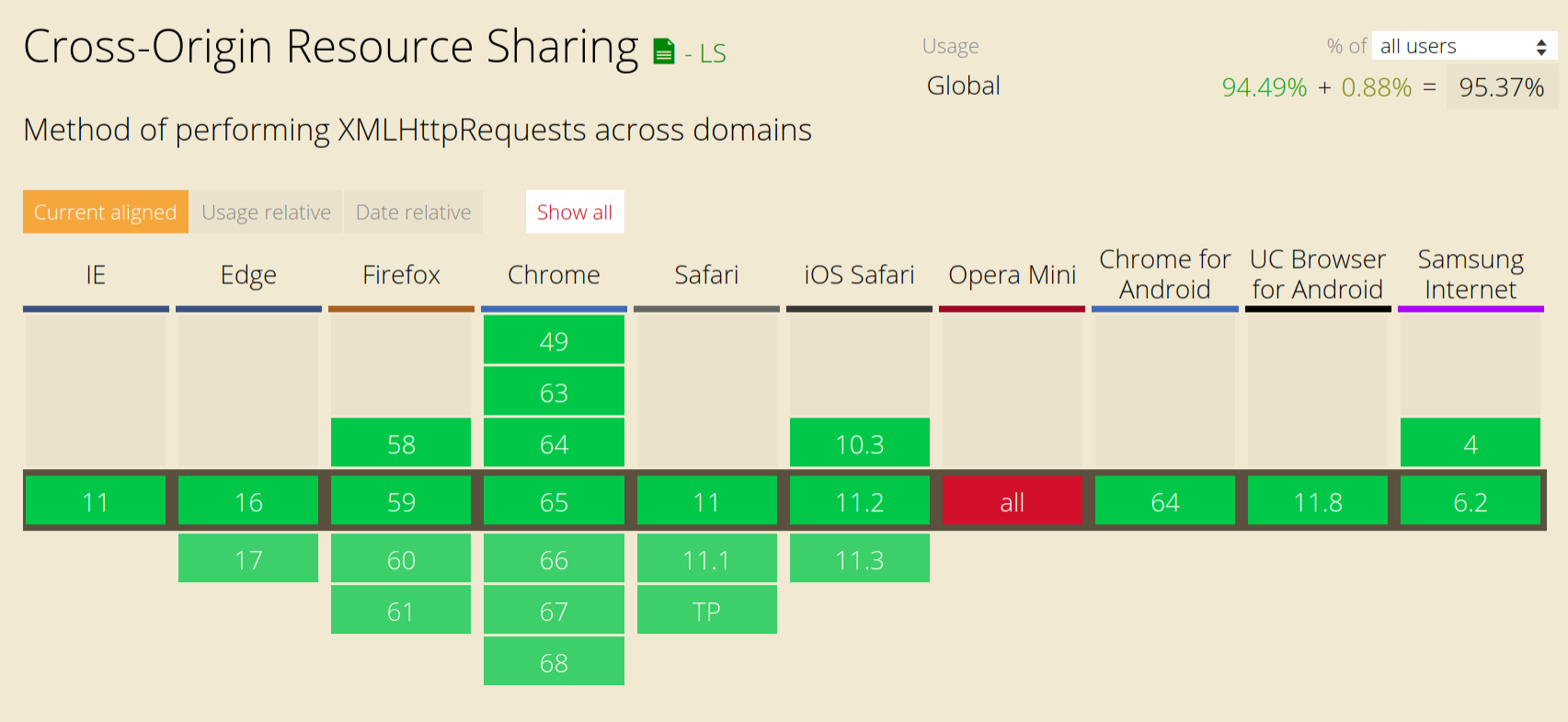
Therefore, the only thing we need to do is set up our Express server to enable CORS. To make things easy, there's a really handy site, enable-cors.org, that provides sample code of how to enable CORS for your specific server. We can find the instruction for Express at enable-cors.org/server_expressjs.html. All we need to do is add the following middleware before our other middlewares:
app.use((req, res, next) => {
res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');
res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Headers', 'Origin, X-Requested-With, Content-Type, Accept');
next();
});
The Access-Control-Allow-Origin header specifies requests from which origins are allowed to make cross-site requests. Here, we are using the glob wildcard '*' to allow cross-site requests from all origins.
If we paste in their sample code into src/index.js, reload our server, and also reload the Swagger UI documentation page, the CORS issue should be resolved and we should see details about our API displayed on-screen:
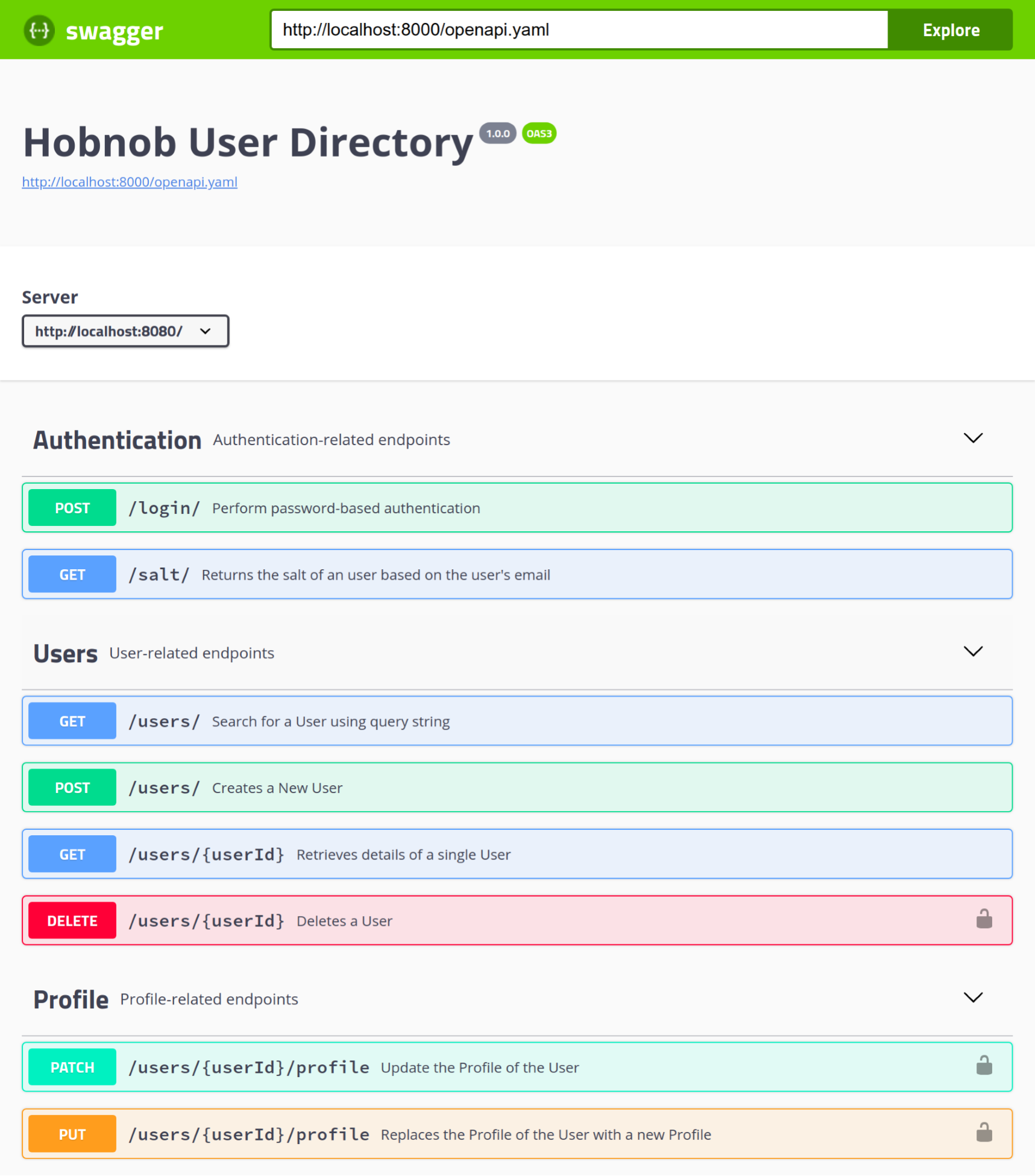
However, allowing CORS requests for all origins is the same as disregarding the same-origin policy set by browsers, which, as we've demonstrated, is an important policy to keep. Therefore, if possible, we should specify a whitelist of origins that are allowed to make CORS requests. At the moment, this is only the Swagger UI documentation site.
Therefore, we can update our code to whitelist the documentation site's origin:
res.header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "http://127.0.0.1:8000");
However, when we deploy our application and make our documentation publically available, we know that the docs would be served as a publicly-accessible URL, and not at 127.0.0.1:8000. Therefore, it makes little sense for us to hard-code the origin into the code. Instead, consistent with our approach so far, we should define the origin as a set of environment variables, use those variables within our code, and update our code to use these variables.
res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', `${process.env.SWAGGER_UI_PROTOCOL}://${process.env.SWAGGER_UI_HOSTNAME}:${process.env.SWAGGER_UI_PORT}`);
Save and restart your API server, and our Swagger UI documentation should still work.
