Now, we are ready to configure Jenkins. Navigate to jenkins.hobnob.social on your browser; there you'll see a setup wizard.
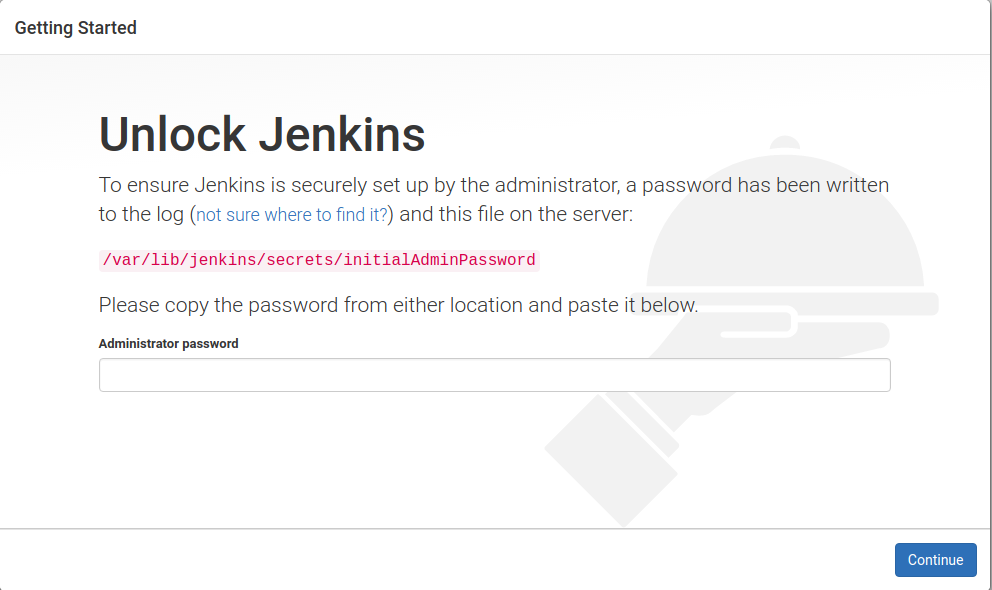
When Jenkins was installed, a password was written to a file at /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword, which only the system administrator (or users with sudo privileges) will have access to. This is to ensure that the person accessing the setup wizard is the system administrator and not some malicious party.
Therefore, the first step is to copy the contents of the /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword file and paste it into the wizard:
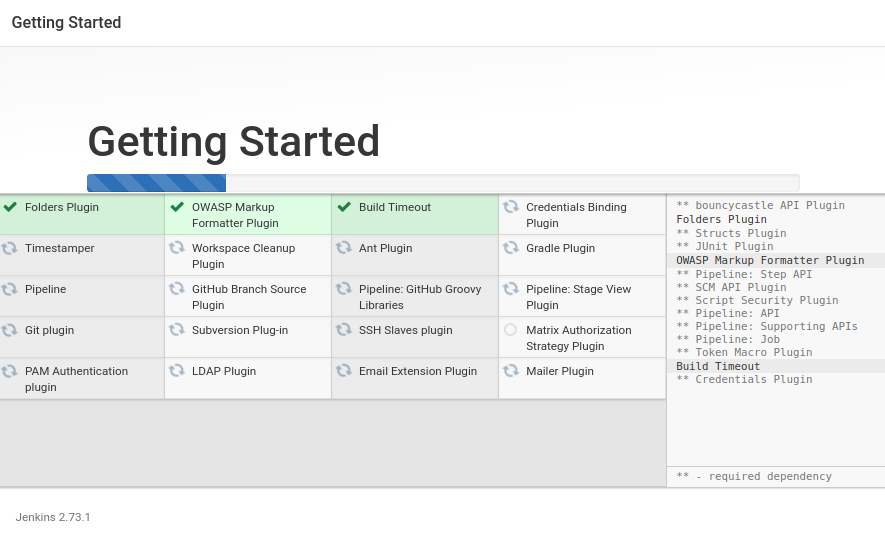
On the next screen, you'll be presented with the Customize Jenkins screen, where you can choose to install plugins. Jenkins, on its own, is just a platform that enables automation and has few features itself. Its functionalities are modularized into plugins. There are over 1,300 plugins, including integration with the following:
- Version control systems
- Bug databases
- Build tools
- Testing frameworks
Pick Install suggested plugins to install the most commonly used plugins, including the Git and GitHub plugins we will use later. You can track the progress of the installation on the next screen:
Lastly, you'll be prompted to create an administrative user for the web interface, which you'll use to continue the setup process (so remember your username and password!).
Great, now we will have successfully installed Jenkins and have it running on a public URL: