Now that we have added the Swagger UI into our repository, the next task is to write a script to serve it on a web server. Since these are simply static files with no backend involvement, any web server would be sufficient. Here, we will use the http-server package.
$ yarn add http-server --dev
By default, the http-server package uses the port 8080, which we are already using for our API. Therefore, we must use the -p flag to specify an alternate port. However, we don't want to hard-code this value into our NPM script; instead, we want to take it from our environment variable SWAGGER_UI_PORT. To achieve this, we need to create a new Bash script at scripts/swagger-ui/serve.sh with the following content:
#!/usr/bin/env bash
source <(dotenv-export | sed 's/\\n/\n/g')
yarn run docs:update
http-server docs/dist/ -p $SWAGGER_UI_PORT
Then, inside .env and .env.example, define the following environment variables:
SWAGGER_UI_PROTOCOL=http
SWAGGER_UI_HOSTNAME=127.0.0.1
SWAGGER_UI_PORT=8000
And add a new NPM script to serve our docs:
"docs:serve": "dotenv -e envs/.env ./scripts/swagger-ui/serve.sh",
This will download or update the Swagger UI source code and serve the site from the docs/dist/ directory. Now, navigate to http://127.0.0.1:8000 from your browser and you should see a page like this:
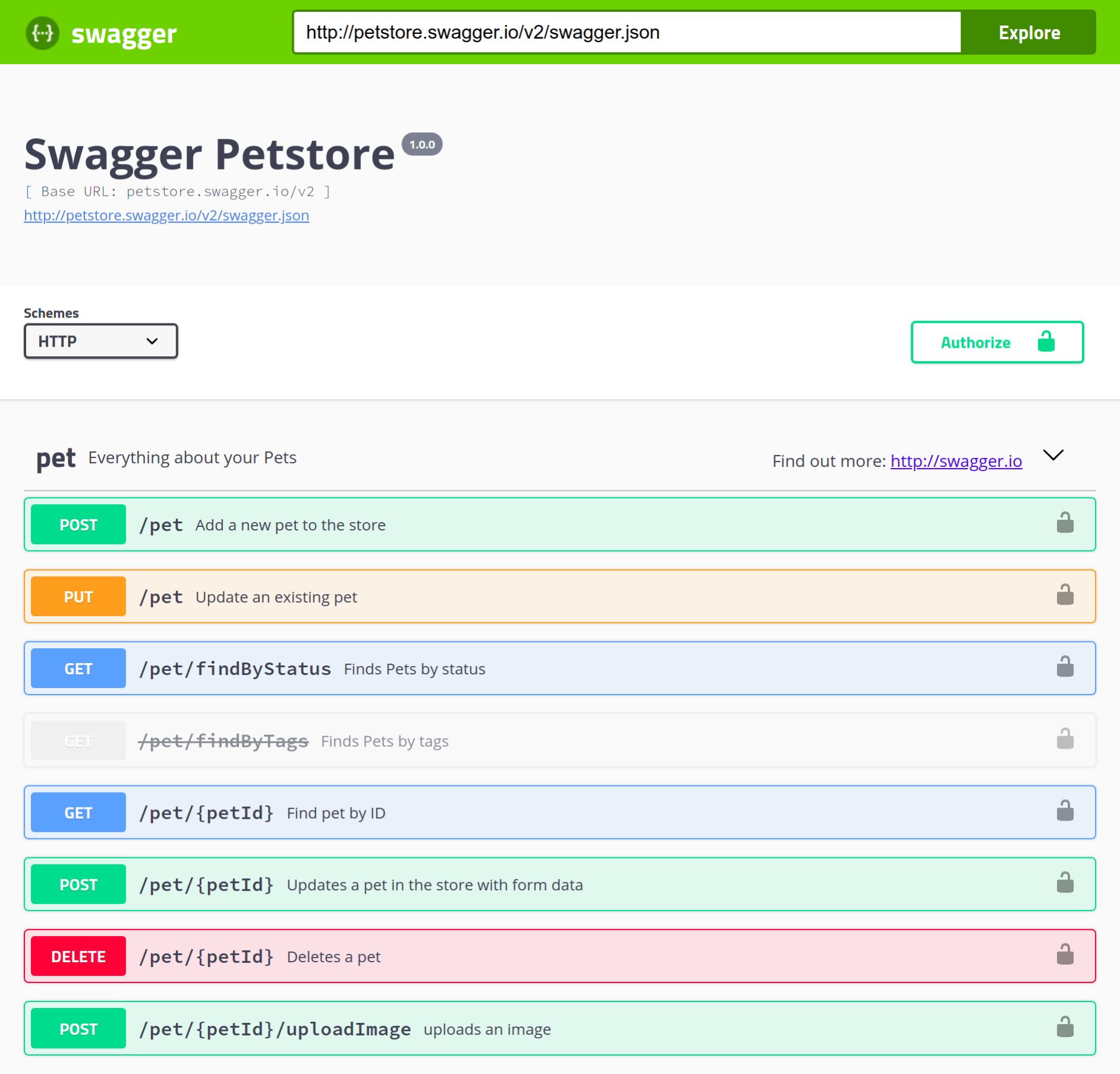
By default, dist/index.html uses a demo specification available at petstore.swagger.io/v2/swagger.json, which is what is shown here. To make Swagger UI display documentation for our own API, we need to do the following:
- Expose the hobnob.yaml file in a publicly-accessible location.
- Write a script to replace the demo URL with our own.
