You can move a value from a register to memory by swapping operands so that the memory address is on the left-hand side (destination) and the register is on the right-hand side (source):
mov [0x403000],eax ; moves 4 byte value in eax to memory location starting at 0x403000
mov [ebx],eax ; moves 4 byte value in eax to the memory address specified by ebx
Sometimes, you will come across instructions like those that follow. These instructions move constant values into a memory location; dword ptr just specifies that a dword value (4 bytes) is moved into the memory location. Similarly, word ptr specifies that a word (2 bytes) is moved into the memory location:
mov dword ptr [402000],13498h ; moves dword value 0x13496 into the address 0x402000
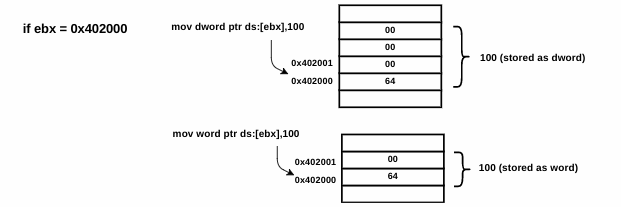
mov dword ptr [ebx],100 ; moves dword value 100 into the address specified by ebx
mov word ptr [ebx], 100 ; moves a word 100 into the address specified by ebx
In the preceding case, if ebx contained the memory address 0x402000, then the second instruction copies 100 as 00 00 00 64 (4 bytes) into the memory location starting at the address 0x402000, and the third instruction copies 100 as 00 64 (2 bytes) into the memory location starting at 0x40200, as shown here:
Let's take a look at a simple challenge.
