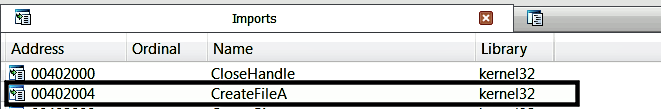
To demonstrate how malware makes use of the Windows API and to help you understand how to get more information about an API, let's look at a malware sample. Loading the malware sample in IDA and inspecting the imported functions in the Imports window show reference to the CreateFile API function, as shown in the following screenshot:
Before we determine the location where this API is referenced in the code, let's try to get more information about the API call. Whenever you encounter a Windows API function (like the one shown in the preceding example), you can learn more about the API function by simply searching for it in the Microsoft Developer Network (MSDN) at https://msdn.microsoft.com/, or by Googling it. The MSDN documentation gives a description of the API function, its function parameters (their data types), and the return value. The function prototype for CreateFile (as mentioned in the documentation at https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/aa363858(v=vs.85).aspx) is shown in the following snippet. From the documentation, you can tell that this function is used to create or open a file. To understand what file the program creates or opens, you will have to inspect the first parameter (lpFilename), which specifies the filename. The second parameter (dwDesiredAccess) specifies the requested access (such as read or write access), and the fifth parameter specifies the action to take on the file (such as creating a new file or opening an existing file):
HANDLE WINAPI CreateFile(
_In_ LPCTSTR lpFileName,
_In_ DWORD dwDesiredAccess,
_In_ DWORD dwShareMode,
_In_opt_ LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpSecurityAttributes,
_In_ DWORD dwCreationDisposition,
_In_ DWORD dwFlagsAndAttributes,
_In_opt_ HANDLE hTemplateFile
);
The Windows API uses Hungarian notation for naming variables. In this notation, the variable is prefixed with an abbreviation of its datatype; this makes it easy to understand the data type of a given variable. In the preceding example, consider the second parameter, dwDesiredAccess; the dw prefix specifies that it is of the DWORD data type. The Win32 API supports many different data types (https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/aa383751(v=vs.85).aspx). The following table outlines some of the relevant data types:
| Data Type |
Description |
| BYTE (b) |
Unsigned 8-bit value. |
| WORD (w) |
Unsigned 16-bit value. |
| DWORD (dw) | Unsigned 32-bit value. |
| QWORD (qw) | Unsigned 64-bit value. |
| Char (c) | 8-bit ANSI character. |
| WCHAR | 16-bit Unicode character. |
| TCHAR |
Generic character (1-byte ASCII character or wide, 2-byte Unicode character). |
| Long Pointer (LP) |
This is a pointer to another data type. For example, LPDWORD is a pointer to DWORD, LPCSTR is a constant string, LPCTSTR is a const TCHAR (1-byte ASCII characters, or wide, 2-byte Unicode characters) string, LPSTR is a non-constant string, and LPTSTR is a non-constant TCHAR (ASCII or Unicode) string. Sometimes, you will see Pointer (P) used instead of Long Pointer(LP). |
| Handle (H) | It represents the handle data type. A handle is a reference to an object. Before a process can access an object (such as a file, registry, process, Mutex, and so on), it must first open a handle to the object. For example, if a process wants to write to a file, the process first calls the API, such as CreateFile, which returns the handle to the file; the process then uses the handle to write to the file by passing the handle to the WriteFile API. |
Apart from the datatypes and variables, the preceding function prototype contains annotations, such as _In_ and _Out_, which describe how the function uses its parameters and return value. The _In_ specifies that it is an input parameter, and the caller must provide valid parameters for the function to work. The _IN_OPT specifies that it is an optional input parameter (or it can be NULL). The _Out_ specifies output parameter; it means that the function will fill in the parameter on return. This convention is useful to know if the API call stores any data in the output parameter after the function call. The _Inout_ object tells you that the parameter both passes values to the function and receives the output from the function.
With an understanding of how to get information about an API from the documentation, let's go back to our malware sample. Using the cross-references to CreateFile, we can determine that the CreateFile API is referenced in two functions, StartAddress and start, as shown here:

Double-clicking the first entry in the preceding screenshot jumps the display to the following code in the disassembly window. The following code highlights another great feature of IDA. Upon disassembly, IDA employs a technology called Fast Library Identification and Recognition Technology (FLIRT), which contains pattern matching algorithms to identify whether the disassembled function is a library or an imported function (a function imported from DLLs). In this case, IDA was able to recognize the disassembled function at ➊ as an imported function, and named it CreateFileA. IDA's capability to identify libraries and imported functions is extremely useful, because when you are analyzing malware, you really don't want to waste time reverse engineering a library or import function. IDA also added names of parameters as comments to indicate which parameter was being pushed at each instruction leading up to the CreateFileA Windows API call:
push 0 ; hTemplateFile
push 80h ; dwFlagsAndAttributes
push 2 ➍ ; dwCreationDisposition
push 0 ; lpSecurityAttributes
push 1 ; dwShareMode
push 40000000h ➌ ; dwDesiredAccess
push offset FileName ➋ ; "psto.exe"
call CreateFileA ➊
From the preceding disassembly listing, you can tell that malware either creates or opens a file (psto.exe) that is passed as the first argument (➋) to CreateFile. From the documentation, you know that the second argument (➌) specifies the requested access (such as read or write). The constant 40000000h, passed as the second argument, represents the symbolic constant GENERIC_WRITE. Malware authors often use symbolic constants, such as GENERIC_WRITE, in their source code; but during the compilation process, these constants are replaced with their equivalent values (such as 40000000h), making it difficult to determine whether it is a numeric constant or a symbolic constant. In this case, from the Windows API documentation, we know that the value 40000000h at ➌ is a symbolic constant that represents GENERIC_WRITE. Similarly, the value 2, passed as the fifth argument (➍), represents the symbolic name CREATE_ALWAYS; this tells you that malware creates the file.
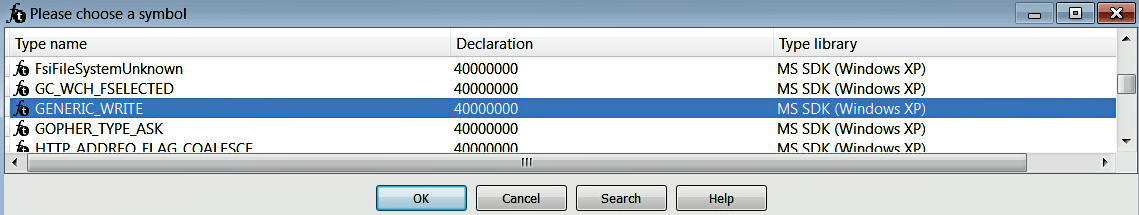
Another feature of IDA is that it maintains a list of standard symbolic constants for the Windows API or the C standard library function. To replace the constant value such as 40000000h at ➌, with the symbolic constant, just right-click on the constant value and choose the Use standard symbolic constant option; this will bring up the window displaying all of the symbolic names for the selected value (in this case, 40000000h), as shown in the following screenshot. You need to select the one that is appropriate; in this case, the appropriate one is GENERIC_WRITE. In the same manner, you can also replace the constant value 2, passed as the fifth argument, to its symbolic name, CREATE_ALWAYS:
After replacing the constants with symbolic names, the disassembly listing is translated to the one shown in the following snippet. The code is now more readable, and from the code, you can tell that malware creates the file psto.exe on the filesystem. After the functional call, the handle to the file (which can be found in the EAX register) is returned. The handle to the file returned by this function can be passed to other APIs, such as ReadFile() or WriteFile(), to perform subsequent operations:
push 0 ; hTemplateFile
push 80h ; dwFlagsAndAttributes
push CREATE_ALWAYS ; dwCreationDisposition
push 0 ; lpSecurityAttributes
push 1 ; dwShareMode
push GENERIC_WRITE ; dwDesiredAccess
push offset FileName ; "psto.exe"
call CreateFileA
