The simplest type of malware that you will encounter during malware analysis is a Downloader. A downloader is a program that downloads another malware component from the internet and executes it on the system. It does that by calling the UrlDownloadToFile() API, which downloads the file onto the disk. Once downloaded, it then uses either ShellExecute(), WinExec(), or CreateProcess() API calls to execute the downloaded component. Normally, you will find that downloaders are used as part of the exploit shellcode.
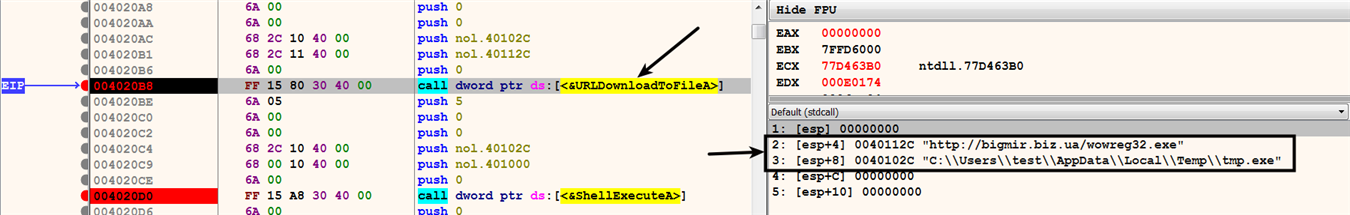
The following screenshot shows a 32-bit malware downloader using UrlDownloadToFileA() and ShellExecuteA() to download and execute a malware binary. To determine the URL from where the malware binary is being downloaded, a breakpoint was set at the call to UrlDownloadToFileA(). After running the code, the breakpoint was triggered, as shown in the following screenshot. The second argument to UrlDownloadToFileA() shows the URL from where the malware executable (wowreg32.exe) will be downloaded, and the third argument specifies the location on the disk where the downloaded executable will be saved. In this case, the downloader saves the downloaded executable in the %TEMP% directory as temp.exe:
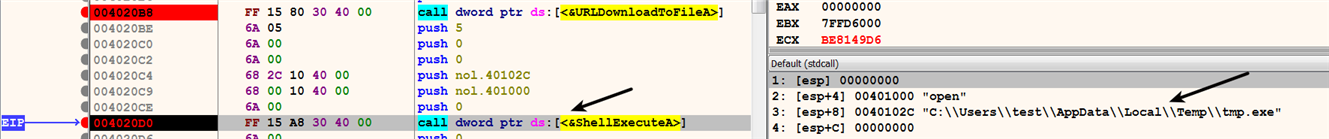
After downloading the malware executable into the %TEMP% directory, the downloader executes it by calling the ShellExecuteA() API, as shown in the following screenshot. Alternatively, malware may also use the WinExec() or CreateProcess() API to execute the downloaded file: