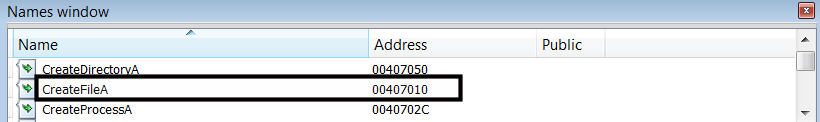
If you recall, upon disassembly, IDA tries to identify whether the disassembled function is a library function or an import function by using pattern matching algorithms. It also derives the list of names from the symbol table; such derived names can be accessed by using the Names window (via View | Open subview | Names or Shift + F4). The Names window contains the list of imported, exported, and library functions, and named data locations. The following screenshot displays the CreateFileA API functions in the Names window:
You can also programmatically access the named items. The following IDAPython script checks for the presence of the CreateFile API function by iterating through each named item:
import idautils
for addr, name in idautils.Names():
if "CreateFile" in name:
print hex(addr),name
The preceding script calls the idautils.Names() function, which returns a named item (tuple), containing the virtual address and the name. The named item is iterated and checked for the presence of CreateFile. Running the preceding script returns the address of the CreateFileA API, as shown in the following snippet. Since the code for an imported function resides in a shared library (DLL) that will only be loaded during runtime, the address (0x407010) listed in the following snippet is the virtual address of the associated import table entry (not the address where the code for the CreateFileA function can be found):
0x407010 CreateFileA
Another method to determine the presence of the CreateFileA function is by using the following code. The idc.get_name_ea_simple() function returns the virtual address of CreateFileA. If CreateFileA does not exist, then it returns a value of -1 (idaapi.BADADDR):
import idc
import idautils
ea = idc.get_name_ea_simple("CreateFileA")
if ea != idaapi.BADADDR:
print hex(ea), idc.generate_disasm_line(ea,0)
else:
print "Not Found"
