Test-driven development (TDD) is an extreme programming practice. In TDD, we start with a test case and incrementally write the production code that is required to make the test case succeed. The idea is that one should focus on one test case or scenario at a time and once the test case passes, they can then move on to the next scenario. In this process, if the new test case passes, we shouldn't modify the production code. In other words, in the process of developing a new feature or while fixing a bug, we can modify the production code only for two reasons: either to ensure the test case passes or to refactor the code. The primary focus of TDD is unit testing; however, it can be extended to integration and interaction testing to some extent.
The following figure demonstrates the TDD process visually:
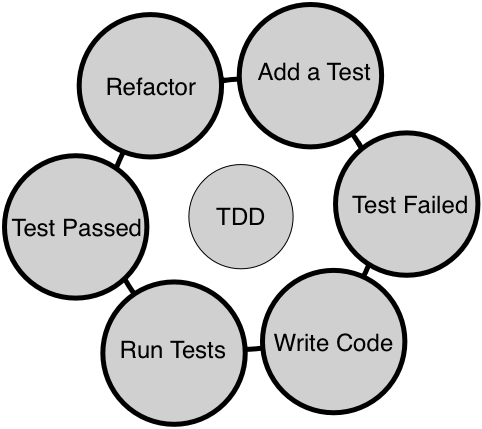
When TDD is followed religiously, one can achieve both functional and structural quality of the code. It is very crucial that you write the test case first before writing the production code as opposed to writing test cases at the end of the development phase. This makes quite a lot of difference. For instance, when a developer writes unit test cases at the end of development, it is very unlikely that the test cases will find any defect in the code. The reason is that the developers will unconsciously be inclined to prove their code is doing the right thing when the test case is written at the end of development. Whereas, when developers write test cases upfront, as no code is written yet, they start thinking from the end user's point of view, which would encourage them to come up with numerous scenarios from the requirement specification point of view.
In other words, test cases written against code that is already written will generally not find any bug as it tends to prove the code written is correct, instead of testing it against the requirement. As developers think of various scenarios before writing code, it helps them write better code incrementally, ensuring that the code does take care of those scenarios. However, when the code has loopholes, it is the test case that helps them find issues, as test cases will fail if they don't meet the requirements.
TDD is not just about using some unit test framework. It requires cultural and mindset change while developing or fixing defects in the code. Developers' focus should be to make the code functionally correct. Once the code is developed in this fashion, it is highly recommended that the developers should also focus on removing any code smells by refactoring the code; this will ensure the structural quality of the code would be good as well. In the long run, it is the structural quality of the code that would make the team deliver features faster.
