FTP is obsolete. It is not feasible for today, it makes things slow, and a normal FTP connection is insecure. It is hard for a team to deploy their changes using FTP because it creates huge conflicts in their code and this may cause problems, while uploading changes and can override each other's changes.
Using a Git versioning system, such as GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket, we can make our deployment automatic. Different developers use different setups for automatic deployments, and it all depends on their own choice and ease. The general rules of using automatic deployments are to make them easy for a team and to not use FTP.
The following is a general flowchart for a deployment setup:
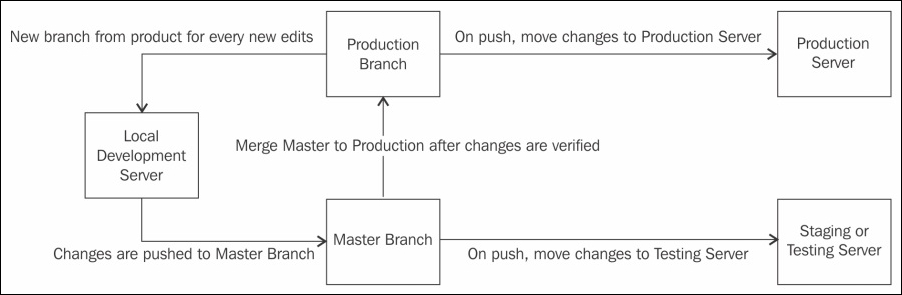
As shown in the preceding flowchart, we have two servers: the staging or testing the server and production server. On the staging server, we have an exact copy of the website to test new features and others, and the production server has our live website.
Now, we have a repository that has two main branches: the master branch and the production branch. The master branch is used for development and testing purposes, and the production branch is used for final production features. Note that the production branch should only accept merging, and it should not accept commits so that the production environment is completely safe.
Now, let's say that we want to add a customer registration feature to our application. We will perform the following steps:
- The first and most important thing to do is to create a new branch from the production branch head. Let's name this branch
customer-registration. - Now, add all the new features to this
customer-registrationbranch and while verifying on the local development server, merge this branch to the local master branch. - After merging the new branch to the local master branch, push the master branch to remote master branch. A successful push will cause the new features to be moved to the staging server.
- Now, test all the new features on the staging server.
- When everything works fine, merge the remote master branch with the remote production branch. This will cause all the changes to be moved to the production branch, and this merge will cause all the new changes to be moved to the production server.
- An ideal setup similar to the preceding one makes deployment very easy, and a complete team can work on the application regardless of the geographical location. In case any issue occurs during the deployment, one can be easily fall back to the old version of the production branch.
Continuous Integration (CI) is a technique in which all the members of a team have to integrate their code into a shared repository, and then each check by the team member is verified by automatic builds to catch errors and problems in the early stages.
There are several tools that are used for CI for PHP; some of these are PHPCI, Jenkins, Travis CI, and others.
