The classic bubble sort is an exercise often assigned to university students. Nonetheless, it's important to master this algorithm as there are many occasions where built-in PHP sorting functions do not apply. An example would be sorting a multi-dimensional array where the sort key is not the first column.
The way the bubble sort works is to recursively iterate through the list and swap the current value with the next value. If you want items to be in ascending order, the swap occurs if the next item is less than the current item. For descending order, the swap occurs if the reverse is true. The sort is concluded when no more swaps occur.
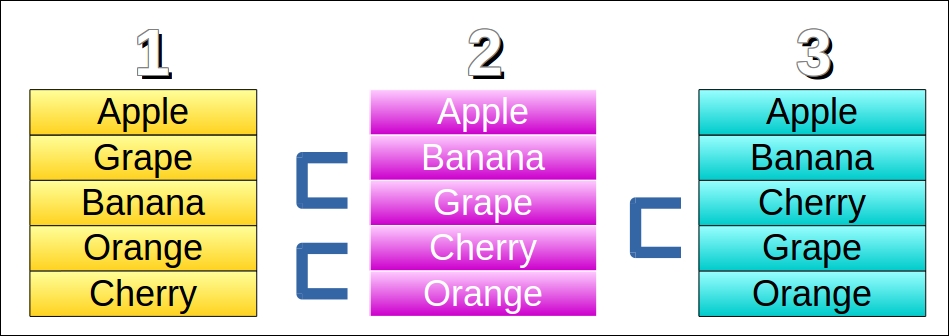
In the following diagram, after the first pass, Grape and Banana are swapped, as are Orange and Cherry. After the 2nd pass, Grape and Cherry are swapped. No more swaps occur on the last pass, and the bubble sort ends:
- We do not want to actually move the values around in the array; that would be horribly expensive in terms of resource usage. Instead, we will use a linked list, discussed in the previous recipe.
- First we build a linked list using the
buildLinkedList()function discussed in the previous recipe. - We then define a new function,
bubbleSort(), which accepts the linked list by reference, the primary list, a sort field, and a parameter that represents sort order (ascending or descending):function bubbleSort(&$linked, $primary, $sortField, $order = 'A') { - The variables needed include one that represents the number of iterations, the number of swaps, and an iterator based upon the linked list:
static $iterations = 0; $swaps = 0; $iterator = new ArrayIterator($linked);
- In the
while()loop, we only proceed if the iteration is stillvalid, which is to say still in progress. We then obtain the current key and value, and the next key and value. Note the extraif()statement to ensure the iteration is still valid (that is, to make sure we don't drop off the end of the list!):while ($iterator->valid()) { $currentLink = $iterator->current(); $currentKey = $iterator->key(); if (!$iterator->valid()) break; $iterator->next(); $nextLink = $iterator->current(); $nextKey = $iterator->key(); - Next we check to see whether the sort is to be ascending or descending. Depending on the direction, we check to see whether the next value is greater than, or less than, the current value. The result of the comparison is stored in
$expr:if ($order == 'A') { $expr = $primary[$linked->offsetGet ($currentKey)][$sortField] > $primary[$linked->offsetGet($nextKey)][$sortField]; } else { $expr = $primary[$linked->offsetGet ($currentKey)][$sortField] < $primary[$linked->offsetGet($nextKey)][$sortField]; } - If the value of
$exprisTRUE, and we have valid current and next keys, the values are swapped in the linked list. We also increment$swaps:if ($expr && $currentKey && $nextKey && $linked->offsetExists($currentKey) && $linked->offsetExists($nextKey)) { $tmp = $linked->offsetGet($currentKey); $linked->offsetSet($currentKey, $linked->offsetGet($nextKey)); $linked->offsetSet($nextKey, $tmp); $swaps++; } } - Finally, if any swaps have occurred, we need to run through the iteration again, until there are no more swaps. Accordingly, we make a recursive call to the same method:
if ($swaps) bubbleSort($linked, $primary, $sortField, $order);
- The real return value is the re-organized linked list. We also return the number of iterations just for reference:
return ++$iterations; }
Add the bubbleSort() function discussed previously to the include file created in the previous recipe. You can use the same logic discussed in the previous recipe to read the customer.csv file, producing a primary list:
<?php
define('CUSTOMER_FILE', __DIR__ . '/../data/files/customer.csv');
include __DIR__ . '/chap_10_linked_list_include.php';
$headers = array();
$customer = readCsv(CUSTOMER_FILE, $headers);You can then produce a linked list using the first column as a sort key:
$makeLink = function ($row) {
return $row[0];
};
$linked = buildLinkedList($customer, $makeLink);Finally, call the bubbleSort() function, providing the linked list and customer list as arguments. You can also provide a sort column, in this illustration column 2, that represents the account balance, using the letter 'A' to indicate ascending order. The printCustomer() function can be used to display output:
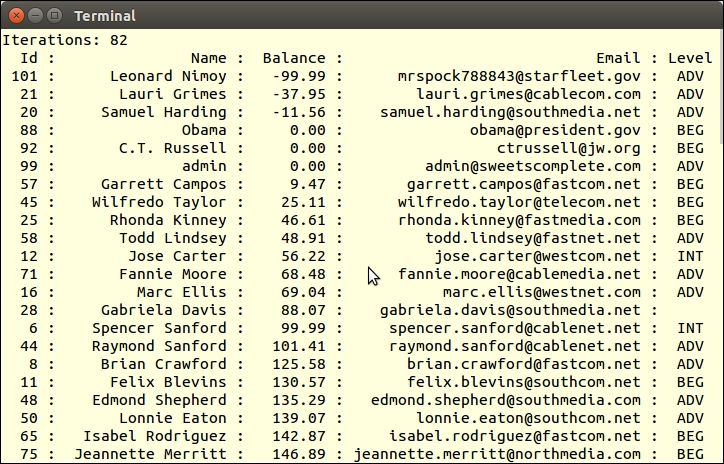
echo 'Iterations: ' . bubbleSort($linked, $customer, 2, 'A') . PHP_EOL; echo printCustomer($headers, $linked, $customer);
Here is an example of the output: