Creating a program to display a calendar is something you would most likely do as a student at secondary school. A nested for() loop, where the inside loop generates a list of seven days, will generally suffice. Even the problem of how many days there are in the month is easily solved in the form of a simple array. Where it starts to get tricky is when you need to figure out, for any given year, on what day of the week does the 1st of January fall. Also, what if you want to represent the months and days of the week in a language and format acceptable to a specific locale? As you have probably guessed, we will build a solution using the previously discussed Application\I18n\Locale class.
- First we need to create a generic class that will hold information for a single day. Initially it will only hold an integer value,
$dayOfMonth. Later, in the next recipe, we'll expand it to include events. As the primary purpose of this class will be to yield$dayOfMonth, we'll incorporate this value into its constructor, and define__invoke()to return this value as well:namespace Application\I18n; class Day { public $dayOfMonth; public function __construct($dayOfMonth) { $this->dayOfMonth = $dayOfMonth; } public function __invoke() { return $this->dayOfMonth ?? ''; } } - Create a new class that will hold the appropriate calendar-generation methods. It will accept an instance of
Application\I18n\Locale, and will define a couple of class constants and properties. The format codes, such asEEEEEandMMMM, are drawn from ICU date formats:namespace Application\I18n; use IntlCalendar; class Calendar { const DAY_1 = 'EEEEE'; // T const DAY_2 = 'EEEEEE'; // Tu const DAY_3 = 'EEE'; // Tue const DAY_FULL = 'EEEE'; // Tuesday const MONTH_1 = 'MMMMM'; // M const MONTH_3 = 'MMM'; // Mar const MONTH_FULL = 'MMMM'; // March const DEFAULT_ACROSS = 3; const HEIGHT_FULL = '150px'; const HEIGHT_SMALL = '60px'; protected $locale; protected $dateFormatter; protected $yearArray; protected $height; public function __construct(Locale $locale) { $this->locale = $locale; } // other methods are discussed in the following bullets } - Then we define a method that returns an
IntlDateFormatterinstance from ourlocaleclass. This is stored in a class property, as it will be used frequently:protected function getDateFormatter() { if (!$this->dateFormatter) { $this->dateFormatter = $this->locale->getDateFormatter(Locale::DATE_TYPE_FULL); } return $this->dateFormatter; } - Next we define a core method,
buildMonthArray(), which creates a multi-dimensional array where the outer key is the week of the year, and the inner array is seven elements representing the days of the week. We accept the year, month, and optional time zone as arguments. Note, as part of variable initialization, we subtract 1 from the month. This is because theIntlCalendar::set()method expects a 0-based value for the month, where 0 represents January, 1 is February, and so on:public function buildMonthArray($year, $month, $timeZone = NULL) { $month -= 1; //IntlCalendar months are 0 based; Jan==0, Feb==1 and so on $day = 1; $first = TRUE; $value = 0; $monthArray = array(); - We then create an
IntlCalendarinstance, and use it to determine how many days are in this month:$cal = IntlCalendar::createInstance($timeZone, $this->locale->getLocaleCode()); $cal->set($year, $month, $day); $maxDaysInMonth = $cal->getActualMaximum(IntlCalendar::FIELD_DAY_OF_MONTH);
- After that we use our
IntlDateFormatterinstance to determine what day of the week equates to the 1st of this month. After that, we set the pattern tow, which will subsequently give us the week number:$formatter = $this->getDateFormatter(); $formatter->setPattern('e'); $firstDayIsWhatDow = $formatter->format($cal); - We are now ready to loop through all days in the month with nested loops. An outer
while()loop ensures we don't go past the end of the month. The inner loop represents the days of the week. You will note that we take advantage ofIntlCalendar::get(), which allows us to retrieve values from a wide range of predefined fields. We also adjust the week of the year value to 0 if it exceeds 52:while ($day <= $maxDaysInMonth) { for ($dow = 1; $dow <= 7; $dow++) { $cal->set($year, $month, $day); $weekOfYear = $cal->get(IntlCalendar::FIELD_WEEK_OF_YEAR); if ($weekOfYear > 52) $weekOfYear = 0; - We then check to see whether
$firstis still setTRUE. If so, we start adding day numbers to the array. Otherwise, the array value is set toNULL. We then close all open statements and return the array. Note that we also need to make sure the inner loop doesn't go past the number of days in the month, hence the extraif()statement in the outerelseclause.if ($first) { if ($dow == $firstDayIsWhatDow) { $first = FALSE; $value = $day++; } else { $value = NULL; } } else { if ($day <= $maxDaysInMonth) { $value = $day++; } else { $value = NULL; } } $monthArray[$weekOfYear][$dow] = new Day($value); } } return $monthArray; }
- First, a series of small methods, starting with one that extracts the internationally formatted day based on type. The type determines whether we deliver the full name of the day, an abbreviation, or just a single letter, all appropriate for that locale:
protected function getDay($type, $cal) { $formatter = $this->getDateFormatter(); $formatter->setPattern($type); return $formatter->format($cal); } - Next we need a method that returns an HTML row of day names, calling the newly defined
getDay()method. As mentioned previous, the type dictates the appearance of the days:protected function getWeekHeaderRow($type, $cal, $year, $month, $week) { $output = '<tr>'; $width = (int) (100/7); foreach ($week as $day) { $cal->set($year, $month, $day()); $output .= '<th style="vertical-align:top;" width="' . $width . '%">' . $this->getDay($type, $cal) . '</th>'; } $output .= '</tr>' . PHP_EOL; return $output; } - After that, we define a very simple method to return a row of week dates. Note that we take advantage of
Day::__invoke()using:$day():protected function getWeekDaysRow($week) { $output = '<tr style="height:' . $this->height . ';">'; $width = (int) (100/7); foreach ($week as $day) { $output .= '<td style="vertical-align:top;" width="' . $width . '%">' . $day() . '</td>'; } $output .= '</tr>' . PHP_EOL; return $output; } - And finally, a method that puts the smaller methods together to generate a calendar for a single month. First we build the month array, but only if
$yearArrayis not already available:public function calendarForMonth($year, $month, $timeZone = NULL, $dayType = self::DAY_3, $monthType = self::MONTH_FULL, $monthArray = NULL) { $first = 0; if (!$monthArray) $monthArray = $this->yearArray[$year][$month] ?? $this->buildMonthArray($year, $month, $timeZone); - The month needs to be decremented by
1asIntlCalendarmonths are 0-based: Jan = 0, Feb = 1, and so on. We then build anIntlCalendarinstance using the time zone (if any), and the locale. We next create aIntlDateFormatterinstance to retrieve the month name and other information according to locale:$month--; $cal = IntlCalendar::createInstance($timeZone, $this->locale->getLocaleCode()); $cal->set($year, $month, 1); $formatter = $this->getDateFormatter(); $formatter->setPattern($monthType);
- We then loop through the month array, and call the smaller methods just mentioned to build the final output:
$this->height = ($dayType == self::DAY_FULL) ? self::HEIGHT_FULL : self::HEIGHT_SMALL; $html = '<h1>' . $formatter->format($cal) . '</h1>'; $header = ''; $body = ''; foreach ($monthArray as $weekNum => $week) { if ($first++ == 1) { $header .= $this->getWeekHeaderRow($dayType, $cal, $year, $month, $week); } $body .= $this->getWeekDaysRow($dayType, $week); } $html .= '<table>' . $header . $body . '</table>' . PHP_EOL; return $html; } - In order to generate a calendar for the entire year, it's a simple matter of looping through months 1 to 12. To facilitate outside access, we first define a method that builds a year array:
public function buildYearArray($year, $timeZone = NULL) { $this->yearArray = array(); for ($month = 1; $month <= 12; $month++) { $this->yearArray[$year][$month] = $this->buildMonthArray($year, $month, $timeZone); } return $this->yearArray; } public function getYearArray() { return $this->yearArray; } - To generate a calendar for a year, we define a method,
calendarForYear(). If the year array has not been build, we callbuildYearArray(). We take into account how many monthly calendars we wish to display across and then callcalendarForMonth():public function calendarForYear($year, $timeZone = NULL, $dayType = self::DAY_1, $monthType = self::MONTH_3, $across = self::DEFAULT_ACROSS) { if (!$this->yearArray) $this->buildYearArray($year, $timeZone); $yMax = (int) (12 / $across); $width = (int) (100 / $across); $output = '<table>' . PHP_EOL; $month = 1; for ($y = 1; $y <= $yMax; $y++) { $output .= '<tr>'; for ($x = 1; $x <= $across; $x++) { $output .= '<td style="vertical-align:top;" width="' . $width . '%">' . $this->calendarForMonth($year, $month, $timeZone, $dayType, $monthType, $this->yearArray[$year][$month++]) . '</td>'; } $output .= '</tr>' . PHP_EOL; } $output .= '</table>'; return $output; }
First of all, make sure you build the Application\I18n\Locale class as defined in the previous recipe. After that, create a new file, Calendar.php, in the Application\I18n folder, with all the methods described in this recipe.
Next, define a calling program, chap_08_html_calendar.php, which sets up autoloading and creates Locale and Calendar instances. Also be sure to define the year and month:
<?php
require __DIR__ . '/../Application/Autoload/Loader.php';
Application\Autoload\Loader::init(__DIR__ . '/..');
use Application\I18n\Locale;
use Application\I18n\Calendar;
$localeFr = new Locale('fr-FR');
$localeUs = new Locale('en_US');
$localeTh = new Locale('th_TH');
$calendarFr = new Calendar($localeFr);
$calendarUs = new Calendar($localeUs);
$calendarTh = new Calendar($localeTh);
$year = 2016;
$month = 1;
?>You can then develop appropriate view logic to display the different calendars. For example, you can include parameters to display the full month and day names:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>PHP 7 Cookbook</title>
<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html;charset=utf-8" />
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="php7cookbook_html_table.css">
</head>
<body>
<h3>Year: <?= $year ?></h3>
<?= $calendarFr->calendarForMonth($year, $month, NULL, Calendar::DAY_FULL); ?>
<?= $calendarUs->calendarForMonth($year, $month, NULL, Calendar::DAY_FULL); ?>
<?= $calendarTh->calendarForMonth($year, $month, NULL, Calendar::DAY_FULL); ?>
</body>
</html>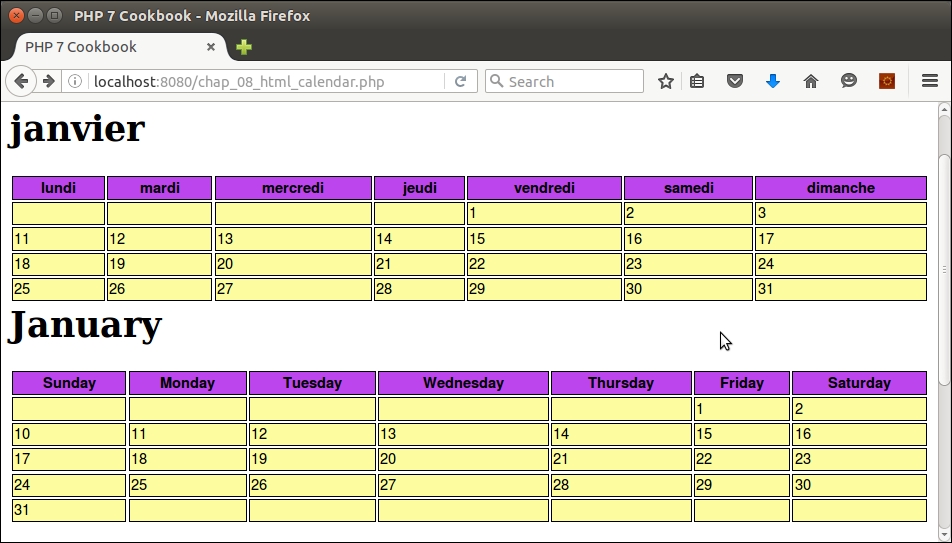
With a couple of modifications, you can also display a calendar for the entire year:
$localeTh = new Locale('th_TH');
$localeEs = new Locale('es_ES');
$calendarTh = new Calendar($localeTh);
$calendarEs = new Calendar($localeEs);
$year = 2016;
echo $calendarTh->calendarForYear($year);
echo $calendarEs->calendarForYear($year);Here is the browser output showing a full year calendar in Spanish:
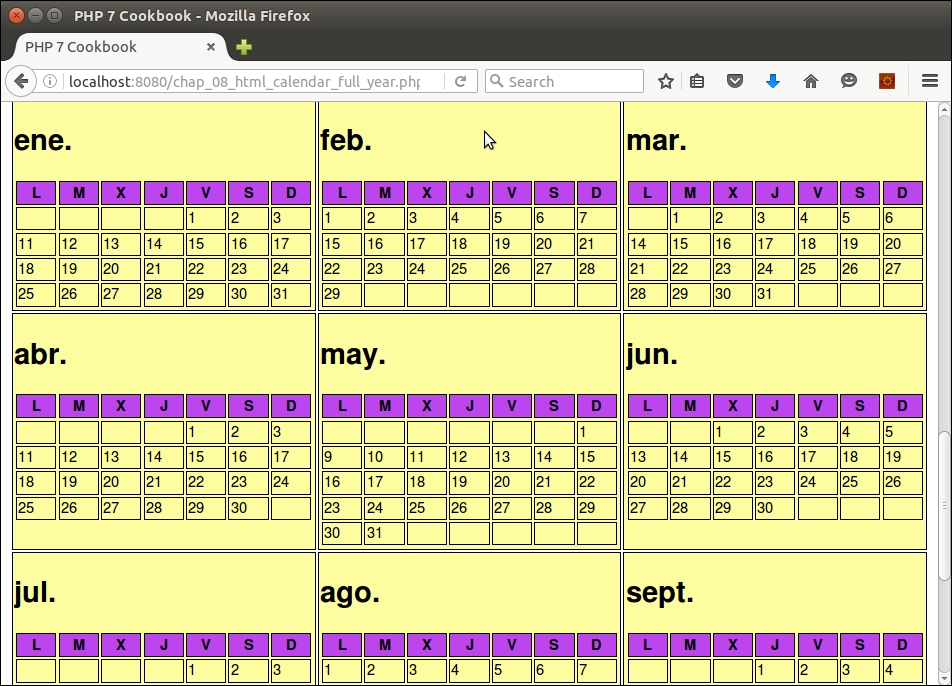
- For more information on codes used by
IntlDateFormatter::setPattern(), see this article: http://userguide.icu-project.org/formatparse/datetime
